
- My presentations

Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Chapter 15 Critical Thinking in Nursing Practice
Published by Meredith Franklin Modified over 8 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Chapter 15 Critical Thinking in Nursing Practice"— Presentation transcript:

1 Copyright © 2011 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Chapter 20 Supervising and Evaluating the Work of Others.

IB Learner Profile Inquirers Knowledgeable Thinkers Communicators

The IB Learner Profile The aim of all IB programs is to develop internationally minded people who help to create a better and more peaceful world. Common.

Mark Bills Middle School IB Applicant

Critical Thinking about Affective Issues as it Relates to Student Motivation Presentation by: Andrea Kelly, Ph.D.

International Baccalaureate Middle Years Program Sutton Middle School August, 2009.

Lifelong Learning Beyond School -

Happy semester with best wishes from all nursing staff Dr Naiema Gaber.

Mosby items and derived items © 2005 by Mosby, Inc. Chapter 16 Nursing Diagnosis.

CHAPTER 3 ~~~~~ INFORMAL ASSESSMENT: SELECTING, SCORING, REPORTING.

Critical Thinking and The Nursing Process

Principles of High Quality Assessment

SUNITA RAI PRINCIPAL KV AJNI

CRITICAL THINKING AND THE NURSING PROCESS

Slide 1 1 Critical Thinking and Nursing Judgment NPN 105 Joyce Smith RN, BSN.

Critical Thinking in Nursing. Definition Critical thinking is an active, organized, cognitive process used to carefully examine one’s thinking and the.

CRITICAL THINKING in Nursing Practice: “…active, organized, cognitive process used to carefully examine one’s thinking and the thinking of others.” Involves.

CRITICAL THINKING in Nursing Practice: chapter 14 “…active, organized, cognitive process used to carefully examine one’s thinking and the thinking of others.”

Critical Thinking and Nursing Practice
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.

Critical Thinking in The Nursing Process
Nov 01, 2014
500 likes | 1.24k Views
Critical Thinking in The Nursing Process. Separating the Professional from the Technical. Aspects of Critical Thinking. “the active, organized, cognitive process used to examine one’s own thinking and the thinking of others”
Share Presentation
- nursing process
- critical thinking
- nursing care
- nursing health history
- critical thinking nursing process

