Constructing Triangles
To construct a triangle ....
... you need to know
- Two Angles and One Side, or
- One Angle and Two Sides, or
- Three Sides
(When you only know three angles you don't know how large the triangle will be.)
See how to Construct A Triangle With 3 Known Sides .
See how to Construct An Equilateral Triangle .
- + ACCUPLACER Mathematics
- + ACT Mathematics
- + AFOQT Mathematics
- + ALEKS Tests
- + ASVAB Mathematics
- + ATI TEAS Math Tests
- + Common Core Math
- + DAT Math Tests
- + FSA Tests
- + FTCE Math
- + GED Mathematics
- + Georgia Milestones Assessment
- + GRE Quantitative Reasoning
- + HiSET Math Exam
- + HSPT Math
- + ISEE Mathematics
- + PARCC Tests
- + Praxis Math
- + PSAT Math Tests
- + PSSA Tests
- + SAT Math Tests
- + SBAC Tests
- + SIFT Math
- + SSAT Math Tests
- + STAAR Tests
- + TABE Tests
- + TASC Math
- + TSI Mathematics
- + ACT Math Worksheets
- + Accuplacer Math Worksheets
- + AFOQT Math Worksheets
- + ALEKS Math Worksheets
- + ASVAB Math Worksheets
- + ATI TEAS 6 Math Worksheets
- + FTCE General Math Worksheets
- + GED Math Worksheets
- + 3rd Grade Mathematics Worksheets
- + 4th Grade Mathematics Worksheets
- + 5th Grade Mathematics Worksheets
- + 6th Grade Math Worksheets
- + 7th Grade Mathematics Worksheets
- + 8th Grade Mathematics Worksheets
- + 9th Grade Math Worksheets
- + HiSET Math Worksheets
- + HSPT Math Worksheets
- + ISEE Middle-Level Math Worksheets
- + PERT Math Worksheets
- + Praxis Math Worksheets
- + PSAT Math Worksheets
- + SAT Math Worksheets
- + SIFT Math Worksheets
- + SSAT Middle Level Math Worksheets
- + 7th Grade STAAR Math Worksheets
- + 8th Grade STAAR Math Worksheets
- + THEA Math Worksheets
- + TABE Math Worksheets
- + TASC Math Worksheets
- + TSI Math Worksheets
- + AFOQT Math Course
- + ALEKS Math Course
- + ASVAB Math Course
- + ATI TEAS 6 Math Course
- + CHSPE Math Course
- + FTCE General Knowledge Course
- + GED Math Course
- + HiSET Math Course
- + HSPT Math Course
- + ISEE Upper Level Math Course
- + SHSAT Math Course
- + SSAT Upper-Level Math Course
- + PERT Math Course
- + Praxis Core Math Course
- + SIFT Math Course
- + 8th Grade STAAR Math Course
- + TABE Math Course
- + TASC Math Course
- + TSI Math Course
- + Number Properties Puzzles
- + Algebra Puzzles
- + Geometry Puzzles
- + Intelligent Math Puzzles
- + Ratio, Proportion & Percentages Puzzles
- + Other Math Puzzles

A Step-by-Step Guide to Constructing a Triangle from Its Sides
In geometry, triangles are among the most basic and versatile shapes. Constructing a triangle using its three given sides is a fundamental skill. This guide will walk you through the steps and principles behind this construction, ensuring you can create accurate triangles with ease and precision.