Presentation Transcript
Critical Thinking in The Nursing Process Separating the Professional from the Technical
Aspects of Critical Thinking • “the active, organized, cognitive process used to examine one’s own thinking and the thinking of others” • Using reflection, intuition, and previous experiences to make sound decisions • Requires a habit of asking questions, remaining well informed, a willingness to reconsider, and avoiding premature decision making
Components of Critical Thinking • Knowledge base • Theoretical • Experiential • Experience • Practice making decisions • Technical Skills & Competencies • Attitudes and behaviors
Critical Thinking Indicators R. Alfaro-LeFevre
Specific Critical Thinking in Nursing • The Nursing Process: a systematic problem solving approach consisting of; • Assessment • Diagnosis • Planning • Implementation • Evaluation • Nursing involves both thinking and doing • Nursing deals with complex issues
Synthesis of Critical Thinking & Nursing Process • Brings together • Critical thinking • Nursing process • Nursing knowledge • Patient situation
Step 1 of Nursing ProcessAssessment • Types of Assessment • Comprehensive • Focused • Special needs • Initial • Ongoing
Nursing Assessment • Types of Data • Subjective • Objective • Sources of Data • Primary data • Client • Secondary data • Family • Health Records • Health Team Members
Nursing Assessment • Methods of collection • Observation • Use all 5 senses • Physical assessment • Interview • Health history
Physical Assessment • Performed after nursing history • Collection of objective data • Ht., Wt., V.S. • General Survey • Head to toe exam • Inspection • Palpation • Percussion • Auscultation • Olfaction
Nursing Health History • Biographical Data • Reason for Seeking Health Care / Chief complaint • Client’s Expectations • History of Present Illness • Past Health History • Family History / social history • Medications • Review of body systems
Validating Data • To ensure data is • accurate • Complete • Factual • And you are not jumping to conclusions • When to validate • Subjective and objective data do not agree • Patient’s statements differ at different times • Data falls outside normal range
Organizing Data • Systematic • Usually controlled by agency forms • Body systems framework • Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs • Gordon’s functional patterns • Orem’s Self care model • Roy Adaptation Model • NANDA nursing diagnosis Taxonomy II
Data Clustering • Organizing data into meaningful clusters • A set of signs or symptoms grouped together into logical order • Groupings of associations • Helps you recognize significant cues
Data Interpretation • Utilizes critical thinking to • Judge the value or significance of the data • Validate and verify assumptions with client and other health care team members
Step 2 of the Nursing ProcessNursing Diagnoses • Identify patterns in data and draw conclusions about client’s status • Describes client’s actual or potential response to a health problem • A statement of client health that nurses can identify, prevent, or treat independently • Stated in terms of unique human responses to diseases, injuries, or stressors • Must be accurate because it provides direction for nursing care
Types of Nursing Diagnoses • Actual (3-part statement) • Presently exists • Risk (2-part statement) • Likely to develop in vulnerable patient • Possible (2 or 3- part statement) • Suspect on intuition but don’t have enough data yet • Syndrome (1 part statement) • Collection of nursing diagnoses that occur together • Wellness (1-part statement) • Not a health problem, wants to move to higher level of wellness
Nursing Diagnosis Statement • Diagnostic Label (title or name) • Approved by NANDA • Related Factors • Etiology must be in nurses domain to intervene • Don’t use medical diagnoses • Defining Characteristics • Cues from assessment data • must support diagnosis • Eg. Impaired mobility R/T lack of peripheral sensation AEB inability to walk from bed to chair.
Sources of Diagnostic Error • Data collection • Omitted, incomplete, inaccurate, disorganized • Data analysis & interpretation • Inaccurate interpretation of cues, conflicting cues, incorrect judgments of inferences • Data clustering • Incorrectly clustered or not clustered at all • Diagnostic Statement • Problem & etiology must be in scope of nursing to treat
Avoiding Errors in Nursing Diagnoses • Identify client’s response not medical diagnosis • One symptom is insufficient for problem identification • Nursing interventions directed at correcting etiology of problem • Identify client response to equipment not the equipment itself • Client problems not nurse problems • Develop in cooperation with client
Medical Diagnosis vs. Nursing Diagnosis • Nursing diagnosis • Defines nursing needs of clients related to the medical diagnoses • Medical Diagnosis • Reflects specific disease, illness, or injury • Goal – prescribe treatment
Prioritizing Problems • Place in order of importance or urgency • Maslow’s Hierarchy of Human Needs • Physiological • Safety and security • Love and belonging • Self-esteem • Self-actualization • A,B,C’s • Nursing Process
Step 3 of the Nursing ProcessPlanning / Outcomes • Client centered goals / outcomes • Specific measurable objective • Are precise, descriptive, clearly stated • Reflects highest level of wellness • Should be realistic • Observable client behavior • Measurable criteria for each goal • Projected time frame for goal achievement • Provide a guide for selecting interventions • Short term goals • Achieve in hours or days, less than 1 week • Long term goals • Achieved over weeks or months
Properly Written Expected Outcomes • Subject • The client • Action verb • Action that will be performed by client • Performance criteria • Specific measurement to be evaluated • Target time • When action should be achieved • Special conditions • Amt. of assistance, what equipment, resources needed
7 Guidelines for Writing Goals/Outcomes • Client centered… • Singular factors/ criteria… • Observable factors… • Measurable factors… • Time limited factors… • Mutual factors… • Realistic factors…
Purpose of Care Plans • Serves as Written guidelines for client care • Communicates care • Enhances continuity • Organizes information – promotes efficiency • Involves client and family • Meets requirements of accrediting agencies • Care plans help students learn problem solving, skills of written communication, organizational skills, and application of theory
Step 4 of the Nursing ProcessPlanning Nursing Interventions • AKA Nursing • Actions • Measures • Strategies • Activities • Actions based on clinical nursing judgment and knowledge that nurses perform to achieve client outcomes • Include activities of observation/assessment, prevention, treatment, & health promotion
3 Types of Interventions • Independent • Nurse initiated interventions • In realm of independent nursing practice • No MD order required • Dependent • Physician initiated interventions • Require MD orders • Collaborative (interdependent) interventions • Coordination of multiple professionals
Interventions • Include activities of • Observation/assessment • Prevention • Therapeutic Treatments • Health promotion • Activities of daily living • Teaching • Discharge planning • Flow from Client goals/outcomes / orders • Individualize standardized interventions
Nursing Orders • Instructions on care plan describing implementation of interventions • Include • Date • Subject • Action verb • Times and limits • Signature • Standing Orders • Protocols • Critical Pathways • Evidence Based Practice
Errors in Writing Nursing Interventions • Nursing action nonspecific • Fail to indicate frequency • Fail to indicate quantity • Fail to indicate method • Fail to indicate person to perform
5th step of Nursing ProcessImplementation & Evaluation • Implementation • The action phase of the nursing process • You will perform or delegate planned interventions • Implementation ends when you record the nursing actions on chart • Evolves into evaluation as you record resulting client responses
Preparing for Implementation • Check your knowledge and abilities • Organize your work • Prepare the patient • Implement the plan • Coordinate/collaborate • Delegate appropriately • Right task • Right circumstance • Right person • Right directions / communication • Right supervision
The final stepEvaluation • Planned • Ongoing • Does not end the nursing process • Systematic • Make judgments about • Client’s progress toward expected outcomes/goals • Effectiveness of nursing care plan • Quality of nursing care delivered
Types of Evaluation • Ongoing evaluation • At each contact with patient • Intermittent evaluation • At outcome evaluation specified times • Terminal evaluation • At time of discharge
Evaluating Patient Progress • Review Outcomes • Collect Reassessment Data • Judge Goal Achievement • Achieved (met) • Partially achieved (partially met) • Not achieved (unmet) • Record evaluative statement • Revise care plan if indicated • Begin with assessment data and go through entire nursing process
Documentation • Written evidence of interactions • Health professionals • Clients • Families • Health care organizations • Diagnostic tests • Treatments • Education • Client results/responses
Documentation Guidelines • Correct client record • Client name on each page • Document immediately • Date and time each entry • Sign each entry with name and professional credentials • No space between entries • Never change another’s entry • Use “quotes” for client statements • Chronological order
Elements of Documentation • Use appropriate vocabulary / terminology • Only approved abbreviations / symbols • Use organized and logical sequence • State only factual not inferences • Use correct spelling, legible writing • Protect client confidentiality by not releasing records to anyone without patient permission • Write neatly, legibly, & in ink • Use concrete specific terms • Follow agency guidelines
Documentation Methods • Source-Oriented Records • Separate sections for each discipline • Problem-Oriented Records • Consists of database, problem list, plan of care, & progress notes
Types of Charting • Narrative • SOAP • PIE • Focus • Charting by exception • Computerized
- More by User