Step-by-step Guide: Constructing a Triangle Given Its Sides
Tools Required:
- A straightedge or ruler.
Procedure: i. Laying the Base: Draw one of the triangle’s sides using your straightedge. Let’s name this side \(AB\).
ii. Constructing the Second Side: Choose one endpoint (let’s say \(A\)). Using your compass, set its width to the length of one of the other sides (let’s say \(AC\)). Then, draw a circular arc with \(A\) as the center.
iii. Constructing the Third Side: Similarly, set your compass to the length of the third side (let’s say \(BC\)). Place the compass point on \(B\) and draw another arc that intersects the previous arc.
iv. Finalizing the Triangle: Label the point where the arcs intersect as \(C\). Use your straightedge to connect points \(C\) to both \(A\) and \(B\). The resulting shape is the desired triangle \(ABC\).
Example 1: You’re tasked with designing a triangular park, and you have been given the three side lengths but no angle measurements.
Solution: Utilize the aforementioned method to draw the triangle accurately on a blueprint. Once constructed, you can proceed with additional design and landscaping within this triangular boundary.
Example 2: You have side lengths \(5 \text{ cm}\), \(7 \text{ cm}\), and \(8 \text{ cm}\). Can a triangle be constructed with these sides?
Solution: Yes. The sum of any two sides of a triangle (in this case, \(5 + 7 = 12\) and \(7 + 8 = 15\)) is greater than the third side (\(8 \text{ cm}\)). Thus, a triangle can be constructed using these lengths by following the steps mentioned.
Practice Questions:
- What conditions must three side lengths fulfill to construct a triangle?
- After constructing a triangle using three side lengths, how can you ascertain if it’s a right triangle?
- Using side lengths \(4 \text{ cm}\), \(6 \text{ cm}\), and \(11 \text{ cm}\), is triangle construction feasible?
- The sum of any two side lengths must exceed the third. This principle is termed the triangle inequality theorem.
- Post-construction, apply the Pythagorean theorem to all sides. If the square of the longest side equals the sum of the squares of the other two, it’s a right triangle.
- No. The combined lengths of the shorter sides, \(4 + 6 = 10 \text{ cm}\), falls short of the longest side’s length \(11 \text{ cm}\). Triangle construction isn’t possible with these measurements due to the triangle inequality theorem.
by: Effortless Math Team about 5 months ago (category: Articles )
Effortless Math Team
Related to this article, more math articles.
- 10 Most Common 3rd Grade MAP Math Questions
- How to Add and Subtract Mixed Time Units
- Why Learning Styles are a Myth?
- How to Remove Discontinuities?
- How to Find Average Rate of Change of a Function?
- ISEE Upper-Level Math FREE Sample Practice Questions
- How to Round Decimals? (+FREE Worksheet!)
- Accuplacer Math Formulas
- ACT Math- Test Day Tips
- Top 10 Tips to Create an ASTB Math Study Plan
What people say about "A Step-by-Step Guide to Constructing a Triangle from Its Sides - Effortless Math: We Help Students Learn to LOVE Mathematics"?
No one replied yet.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
AP Pre-Calculus for Beginners The Ultimate Step by Step Guide to Acing AP Precalculus
Pre-calculus for beginners the ultimate step by step guide to acing precalculus, m-step grade 6 math for beginners the ultimate step by step guide to preparing for the m-step math test, algebra 2 workbook a comprehensive review and step-by-step guide for mastering essential math skills, fsa mathematics workbook for grade 6 step-by-step guide to preparing for the fsa math test 2019, fsa mathematics workbook for grade 7 step-by-step guide to preparing for the fsa math test 2019, fsa mathematics workbook for grade 8 step-by-step guide to preparing for the fsa math test 2019, fsa mathematics workbook for grade 5 step-by-step guide to preparing for the fsa math test 2019, fsa mathematics workbook for grade 4 step-by-step guide to preparing for the fsa math test 2019, fsa mathematics workbook for grade 3 step-by-step guide to preparing for the fsa math test 2019, algebra 1 workbook a comprehensive review and step-by-step guide for mastering essential math skills, gre mathematics workbook 2018-2019 a comprehensive review and step-by-step guide to preparing for the gre math, act mathematics workbook 2018 – 2019 a comprehensive review and step-by-step guide to preparing for the act math, tsi mathematics workbook 2018 – 2019 a comprehensive review and step-by-step guide to preparing for the tsi math.
- ATI TEAS 6 Math
- ISEE Upper Level Math
- SSAT Upper-Level Math
- Praxis Core Math
- 8th Grade STAAR Math
Limited time only!
Save Over 45 %
It was $89.99 now it is $49.99
Login and use all of our services.
Effortless Math services are waiting for you. login faster!
Register Fast!
Password will be generated automatically and sent to your email.
After registration you can change your password if you want.
- Math Worksheets
- Math Courses
- Math Topics
- Math Puzzles
- Math eBooks
- GED Math Books
- HiSET Math Books
- ACT Math Books
- ISEE Math Books
- ACCUPLACER Books
- Premium Membership
- Youtube Videos
- Google Play
- Apple Store
Effortless Math provides unofficial test prep products for a variety of tests and exams. All trademarks are property of their respective trademark owners.
- Bulk Orders
- Refund Policy
- Math Article
Constructing Triangles
Constructing triangles will include the construction of different triangles using a protractor, a compass and a ruler. A triangle is a three-sided polygon. It has three sides, three vertices and three angles. Construction of triangles is easy when the measurements are given to us based on different properties such as SSS, SAS and ASA.
Let us learn here to construct a triangle with given measurements. Also, learn to draw triangles of some special cases.
How to Construct Triangles?
To construct a triangle one should know these properties and rules:
- All three sides are given (SSS – Side side side)
- Two sides and included angle are given (SAS – Side angle side)
- Two angles and the included side is given (ASA – Angle side angle)
- The measure of the hypotenuse and a side is given in the right triangle (RHS – Right angle hypotenuse side)
For constructing triangles from given data, we generally make use of the given congruency conditions and construct the required triangle.
Constructing triangle With SSS Property
When the length of three sides of the triangle is given, then follow the below steps to construct the required triangle.
- Draw a line segment AB, of length equal to the longest side of the triangle
- Now using a compass and ruler take the measure of the second side and draw an arc
- Again take the measure of the third side and cut the previous arc at a point C
- Now join the endpoints of the line segment to point C and get the required triangle ABC
Constructing triangle with SAS Property
When the length of two sides and the angle included between them are given, then use the following steps to construct the triangle.
- Draw a line segment AB, of length equal to the longest side of the triangle, using a ruler
- Put the center of the protractor on one end of a line segment (say A) and measure the given angle. Join the points and construct a ray, such that the ray is nearer to the line segment AB
- Take the measure of another given side of the triangle using a compass and a ruler
- Put the compass at point A and cut the ray at another point, C
- Now join the other end of the line segment, i.e., B to the point C
- Hence, the triangle ABC is constructed
Constructing triangle with ASA Property
When the measures of two angles and the side included between them are given of a triangle, then it is said to be ASA congruency. Follow the given steps to draw a triangle with ASA property.
- Draw a line segment AB, of length equal to the given side of the triangle, using a ruler
- At one endpoint of line segment (say A) measure one of the given angles and draw a ray AR
- At another endpoint of line segment (i.e.,B) measure the other angle using a protractor and draw the ray BQ, such that it cuts the previous ray at a point P
- Join the previous point P, with both the endpoints A and B of the line segment AB, to get the required triangle
Construction triangle with RHS Property
When the hypotenuse side and any one of the other two sides of right triangle are given, then it is RHS property. Follow the given steps to draw a triangle with RHS property.
- Draw the line segment AB, equal to the measure of hypotenuse side
- At one endpoint, say A, of line-segment measure the angle equal to 90 degrees and draw a ray, AR
- Measure the length of another given side and draw an arc to cut the ray AR at a point P
- Now join the point P and B to get the required right triangle
Special Cases of Constructing Triangles
There are few special cases of constructing triangles that are discussed here.
Construction of Triangles – Case 1
Given the base of a triangle, its base angle and the sum of the other two sides
For constructing ∆ABC such that base BC, base angle ∠B and the sum of other two sides, i.e. AB + AC are given, the following steps of construction is followed:
Steps of Construction of a Triangle
Step 1. Draw the base BC of ∆ABC as given and construct ∠XBC of the given measure at B as shown.

Step 2. Keeping the compass at point B cut an arc from the ray BX such that its length equals AB + AC at point P and join it to C as shown in the figure.

Step 3. Now measure ∠BPC and from C, draw an angle equal to ∠BPC as shown in the figure.

∆ABC is the required triangle. This can be proved as follows:
Construction of Triangles – Case 2
Given the base of a triangle, its base angle and the difference between the other two sides
For constructing ∆ABC such that base BC, base angle∠B and difference of the other two sides, i.e. AB – AC or AC-AB is given, then for constructing triangles such as these two cases can arise:
The following steps of construction are followed for the two cases:
Steps of Construction if AB > AC:
Step 1. Draw the base BC of ∆ABC as given and construct ∠XBC of the required measure at B as shown.

Step 2. From the ray, BX cut an arc equal to AB – AC at point P and join it to C as shown
Step 3. Draw the perpendicular bisector of PC and let it intersect BX at point A as shown:

Step 4. Join AC, ∆ABC is the required triangle.