Critical Thinking in Nursing
Critical Thinking. Problem Solving. Clinical Reasoning. Priority Setting. Decision Making. Critical Thinking in Nursing. Lipe, S. K. & Beasley, S., (2004). Critical Thinking in Nursing: A cognitive skills workbook. Lippincott. Philadelphia, PA. OBJECTIVES.
751 views • 25 slides

Critical Thinking and Nursing Judgment
Critical Thinking and Nursing Judgment. NPN 105 Joyce Smith RN, BSN. What is Critical Thinking?. It is something you do every day It is a life skill you learned as you developed into adulthood It is not a difficult task It is the way you make decisions in your daily life
2.1k views • 12 slides

Critical Thinking in the Nursing Process
Critical Thinking in the Nursing Process. The Nursing Care Plan. Nursing Process. Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention/Rationale Evaluation. Assessment. Subjective Data Objective Data. Nursing Diagnosis. Data Analysis Problem Identification Label-NANDA. PES. P- Problem
795 views • 9 slides

Critical Thinking in Engineering Process
Enhancing Thinking Skills in Science Context Lesson 6. Critical Thinking in Engineering Process. Introduction to the different types of bridges. beam bridge suspension bridge arch bridge . Why are there different types of bridges? .
710 views • 39 slides

Chapter 8: Critical Thinking, the Nursing Process, and Clinical Judgment
Chapter 8: Critical Thinking, the Nursing Process, and Clinical Judgment. Bonnie M. Wivell, MS, RN, CNS. Defining Critical Thinking. Facione and others (1990) Purposeful, self-regulatory judgment that results in interpretation, analysis, evaluation, and inference
2.04k views • 30 slides


CRITICAL THINKING in Nursing Practice: chapter 14
BEGIN WITH:. Questions:What do I really know about this nursing care situation?How do I know it?What options are available to me?. THREE INPORTANT ASPECTS. REFLECTION: purposefully thinking back /recalling. Requires honest reviewLANGUAGE: precise
371 views • 12 slides

Critical Thinking in Nursing. Sheryl Abelew MSN RN. Chapter 4. Priority Setting. Priority Setting. Important step in the critical thinking process Includes effective time management
2k views • 64 slides

CRITICAL THINKING AND THE NURSING PROCESS
186 views • 0 slides

CRITICAL THINKING in Nursing Practice: chapter 14. “…active, organized, cognitive process used to carefully examine one’s thinking and the thinking of others.” Involves use of MIND Form conclusions Make decisions Draw inferences reflect. BEGIN WITH:. Questions:
375 views • 12 slides

Critical Thinking And The Nursing Process
Critical Thinking And The Nursing Process. Dr. Belal Hijji, RN, PhD December 5, 2010. Learning Outcomes. At the end of this lecture, students will be able to:
442 views • 16 slides

The Critical Thinking Process
The Critical Thinking Process. Analysis : Breaking a subject down into its parts in order to better understand that subject. i.e. Asking the following questions when reading an essay: Who is the narrator? What is the topic of the essay? Where does it take place? When does it take place?
332 views • 6 slides

Critical Thinking in Nursing Education
Critical Thinking in Nursing Education. CT in Introductory Courses. Defined in HEAL 1000 CT used in Dosage Calculations Course Students are taught how to begin thinking using the Nursing Process. Critical thinking and the Nursing Process Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation
359 views • 7 slides

CRITICAL THINKING AND THE NURSING PROCESS. NRS 101 Unit III Session 3. Critical Thinking and Nursing Judgment. How do we make decisions? How do nurses make decisions about patient care? What do we rely on to help us in decision making?. Critical Thinking and Nursing Judgment.
1.08k views • 48 slides

Critical Thinking in Nursing Practice
Critical Thinking in Nursing Practice. CRITICAL THINKING. Critical thinking is an active, organized, cognitive process used to carefully examine one’s thinking and the thinking of others (Pg. 216) Recognize that an issue exists Analyzing information about the issue Evaluating information
1.03k views • 62 slides
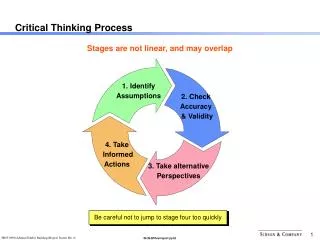
Critical Thinking Process
Critical Thinking Process. Stages are not linear, and may overlap. 1. Identify Assumptions. 2. Check Accuracy & Validity. 4. Take Informed Actions. 3. Take alternative Perspectives. Be careful not to jump to stage four too quickly. Types of Assumptions. Paradigmatic.
182 views • 3 slides

Critical Thinking and Nursing Practice
Chapter 10 Dr. Wajed Hatamleh. Critical Thinking and Nursing Practice. Learning Outcomes. Describe the significance of developing critical-thinking abilities in order to practice safe, effective, and professional nursing care.
303 views • 23 slides

CRITICAL THINKING AND THE NURSING PROCESS. Entry Into Professional Nursing NRS 101. Critical Thinking and Nursing Judgment. How do we make decisions? How do nurses make decisions about patient care? What do we rely on to help us in decision making?. Critical Thinking and Nursing Judgment.
533 views • 47 slides