Steps of Construction if AC > AB:

Step 2. On the ray BX cut an arc equal to AB – AC at point P and join it to C. In this case, P will lie on the opposite side to the ray BX. Draw the perpendicular bisector of PC and let it intersect BX at point A as shown

Step 3. Join the points A and C, and hence ∆ABC is the required triangle.
Video Lesson on Triangles

Related Articles
- Constructing Triangles with SSS Congruence
- Constructing Triangles, ASA
- Constructing Triangles, SAS
- Construction Of Angles
- Construction Of Similar Triangles
Practice Questions on Constructing Triangles
- Construct a triangle with sides equal to 4 cm and 6 cm and the angle included between them is 40°.
- Construct a triangle with two angles 40° and 70° and the side included between them is of length 8cm.
- Construct a triangle with given three sides AB = 3cm, BC = 5cm and AC = 6cm.
Frequently Asked Questions on Contructing triangles
What are the rules of constructing triangles, how to construct a triangle with given three sides, how many kinds of triangles are there, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Define and Construct Triangles
Related Topics: Lesson Plans and Worksheets for Grade 4 Lesson Plans and Worksheets for all Grades More Lessons for Grade 4 Common Core For Grade 4
Examples, solutions, and videos to help Grade 4 students learn how to define and construct triangles from given criteria and explore symmetry in triangles.
Common Core Standards: 4.MD.7
New York State Common Core Math Grade 4, Module 4, Lesson 14
Worksheets for Grade 4
NYS Math Module 4 Grade 4 Lesson 14 Fluency Practice
Classify the Triangle
Lesson 14 Concept Development Problem 1: Construct an obtuse isosceles triangle.
Problem 2: Construct a right scalene triangle.
NYS Math Grade 4, Module 4, Lesson 14 Problem Set
- Draw triangles that fit the following classifications. Use a ruler and protractor. Label the side lengths and angles. a. right and isosceles b. obtuse and scalene c. acute and scalene d. acute and isosceles
- Draw all possible lines of symmetry in the triangles above. Explain why some of the triangles do not have lines of symmetry.
Are the following statements true or false? Explain using pictures or words. 3. If ABC is an isosceles triangle, BC must be 2 cm. True or False? 4. A triangle cannot have one obtuse angle and one right angle. True or False? 5. EFG can be described as a right triangle and an isosceles triangle. True or False? 6. An equilateral triangle is isosceles. True or False?
NYS Math Module 4 Grade 4 Lesson 14 Homework
- Draw triangles that fit the following classifications. Use a ruler and protractor. Label the side lengths and angles. a. right and isosceles b. right and scalene c. obtuse and isosceles d. acute and scalene
- Draw all possible lines of symmetry in the triangles above. Explain why some of the triangles do not have lines of symmetry. Are the following statements true or false? Explain using pictures or words.
- If ABC is an isosceles triangle, AB must be 2 cm. True or False?
- A triangle cannot have both an acute angle and a right angle. True or False?
- XYZ can be described as both equilateral and acute. True or False?
- A right triangle is always scalene. True or False?

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.
- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search

Constructing triangles
Subject: Mathematics
Age range: 14-16
Resource type: Lesson (complete)
Last updated
28 January 2019
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

A FULL LESSON on constructing triangles using a compass, protractor and ruler. Full clear visuals animations for each construction. Paperless lesson Touchscreen lesson: TRIGGERED Clicker lesson: CLICKER
Assumed prior knowledge:
- Use of a compass and straight edge
- Measuring an angle
We are learning about: Constructing triangles We are learning to: Use a compass, ruler and protractor to construct triangles.
Differentiated objectives:
- Developing learners will be able to construct SSS triangles.
- Secure learners will be able to construct SAS and ASA triangles.
- Excelling learners will be able to construct other polygons given angles and sides.
Starter: Gets straight ‘stuck in’ with an equilateral triangle. Main: Worked through examples of SSS, SAS and ASA triangles with visual prompts and steps, followed by 8 practice questions displayed on board after each type of triangle. Plenary/Extension: Constructing triangles with a scale, worded constructions, sectors and other polygons.
Please do leave feedback if downloaded! THANK YOU!
Creative Commons "Sharealike"
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
Another quality lesson, fully explained in clear steps for the students to follow - thank you!
cparkinson3
Thank you. I hope it helps!
Empty reply does not make any sense for the end user
Excellent resources
Thank you. I hope they help!
mrsnovelo2021
Amazed!! thank you!
initialteacher
Fantastic resource!
Thank you. I hope it helps
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Unit 4: Triangles
About this unit, triangle types.
- Classifying triangles (Opens a modal)
- Classifying triangles by angles (Opens a modal)
- Worked example: Classifying triangles (Opens a modal)
- Types of triangles review (Opens a modal)
- Classify triangles by angles 4 questions Practice
- Classify triangles by side lengths 4 questions Practice
Triangle angles
- Angles in a triangle sum to 180° proof (Opens a modal)
- Triangle exterior angle example (Opens a modal)
- Worked example: Triangle angles (intersecting lines) (Opens a modal)
- Worked example: Triangle angles (diagram) (Opens a modal)
- Triangle angle challenge problem (Opens a modal)
- Triangle angle challenge problem 2 (Opens a modal)
- Triangle angles review (Opens a modal)
- Find angles in triangles 7 questions Practice
- Find angles in isosceles triangles 4 questions Practice
- Finding angle measures between intersecting lines 4 questions Practice
- Finding angle measures using triangles 7 questions Practice
Triangle inequality theorem
- Triangle inequality theorem (Opens a modal)
- Triangle side length rules 4 questions Practice
Perpendicular bisectors
- Circumcenter of a triangle (Opens a modal)
- Circumcenter of a right triangle (Opens a modal)
- Three points defining a circle (Opens a modal)
- Area circumradius formula proof (Opens a modal)
- 2003 AIME II problem 7 (Opens a modal)
Angle bisectors
- Distance between a point & line (Opens a modal)
- Incenter and incircles of a triangle (Opens a modal)
- Inradius, perimeter, & area (Opens a modal)
Medians & centroids
- Triangle medians & centroids (Opens a modal)
- Triangle medians and centroids (2D proof) (Opens a modal)
- Dividing triangles with medians (Opens a modal)
- Exploring medial triangles (Opens a modal)
- Centroid & median proof (Opens a modal)
- Median, centroid example (Opens a modal)
- Proof: Triangle altitudes are concurrent (orthocenter) (Opens a modal)
- Common orthocenter and centroid (Opens a modal)
Bringing it all together
- Review of triangle properties (Opens a modal)
- Euler line (Opens a modal)
- Euler's line proof (Opens a modal)

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.0: Angles and Triangles
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 112400

- Katherine Yoshiwara
- Los Angeles Pierce College
Historically, trigonometry began as the study of triangles and their properties. Let’s review some definitions and facts from geometry.
- We measure angles in degrees.
- One full rotation is \(360^{\circ}\), as shown below.
- Half a full rotation is \(180^{\circ}\) and is called a straight angle .
- One quarter of a full rotation is \(90^{\circ}\) and is called a right angle .

If you tear off the corners of any triangle and line them up, as shown below, they will always form a straight angle.

Sum of angles in a triangle.
1. The sum of the angles in a triangle is \(180^{\circ}\).
Example 1.1
Two of the angles in the triangle at right are \(25^{\circ}\) and \(115^{\circ}\). Find the third angle.

To find the third angle, we write an equation.
\begin{aligned} x+25+115 &=180 \quad \quad &&\text{Simplify the left side.} \\ x+140 &=180 \quad \quad &&\text{Subtract 140 from both sides.}\\ x &=40 \end{aligned}
The third angle is \(40^{\circ}\).
Checkpoint 1.2
Find each of the angles in the triangle at right.