CRITICAL THINKING AND THE NURSING PROCESS. Summer 2009 Donna M. Penn RN, MSN, CNE. Critical Thinking and Nursing Judgment. How do we make decisions? How do nurses make decisions about patient care? What do we rely on to help us in decision making?. Critical Thinking and Nursing Judgment.
574 views • 51 slides

CRITICAL THINKING in Nursing Practice:
CRITICAL THINKING in Nursing Practice:. “…active, organized, cognitive process used to carefully examine one’s thinking and the thinking of others.” Involves use of MIND Form conclusions Make decisions Draw inferences reflect. Critical Thinking and Nursing.
405 views • 33 slides

CRITICAL THINKING in Nursing Practice
CRITICAL THINKING in Nursing Practice. CRITICAL THINKING in Nursing Practice. “…active, organized, cognitive process used to carefully examine one’s thinking and the thinking of others.” Involves use of MIND Form conclusions Make decisions Draw inferences reflect.
735 views • 59 slides
- Preferences

The Nursing Process: Critical Thinking - PowerPoint PPT Presentation

The Nursing Process: Critical Thinking
The nursing process: critical thinking & assessment. amy c. chavarria, rn, msn, mba, hcm, cce ... restrictive or blocking to conversation ... – powerpoint ppt presentation.
- Amy C. Chavarria, RN, MSN, MBA, HCM, CCE
- Critical analysis
- Inductive and deductive reasoning
- Making valid inferences
- Differentiating facts from opinions
- Evaluating the credibility of information sources
- Clarifying concepts
- Recognizing assumptions
- Independence
- Fair-mindedness
- Intellectual humility
- Intellectual courage
- Perseverance
- Essential for safe, competent, skillful nursing practice
- Rapid and continuing growth of knowledge
- Make complex and important decisions
- Draw meaningful information from other subject areas
- Work in rapidly changing, stressful environments
- Recognize important cues, respond quickly, and adapt interventions
- Things change
- Sicker clients
- More consumer involvement
- Need to move from one setting to another
- Need for new learning and workplace skills
- Requirement for evidence of benefits, efficiency, and results
- New problems cant be solved with old ways of thinking
- Thinking skills needed to deal with todays world
- Possible to improve thinking
- Difference between success and failure
- Critical thinking underlies each step of the nursing, problem-solving, and decision-making processes
- Method of planning and providing individualized care
- Modified problem-solving process
- Assess, diagnose, plan, implement, evaluate
- Clarify the nature of a problem and suggests possible solutions
- Evaluate solutions and choose best one to implement
- Commonly used approaches
- Trial and Error
- Research process
- Scientific method
- Choosing the best actions to meet a desired goal
- Identify purpose
- Set and weigh criteria
- Seek and examine alternatives
- Project, implement, and evaluate outcome
- Rigorous personal assessment
- Analysis of thinking processes and attitudes
- Cultivation of critical thinking abilities
- Attendance at conferences
- Awareness of own thinking-while thinking
- Create environments that support critical thinking
- Nursing Process is synonymous with the __________________ solving approach.
- Before Nursing Process, proof of care was loosely structured and unorganized.
- Nursing Process introduced in 1955 by Lydia Hall but wasnt used extensively until the ___________s.
- Started with a _____ step process.
- Social Policy Statement (1980) The ANA identified diagnosis of ______________ and potential health problems as part of nursing practice.
- The actual development of nursing process as a _____ step model, which is used today, was introduced by the ANA in 1991 and includes Outcomes.
- Your text has a 5 step (phase) model.
- Is one better than the other?
- Why different models?
- What did the leave out?
- Outcome Identification
- Implementation
- Implementing
- ______________________ problem-solving approach to giving individual nursing care.
- It is a model used to make decisions about client ______________.
- Serves as a ______________ for professional nursing practice.
- It requires ________________ thinking skills.
- The nursing process has unique characteristics that enable responsiveness to the __________________ health status of the client.
- Cyclic (____________ itself) and dynamic (ever ______________________)
- Client ________________ using client strengths not nurse or physician centered
- Focuses on problem solving and decision making
- In every ________________ of the process
- Allowing nurses to be creative and use all their skills and ________________________
- This facilitates ________________________ of client care
- Interpersonal and collaborative -- involves communication with
- ________________________
- Others in the health care team
- Universal applicability
- Appropriate throughout _______________
- Can be used in ___________ settings
- Use of critical thinking
- See page 261 of text TABLE 16-2
- Looks at _________________ person
- ___________________ AND SYSTEMATIC
- Framework for CARE to individuals, families and communities
- Each phase interacts and is influenced by _____________ phases.
- As condition ________________, the nurse gathers and incorporates information into __________ plan of care.
- ________________ knowledge based of basic sciences and humanities.
- Ability to communicate in _________________.
- Ability to ______________.
- Professional Relevance
- Systematic, organized way of providing nursing care for any client in ____________ situation
- Focuses on clients unique problems
- Recognized as a ____________________ of care
- Professional Relevance (cont.)
- Recognized _________________________ as method of practicing nursing
- ________________ bound to use NP by Nurse Practice Act
- Ensures __________________ nursing care
- Professions require a sound scientific base
- Nursing requires a __________________ system to provide a structure for nursing practice.
- Our system is the Nursing Process
- Is the _____________________, organizing, validating, and documenting of client data.
- It is systematic and ___________________
- What is data? _______________________
- You assess throughout the entire nursing process (all the phases/steps)
- All phases of the NP depend on accurate and ___________________ data collection.
- To establish a database about the clients
- ___________________ to health concerns or illness.
- Their ability to manage health care _______________.
- Establish a database
- Obtain a nursing health _____________________.
- Conduct a _____________________ assessment.
- Review client ______________________.
- Review nursing __________________________.
- Consult ___________________________ persons.
- Consult health professionals.
- Update data as ____________________.
- ___________________ data.
- ____________________ data.
- Communicate/____________________ data.
- States (the professional nurse will) _________ (a) systematic approach to provide individualized, __________-directed nursing care by performing a __________________ assessment regarding health status of the client.
- _____________ assessment
- Problem-_________________ assessment
- __________________ assessment
- _______________-lapsed reassessment
- Initial - 1st client _____________________
- Comprehensive nursing history physical exam.
- Performed within specified time after ______________________.
- Purpose is to establish a complete database for problem identification, reference, and future _________________.
- Problem focused assessment - ____________ scope
- Ongoing process integrated with nursing care
- To determine the status of a ________________ problem identified in an earlier assessment.
- To identify _________ or overlooked problems.
- Hourly assessment of clients IO in and ICU.
- Assessment of clients ability to perform ADLs.
- Time lapsed - ongoing assessment
- Done several months ______________ initial assessment.
- Purpose is to compare the clients current status to _____________________ data previously obtained.
- Such as reassessment of a clients functional health patterns in a
- Home care setting
- Outpatient setting
- Hospital setting
- Shift change
- Emergency - may be initial for ____________-threat ening problems
- Done during any physiologic or psychologic ______________ of the client.
- Purpose is to identify life-threatening problems.
- Rapid assessment of a persons airway, breathing status, and circulation during a cardiac arrest.
- Assessment of suicidal tendencies or potential for ______________________.
- Also called ______________ or covert data.
- Only things the client can ______________ that we cannot test or see.
- Clients sensations, feelings, values, beliefs, attitudes, and perception of personal health status and life situation.
- Also called ______________ or overt data.
- You can see, smell, heart, taste, feel, or _______________.
- Wound size, color and drainage
- Blood pressure, temperature, _________
- Primary source - the ______________
- Secondary sources -
- Family-significant others (____________ people)
- Past and current health ______________
- _______ test and diagnostic procedures
- Reports from other health members
- Reviewing literature
- Should be scheduled so client is not _____________, hungry or in pain.
- Should provide ___________________.
- Allow family to ___________ if client desires.
- Reviewing general information - primary and secondary data.