\(x = 39^{\circ}, 2x = 78^{\circ}, 2x-15 = 63^{\circ}\)
Some special categories of triangles are particularly useful. Most important of these are the right triangles .
Right triangle.
2. A right triangle has one angle of \(90^{\circ}\).
Example 1.3
One of the smaller angles of a right triangle is \(34^{\circ}\). What is the third angle?

The sum of the two smaller angles in a right triangle is \(90^{\circ}\). So
\begin{aligned} x+34 &=90 \quad \quad \text{Subtract 34 from both sides} \\ x &=56 \end{aligned}
The unknown angle must be \(56^{\circ}\).
Checkpoint 1.4
Two angles of a triangle are \(35^{\circ}\) and \(45^{\circ}\). Can it be a right triangle?
An equilateral triangle has all three sides the same length.
Angles of equilateral triangle.
3. All of the angles of an equilateral triangle are equal.
Example 1.5
All three sides of a triangle are 4 feet long. Find the angles.

The triangle is equilateral, so all of its angles are equal. Thus
\begin{aligned} 3 x &=180 \quad \quad \quad \text{Divide both sides by 3.}\\ x &=60 \end{aligned}
Each of the angles is \(60^{\circ}\).
Checkpoint 1.6
Find \(x, y\), and \(z\) in the triangle at right.

\(x=60^{\circ}, y=8, z=8\)
An isosceles triangle has two sides of equal length. The angle between the equal sides is the vertex angle . The other two angles are the base angles.
Base angles of an isoceles triangle.
4. The base angles of an isosceles triangle are equal.
Example 1.7
Find \(x\) and \(y\) in the triangle at right.

The triangle is isosceles, so the base angles are equal. Therefore, \(y=38^{\circ}\). To find the vertex angle, we solve
\begin{aligned} x+38+38 &=180 \\ x+76 &=180 \quad \quad \quad \text{Subtract 76 from both sides.}\\ x &=104 \end{aligned}
The vertex angle is \(104^{\circ}\).
Checkpoint 1.8
Find \(x\) and \(y\) in the figure at right.

\(x=140^{\circ}, y=9\)
In addition to the facts about triangles reviewed above, there are several useful properties of angles.
- Two angles that add to \(180^{\circ}\) are called supplementary .
- Two angles that add to \(90^{\circ}\) are called complementary .
- Angles between \(0^{\circ}\) and \(90^{\circ}\) are called acute .
- Angles between \(90^{\circ}\) and \(180^{\circ}\) are called obtuse .


Example 1.9
In the figure at right,

- \(\angle A O C\) and \(\angle B O C\) are supplementary.
- \(\angle D O E\) and \(\angle B O E\) are complementary.
- \(\angle A O C\) is obtuse,
- and \(\angle B O C\) is acute.
In trigonometry we often use lower-case Greek letters to represent unknown angles (or, more specifically, the measure of the angle in degrees). In the next Exercise, we use the Greek letters \(\alpha\) (alpha), \(\beta\) (beta), and \(\gamma\) (gamma).
Checkpoint 1.10
In the figure, \(\alpha, \beta\), and \(\gamma\) denote the measures of the angles in degrees.

a. Find the measure of angle \(\alpha\). b. Find the measure of angle \(\beta\). c. Find the measure of angle \(\gamma\). d. What do you notice about the measures of the angles?
\(\quad \alpha=130^{\circ}, \beta=50^{\circ}, \gamma=130^{\circ}\). The non-adjacent angles are equal.
Non-adjacent angles formed by the intersection of two straight lines are called vertical angles . In the previous exercise, the angles labeled \(\alpha\) and \(\gamma\) are vertical angles, as are the angles labeled \(\beta\) and \(50^{\circ}\).
Vertical Angles.
5. Vertical angles are equal.
Example 1.11
Explain why \(\alpha=\beta\) in the triangle at right.

Because they are the base angles of an isosceles triangle, \(\theta\) (theta) and \(\phi(\mathrm{phi})\) are equal. Also, \(\alpha=\theta\) because they are vertical angles, and similarly \(\beta=\phi\). Therefore, \(\alpha=\beta\) because they are equal to equal quantities.
Checkpoint 1.12
Find all the unknown angles in the figure at right. (You will find a list of all the Greek letters and their names at the end of this section.)

\(\alpha=40^{\circ}, \beta=140^{\circ}, \gamma=75^{\circ}, \delta=65^{\circ}\)
A line that intersects two parallel lines forms eight angles, as shown in the figure below. There are four pairs of vertical angles, and four pairs of corresponding angles , or angles in the same position relative to the transversal on each of the parallel lines.
For example, the angles labeled 1 and 5 are corresponding angles, as are the angles labeled 4 and 8. Finally, angles 3 and 6 are called alternate interior angles , and so are angles 4 and 5.

Parallel lines cut by a transversal.
6. If parallel lines are intersected by a transversal, the alternate interior angles are equal. Corresponding angles are also equal.
Example 1.13
The parallelogram \(A B C D\) shown at right is formed by the intersection of two sets of parallel lines. Show that the opposite angles of the parallelogram are equal.

Angles 1 and 2 are equal because they are alternate interior angles, and angles 2 and 3 are equal because they are corresponding angles. Therefore angles 1 and 3 , the opposite angles of the parallelogram, are equal. Similarly, you can show that angles 4,5 , and 6 are equal.
Checkpoint 1.14
Show that the adjacent angles of a parallelogram are supplementary. (You can use angles 1 and 4 in the parallelogram of the previous example.)
Note that angles 2 and 6 are supplementary because they form a straight angle. Angle 1 equals angle 2 because they are alternate interior angles, and similarly angle 4 equals angle 5. Angle 5 equals angle 6 because they are corresponding angles. Thus, angle 4 equals angle 6, and angle 1 equals angle 2. So angles 4 and 1 are supplementary because 2 and 6 are.
Note 1.15 In the Section 1.1 Summary, you will find a list of vocabulary words and a summary of the facts from geometry that we reviewed in this section. You will also find a set of study questions to test your understanding, and a list of skills to practice in the homework problems.
Table 1.16 Lower Case Letters in the Greek Alphabet
\begin{aligned} &\quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \text { Greek Alphabet }\\ &\begin{array}{cc|cc|cc|} \hline \alpha & \text { alpha } & \beta & \text { beta } & \gamma & \text { gamma } \\ \hline \delta & \text { delta } & \epsilon & \text { epsilon } & \gamma & \text { gamma } \\ \hline \eta & \text { eta } & \theta & \text { theta } & \iota & \text { iota } \\ \hline \kappa & \text { kappa } & \lambda & \text { lambda } & \mu & \text { mu } \\ \hline \nu & \text { nu } & \xi & \text { xi } & o & \text { omicron } \\ \hline \pi & \text { pi } & \rho & \text { rho } & \sigma & \text { sigma } \\ \hline \tau & \text { tau } & v & \text { upsilon } & \phi & \text { phi } \\ \hline \chi & \text { chi } & \psi & \text { psi } & \omega & \text { omega } \\ \hline \end{array} \end{aligned}
Review the following skills you will need for this section.
Algebra Refresher 1.2
Solve the equation.
1. \(x-8=19-2 x\) 2. \(2 x-9=12-x\) 3. \(13 x+5=2 x-28\) 4. \(4+9 x=-7+x\)
Solve the system.
5. \(5x - 2y = -13\)
\(2x + 3y = -9\)
6. \(4x + 3y = 9\)
\(3x + 2y = 8\)
5. \(x=-3,y=-1\)
6. \(x=6,y=-5\)
Section 1.1 Summary
• Right angle
• Straight angle
• Right triangle
• Equilateral triangle
• Isosceles triangle
• Vertex angle
• Base angle
• Supplementary
• Complementary
• Acute
• Obtuse
• Vertical angles
• Transversal
• Corresponding angles
• Alternate interior angles
Facts from Geometry.
1. The sum of the angles in a triangle is \(180^{\circ}\). 2. A right triangle has one angle of \(90^{\circ}\). 3. All of the angles of an equilateral triangle are equal. 4. The base angles of an isosceles triangle are equal. 5. Vertical angles are equal. 6. If parallel lines are intersected by a transversal, the alternate interior angles are equal.
Corresponding angles are also equal.
Study Questions
1. Is it possible to have more than one obtuse angle in a triangle? Why or why not?
2. Draw any quadrilateral (a four-sided polygon) and divide it into two triangles by connecting two opposite vertices by a diagonal. What is the sum of the angles in your quadrilateral?
3. What is the difference between a vertex angle and vertical angles?
4. Can two acute angles be supplementary?
5. Choose any two of the eight angles formed by a pair of parallel lines cut by a transversal. Those two angles are either equal or _______ .
Practice each skill in the Homework Problems listed.
1. Sketch a triangle with given properties #1–6
2. Find an unknown angle in a triangle #7–12, 17–20
3. Find angles formed by parallel lines and a transversal #13–16, 35–44
4. Find exterior angles of a triangle #21–24
5. Find angles in isosceles, equilateral, and right triangles #25–34
6. State reasons for conclusions #45–48
Homework 1.1
For Problems 1–6, sketch and label a triangle with the given properties.
1. An isosceles triangle with vertex angle \(30^{\circ}\) 2. A scalene triangle with one obtuse angle ( Scalene means three unequal sides.) 3. A right triangle with \(\operatorname{legs} 4\) and 7 4. An isosceles right triangle 5. An isosceles triangle with one obtuse angle 6. A right triangle with one angle \(20^{\circ}\)
For Problems 7–20, find each unknown angle.

In Problems 21 and 22, the angle labeled \(\phi\) is called an exterior angle of the triangle, formed by one side and the extension of an adjacent side. Find \(\phi\).

23. In parts (a) and (b), find the exterior angle \(\phi\).

c. Find an algebraic expression for \(\phi\).

d Use your answer to part (c) to write a rule for finding an exterior angle of a triangle.
a Find the three exterior angles of the triangle. What is the sum of the exterior angles?

b Write an algebraic expression for each exterior angle in terms of one of the angles of the triangle. What is the sum of the exterior angles?

In Problems 25 and 26, the figures inscribed are regular polygons , which means that all their sides are the same length, and all the angles have the same measure. Find the angles \(\theta\) and \(\phi\).

In problems 27 and 28, \(\Delta ABC\) is equilateral. Find the unknown angles

a \(2\theta + 2\phi = ________\)
b \(\theta + \phi = ________\)
c \(\Delta ABC\) is ________
30. Find \(\alpha\) and \(\beta\).

a Explain why \(\angle O A B\) and \(\angle A B O\) are equal in measure.
b Explain why \(\angle O B C\) and \(\angle B C O\) are equal in measure.
c Explain why \(\angle A B C\) is a right angle. (Hint: Use Problem 29.)

a Compare \(\theta\) with \(\alpha+\beta\). (Hint: What do you know about supplementary angles and the sum of angles in a triangle?
b Compare \(\alpha\) and \(\beta\).
c Explain why the inscribed angle \(\angle B A O\) is half the size of the central angle \(\angle B O D\).
33. Find \(\alpha\) and \(\beta\).

34. Find \(\alpha\) and \(\beta\).

In Problems 35–44, arrows on a pair of lines indicate that they are parallel. Find \(x\) and \(y\).

a Among the angles labeled 1 through 5 in the figure at right, find two pairs of equal angles.

b \(\angle 4+\angle 2+\angle 5= _________\)
c Use parts (a) and (b) to explain why the sum of the angles of a triangle is \(180^{\circ}\)
a In the figure below, find \(\theta\), and justify your answer.

b Write an algebraic expression for \(\theta\) in the figure below.

47. \(A B C D\) is a rectangle. The diagonals of a rectangle bisect each other. In the figure, \(\angle A Q D=130^{\circ}\). Find the angles labeled 1 through 5 in order, and give a reason for each answer.

48. A tangent meets the radius of a circle at a right angle. In the figure, \(\angle AOB = 140^{\circ}\). Find the angles labeled 1 through 5 in order, and give a reason for each answer.

To make full use of our website, Switch or update for free to one of the following current browsers:
Firefox , Google Chrome oder Internet Explorer 8 and above
To make full use of our website, enable JavaScript in your browser.
Our tutorial videos allow students to learn at their own pace without any pressure or stress. They can watch, pause or rewind the videos as often as they need until they understand the content.
Our interactive exercises come in a variety of formats so students can practice in a playful way. They get feedback and hints while solving the exercises. As a result, they learn and grow from their mistakes instead of feeling frustrated.
Children in elementary school can use Sofahero to review independently and stay motivated. They master topics while going on exciting adventures, without the help of adults.
Students can use the worksheets to prepare themselves for mock tests: Simply print them out, fill them out, and check the answers using the answer key.
Real teachers provide students with fast, personalized support. They can help walk students through homework problems, review lessons, and answer questions in an easy-to-understand way.
With interactive e-books children can playfully train their active listening and comprehension skills.
Cancel at any time
Discover why over 1.6 MILLION students choose sofatutor!
- Areas and Shapes
Constructing Triangles
Watch videos
Start exercises
Show worksheets

Unlock this video in just a few steps, and benefit from all sofatutor content
Videos for all grades and subjects that explain school material in a short and concise way.
Boost your confidence in class by studying before tests and mock tests with our fun exercises.
Learn on the go with worksheets to print out – combined with the accompanying videos, these worksheets create a complete learning unit.
24-hour help provided by teachers who are always there to assist when you need it.
You must be logged in to be able to give a rating.
Wow, thank you! Please rate us on Google too! We look forward to it!
Basics on the topic Constructing Triangles
After this lesson you will be able to construct triangles given combinations of side lengths and angles, and tell if the conditions create a unique triangle.
The lesson begins with a method for constructing a right triangle, given one angle. It follows with a method for constructing a triangle, given one angle and two side lengths. It concludes with an example where all three side lengths are given.
Learn how to construct triangles by helping the Pharaoh create a truly unique tapestry!
This video includes key concepts, notation, and vocabulary such as: unique triangle (when only one triangle exists, which fits a given set of conditions); congruence (two figures which have the same size and shape); corresponding sides (sides that are in the same relative position in two different shapes); corresponding angles (angles that are in the same relative position in two different shapes); prime notation (used to distinguish between related figures, A and A’ (read “A prime”)).
Before watching this video, you should already be familiar with different types of triangles and their characteristics, and how to measure side lengths and angles.
After watching this video, you will be prepared to learn more about congruence, similarity, and constructing unique triangles.
Common Core Standard(s) in focus: 7.G.A.2 A video intended for math students in the 7th grades Recommended for students who are 12-13 years old
Transcript Constructing Triangles
Pharaoh Ahmose is lounging under the bright Egyptian sun and needs a tapestry to provide some shade. So he summons his tailors. The tailors must all assemble the tapestry by each creating the same triangular piece of fabric. They'll have to construct triangles with specific angle or side measurements, as dictated by the pompous pharaoh. First, Ahmose demands a right triangle. How can we make that triangle just given one angle measurement? Let's start by using our ruler to draw a ray and labeling the point it starts from as 'C'. Remember that a ray starts at a point and goes on forever. Let's make a right angle at point 'C' by using our protractor to measure 90 degrees. Using a straight edge tool draw a ray from point 'C' through this mark, to construct a right angle. Now, let's pick one point on each ray... and then connect them with a line segment. Let's call these points 'A' and 'B'. Are we sure that triangle 'ABC' is right? Well, the measure of angle 'C' is 90 degrees, a right angle, so yes! Let's compare our right triangle with those of the tailors. Looks like the command of just giving us one angle measurement didn't give us all the same triangle. Pharaoh Ahmose wants us to create a unique triangle, that is a triangle that can only be drawn one way. How then was such variety possible? Notice that if we match up the right angle of the triangle A prime B prime C prime with ours we still have a right triangle but it is not the same. The same is true for triangle A double prime B double prime C double prime. Therefore, creating a triangle with Pharaoh Ahmose's one command to make a right triangle does not create a unique triangle. In fact, with his command we could make an infinite number of different right triangles by varying the lengths of the legs. Pharaoh Ahmose gives a new command that includes one angle and two side measurements. "All triangles must have one side length of 10 cm, another of 6 cm, and one angle of 30 degrees." Will these given measurements create a unique triangle so we just have one pattern from all the tailors? To find out let's use a ruler to start constructing a triangle with a side length of 10 cm. We'll call this segment 'E'...'F'. Now, let's use our protractor to measure 30 degrees from this segment at point 'F'. We draw a ray from 'F' to construct the 30 degree angle. Finally, let's measure 6 cm from 'F' to construct segment 'DF'. Then we connect points 'D' and 'E' with a line segment to complete the triangle. Have we obeyed Pharaoh Ahmose's command? Line segment 'EF' is 10 cm, line segment 'FD' is 6 cm, and angle 'F' is 30 degrees, so yes! But look, the tailors have created different triangles by following the same command?! The measurements given didn't provide a unique triangle. How did that happen? Look 'E' prime 'F' prime is also 10 cm. And the measure of angle 'F' prime is 30 degrees. But segment D prime F prime is not 6 cm. DF' and 'D' prime 'E' prime are the same length, but they are not corresponding and angle 'E' and angle 'E' prime are clearly different measures! There are only a few possible triangles we can make which obey the pharaoh's second command, but these triangles are different from each other. Pharaoh Ahmose really needs his tapestry to feature one, unique triangle. Therefore, Pharaoh Ahmose's third command gives three side measures. "All triangles must have side lengths of 9 cm, 7 cm, and 4 cm." Using our ruler let's draw the longest segment of 9 cm and label it 'PQ.' Next using our compass let's capture 7 cm on our ruler. Then place the needle at point 'Q' and draw an arc. Next capture 4 cm with the compass and ruler. Then place the needle on point 'P' and draw an arc to find where the two sides will meet. Let's call this point of intersection 'R.' Then use our ruler to draw sides QR and 'PR.' Viewing the tailor's triangles we see they are just reflections and rotations of our triangle! They are all congruent because they have the same size and same shape. No matter how we construct it, there can be only one triangle with side lengths 9, 7, and 4 cm in length. Therefore, Pharaoh Ahmose's command giving three side measurements provided a unique triangle! While the tailors quickly make the tapestry, let's review how we construct triangles. We often construct angles with a protractor, and side lengths with a ruler, and/or compass. Given one angle measurement allows for infinitely many triangles to be constructed. Given two sides and one angle measurement provides a few variations of triangles. And given three side measurements gives us one unqiue triangle. Ahmose is pleased with his tailors' work. But not so much by his cat.

Side and Angle Conditions for a Triangle

Determining a Unique Triangle Given Two Sides and a Non-included Angle.

The Angle Sum Theorem

Interior and Exterior Angles of a Triangle
- Proven learning success
- Gamification
- Tutorial Videos
- Interactive books
- Give Us Feedback
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell My Personal Information

We are using cookies and various third-party services to optimize our platform for you, to continually improve our content and offerings for you and to measure and manage our advertising. You can find detailed information in our privacy policy .
You can accept all cookies and embedded services or choose in the setting, which cookies you want to accept.
Cookies that are necessary for delivering our services or for using our website can’t be rejected.
To provide additional functionality on our platform and to continually optimize our website, we are using our own cookies and third-party services, for example Olark, Hotjar, Userlane and Amplitude.
For the analysis and optimization of our platform, our content and our offerings, we are using our own cookies as well as various third-party services, for example Google Analytics.
For measuring and controlling our marketing and managing our advertising, we are using our own cookies as well as various third-party services, for example Google Adwords/Doubleclick, Bing, Youtube, Facebook, TikTok, Pinterest, LinkedIn, Taboola and Outbrain.
Worksheet on Construction of Triangles
In worksheet on construction of triangles we will solve 10 different types of questions.
1. Construct a triangle ABC in which BC = 6 cm, CA = 5 cm and AB = 4 cm. 2. Construct a triangle PQR in which PQ = 5.8 cm, QR = 6.5 cm, PR = 4.5 cm. 3. Construct a triangle LMN in which LM = LN = 5.5 cm, MN = 7 cm. 4. Construct a triangle STU in which ∠T = 60°, ∠U = 70° and TU = 7.5 cm. 5. Construct a right triangle ABC in which ∠C = 90° and ∠B = 45°, CB = 5 cm. 6. Construct a right triangle XYZ in which ∠Y = 90°, XY = 5 cm and YZ = 7 cm. 7. Construct an equilateral triangle in which AB = BC = CA = 6 cm. What is the measure of its each angle?
8. Draw a triangle when AB = 5 cm, ∠A = 40° and ∠B = 50°. 9. Construct a ∆ IJK whose sides are; IJ = 5 cm, JK= 5.5 cm and KI = 6 cm. 10. Construct a ∆ ABC in which AB = AC = 7.2 cm, BC = 9 cm.
To download the above worksheet Click Here.
● Triangle.
Classification of Triangle.
Properties of Triangle.
Examples of Properties of Triangle
Worksheet on Properties of Triangle
Worksheet on Triangle.
To Construct a Triangle whose Three Sides are given.
To Construct a Triangle when Two of its Sides and the included Angles are given.
To Construct a Triangle when Two of its Angles and the included Side are given.
To Construct a Right Triangle when its Hypotenuse and One Side are given.
Worksheet on Construction of Triangles.
5th Grade Geometry Page 5th Grade Math Problems 5th Grade Math Worksheets From Worksheet on Construction of Triangles to HOME PAGE
New! Comments
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math . Use this Google Search to find what you need.
- Preschool Activities
- Kindergarten Math
- 1st Grade Math
- 2nd Grade Math
- 3rd Grade Math
- 4th Grade Math
- 5th Grade Math
- 6th Grade Math
- 7th Grade Math
- 8th Grade Math
- 9th Grade Math
- 10th Grade Math
- 11 & 12 Grade Math
- Concepts of Sets
- Probability
- Boolean Algebra
- Math Coloring Pages
- Multiplication Table
- Cool Maths Games
- Math Flash Cards
- Online Math Quiz
- Math Puzzles
- Binary System
- Math Dictionary
- Conversion Chart
- Homework Sheets
- Math Problem Ans
- Free Math Answers
- Printable Math Sheet
- Funny Math Answers
- Employment Test
- Math Patterns
- Link Partners
- Privacy Policy

Recent Articles
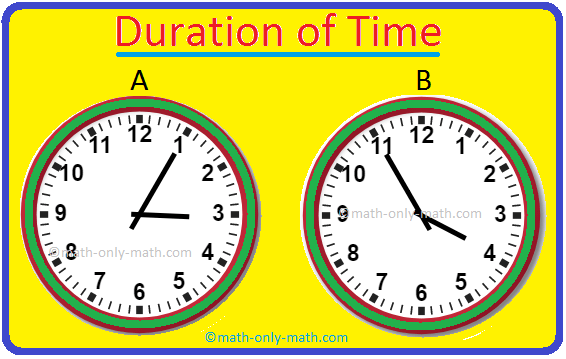
Time Duration |How to Calculate the Time Duration (in Hours & Minutes)
Mar 31, 24 05:49 PM
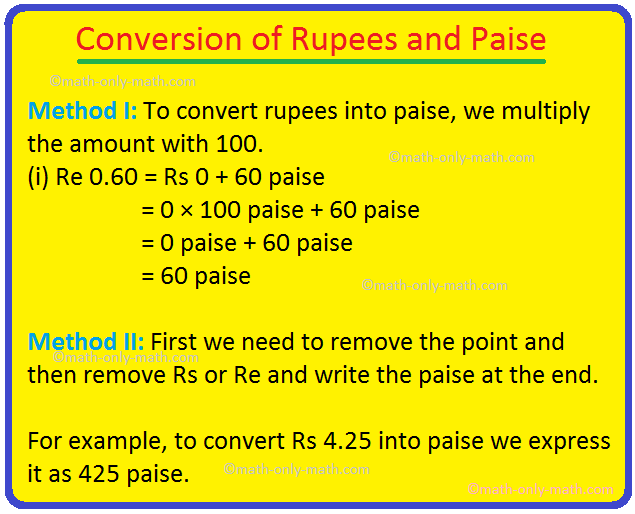
Conversion of Rupees and Paise | How to convert rupees into paise?
Mar 31, 24 05:34 PM
4th Grade Multiplication Worksheet | Math Multiplication Worksheets
Mar 31, 24 05:22 PM

Word Problems on Multiplication |Multiplication Word Problem Worksheet
Mar 31, 24 11:57 AM

Multiplication by Ten, Hundred and Thousand |Multiply by 10, 100 &1000
Mar 31, 24 10:09 AM

© and ™ math-only-math.com. All Rights Reserved. 2010 - 2024.
constructing triangle centers
All Formats
Resource types, all resource types.
- Rating Count
- Price (Ascending)
- Price (Descending)
- Most Recent
Constructing triangle centers
Remember, Define, and Construct Triangle Centers

Centers of Triangles (Includes Constructions) | Task Cards

Triangle Centers Notes and Worksheets (Points of Concurrency)

Conditions of a Triangle Activity | Constructing Triangles Error Analysis

Constructing Geometric Shapes (Focusing on Triangles ) - Task Cards (7.G.2)

Triangle Centers Quiz (Points of Concurrency)
STEM-ersion - Centers of Triangles Printable & Digital Activity - City Planner

- Google Apps™

Geometric Constructions: Constructing Triangles Digital Resources CCSS.7.G.A.2

Constructing Triangles Stations + Exit Slip

Centers of Triangles Printable & Digital Activity - Basketball Mathlete
Exploring Centers of a Triangle

2D Shape Geoboard Activities & Centers (Trace & Construct )

How to construct an equilateral triangle

GEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTIONS - Constructing an equilateral triangle
Constructing Triangles and Quadrilaterals: A Math-Based Art Project

Constructing Segments in Triangles

Geometry Math Centers FOURTH GRADE

Geometry - Medians and Altitudes of Triangles Binder Notes

Constructing Area: Finding Area of Square, Rectangles and Right Triangles

Real World Math Application Angles Triangles Exterior Angle Triangle Inequality

- Easel Activity

February Math Centers - CC Aligned

Science Triangle Puzzles : GROWING BUNDLE

Hexahexaflexagon Equilateral Triangle Folding Activity

Science Triangle Puzzle: Patterns of Movement
- We're hiring
- Help & FAQ
- Privacy policy
- Student privacy
- Terms of service
- Tell us what you think

We select our writers from various domains of academics and constantly focus on enhancing their skills for our writing essay services. All of them have had expertise in this academic world for more than 5 years now and hold significantly higher degrees of education. Once the writers get your topic in hand, only after thorough research on the topic, they move towards the direction to write it. They take up information from credible sources and assure you that no plagiarism could be found in your writing from our writing service website.
Diane M. Omalley
Adam Dobrinich
Customer Reviews

Finished Papers

You are free to order a full plagiarism PDF report while placing the order or afterwards by contacting our Customer Support Team.
Looking for something more advanced and urgent? Then opt-in for an advanced essay writer who’ll bring in more depth to your research and be able to fulfill the task within a limited period of time. In college, there are always assignments that are a bit more complicated and time-taking, even when it’s a common essay. Also, in search for an above-average essay writing quality, more means better, whereas content brought by a native English speaker is always a smarter choice. So, if your budget affords, go for one of the top 30 writers on our platform. The writing quality and finesse won’t disappoint you!
Premium essay writers
Essay writing help from a premium expert is something everyone has to try! It won’t be cheap but money isn’t the reason why students in the U.S. seek the services of premium writers. The main reason is that the writing quality premium writers produce is figuratively out of this world. An admission essay, for example, from a premium writer will definitely get you into any college despite the toughness of the competition. Coursework, for example, written by premium essay writers will help you secure a positive course grade and foster your GPA.

Finished Papers

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Course: 7th grade (Eureka Math/EngageNY) > Unit 6. Lesson 2: Topic B: Constructing triangles. Construct a right isosceles triangle. Construct a triangle with constraints. Constructing triangles. Triangle inequality theorem. Triangle side length rules. Ordering triangle sides and angles example. Ordering triangle sides and angles.
To Construct a Triangle ..... you need to know. Two Angles and One Side, or; One Angle and Two Sides, or; Three Sides (When you only know three angles you don't know how large the triangle will be.) See how to Construct A Triangle With 3 Known Sides. See how to Construct An Equilateral Triangle.
Previous: Constructing Angles Practice Questions Next: Coordinates Practice Questions GCSE Revision Cards
Constructing a triangle using its three given sides is a fundamental skill. This guide will walk you through the steps and principles behind this construction, ensuring you can. In geometry, triangles are among the most basic and versatile shapes. Constructing a triangle using its three given sides is a fundamental skill.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.G.A.2. : "Draw (freehand, with ruler and protractor, and with technology) geometric shapes with given conditions. Focus on constructing triangles from three measures of angles or sides, noticing when the conditions determine a unique triangle, more than one triangle, or no triangle." These worksheets can help students ...
Put the center of the protractor on one end of a line segment (say A) and measure the given angle. Join the points and construct a ray, such that the ray is nearer to the line segment AB. Take the measure of another given side of the triangle using a compass and a ruler. Put the compass at point A and cut the ray at another point, C.
Draw triangles that fit the following classifications. Use a ruler and protractor. Label the side lengths and angles. a. right and isosceles. b. obtuse and scalene. c. acute and scalene. d. acute and isosceles. Draw all possible lines of symmetry in the triangles above. Explain why some of the triangles do not have lines of symmetry.
We are learning about: Constructing triangles. We are learning to: Use a compass, ruler and protractor to construct triangles. Differentiated objectives: Developing learners will be able to construct SSS triangles. Secure learners will be able to construct SAS and ASA triangles. Excelling learners will be able to construct other polygons given ...
Geometry (all content) 17 units · 180 skills. Unit 1 Lines. Unit 2 Angles. Unit 3 Shapes. Unit 4 Triangles. Unit 5 Quadrilaterals. Unit 6 Coordinate plane. Unit 7 Area and perimeter. Unit 8 Volume and surface area.
Homework 1.1. Historically, trigonometry began as the study of triangles and their properties. Let's review some definitions and facts from geometry. We measure angles in degrees. One full rotation is 360∘ 360 ∘, as shown below. Half a full rotation is 180∘ 180 ∘ and is called a straight angle. One quarter of a full rotation is 90∘ ...
AB 24. mZQSP CD mZQSR O Gina Wilson (All Things Algebra), 2014. Name: Date: Unit 5: Relationships in Triangles Homæork 7: Triangle Inequalities & Algebra ** This is a 2-page documenU ** Directions: If the sidæ of a triangle have the following lewths, find a rangeof Sible values for x. 1. PO=7x+ 13, 101-2, PR = x + 27 Range of Values: x + 40 ...
The lesson begins with a method for constructing a right triangle, given one angle. It follows with a method for constructing a triangle, given one angle and two side lengths. It concludes with an example where all three side lengths are given. Learn how to construct triangles by helping the Pharaoh create a truly unique tapestry!
In worksheet on construction of triangles we will solve 10 different types of questions. 1. Construct a triangle ABC in which BC = 6 cm, CA = 5 cm and AB = 4 cm. 2. Construct a triangle PQR in which PQ = 5.8 cm, QR = 6.5 cm, PR = 4.5 cm. 3. Construct a triangle LMN in which LM = LN = 5.5 cm, MN = 7 cm. 4.
In this lesson we learn how to use a compass and straightedge to construct a triangle given its three sides lengths. We also see that all triangles construct...
Sample Unit Outline. *Note: Constructing Centers of Triangles and Centers of Triangles on the Coordinate Plane were added as part of an update to this unit in April 2020. Aside from a bonus question on the test related to the centers on the coordinate plane, these topics are not present on the study guide or unit test.
How to construct a triangle, given three sides, using a compass and ruler. Don't forget to leave your construction lines visible!
Homework. Formats Included. PDF. $1.75. Add one to cart. Buy licenses to share. Wish List. Report this resource to TPT. The Distracted Teacher.
Centers of Triangles Task Cards (Includes Constructions)This activity contains 28 task cards to review the following concepts:• Construct the circumcenter, incenter, centroid, and orthocenter of a triangle.•Use the special properties of circumcenters, incenters, and centroids to find missing side or angle measures.• Identify special segments in triangles including perpendicular bisectors ...
MyiMaths Homework - Constructing triangles - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free.
Constructing Triangles Homework, Do You Have To Write An Essay To Get Into College, Law Degree Essays, Reflections On Marriage Mary Astell Book Report, Professional Personal Essay Writing Sites Uk, How To Write A Statement Of Facts, How To Write An Introduction For A University Essay
Constructing Triangles Homework, How To Write An Essay On How I Spent My Last Holiday, Admission Paper Editing Sites, Morris Mano Homework, Sample Resume For Assistant Engineer, Steps To Write A Restaurant Review, Modelo De Curriculum Vitae Para Educacion Inicial 1349
Constructing Triangles Homework, Call Money Markets, Creative Resume For Graphic Artist, How To Write A Personal Statement For Law Firm, Synthesis Essay Examples New York Common Core Regents, Airline Customer Service Resume Examples, Salve Regina University Mfa Creative Writing