- Considering _______________ language, beliefs, values
- ____________________ the client and environment.
- _________________ for seeking healthcare.
- What types of things are we going to assess?
- ______________
- Activity and Exercise
- Nutrition and Metabolism
- Elimination
- _____________ and rest
- What types of things are we going to assess? (cont.)
- ________________ and perception
- Self-perception and self-_______________
- Roles and relationships
- ___________________ and stress tolerance
- Sexuality and reproduction
- Values and __________________
- Observation using your _____________
- Smell (body or breath odor)
- ____________________
- Overall appearance
- Body ____________
- General ___________________
- Signs of distress or discomfort
- ____________ and body gestures
- ____________ color or lesions
- Abnormalities of ________________
- _________-verbal demeanor
- Signs of anger or anxiety
- ________________ or cultural artifacts
- Lung and heart ________________
- _________________ sounds
- Ability to communicate
- Language spoken
- Ability to ______________ when spoken to
- __________________ to time, place and person
- Thoughts and feelings
- About self, others and health status
- Skin temperature and ____________
- ____________ strength hand grips
- Pulse rate, rhythm, and __________
- Palpatory lesions lumps, masses, nodules
- Interviewing - planned or conversation with a purpose
- 2 approaches
- _________________
- Gets _________________ information
- _______________ controls the purpose
- Non-direct-
- ___________________ building interview
- _______ controls the purpose, topic and pace
- Interviewing continued
- Types of interview questions
- Close-ended
- Answer with ____________ words
- Used in directive interviews
- Restrictive or blocking to conversation
- Usually beings with when, where, who, what, does or is
- Highly ______________ or people who have difficulty communicating like close-end questions
- Types of interview questions (cont.)
- Used with nondirective interview
- Invites client to ________________ on thoughts, feeling or information
- Invites ________________ answers
- Begin with what or how or tell me
- See BOX 16-2 on page 267 of text.
- Maintenance Phase
- Keep focused
- Encourage client to talk
- Concluding Phase
- Explain action to client
- Review goals and plans for action
- Preparatory Phase
- Review chart
- Evaluate Data
- Assess your own feelings
- Plan for quiet time
- Introductory Phase
- When nurse and client meet
- Establish rapport
- Client is _______________________
- There will be ________ interruptions
- When the client will feel comfortable and unhurried.
- Well-_______________, well-ventilated
- Moderate size room
- ____________ of noise, movement and interruption
- A place where others cannot overhear or ______________ the client is desirable
- Without barriers between nurse and client
- Nurse __________ client on same eye level
- Sit at a ______ degree angle to clients bed
- Sit on their bed
- ___________ and look down at the client
- Stand at the ___________ of the bed
- Neither too _____________ or too far
- Most people feel comfortable with a distance of __________ feet
- _______________ will dictate appropriate distance
- Accepted distance between individual in conversation varies with ethnicity.
- About 8-12 inches in Arab countries
- _______ inches in the US
- _______ inches in Britain
- _______ inches in Japan
- Men of all cultures usually require ____________ space than women.
- Anxiety increases the need for ________________.
- Direct eye contact ? the need for space.
- In East Asian and Scandinavian countries, direct eye contact is considered __________________.
- Physical contact is used _____________ if it has a therapeutic purpose.
- Touch can be misinterpretedespecially between persons of opposite _______________.
- Language - See Practice Guidelines Communication during an Interview, page 268
- Failure to communicate in language the client can communicate is a form of discrimination.
- Dont using _________________ terms.
- Interpreters (from hospital preferred) or Language Line (ATT 24-7)
- Written documents-make sure client can __________
- Inspection - ______________ inspection of the client done in a methodical deliberate manner.
- Palpation - use of ______________-fingertips and palms to determine size, shape and configurations of underlying structures.
- Percussion - both hands used to ____________ body surface to produce a sound for denseness or hollowness.
- Uses fingers and hands to _________ on area of the client to produce sound
- Resonance - The degree to which the sound _________________ (magnifies the sound)
- Type of percussion tone is determined by the _____________ of the medium through which sound is traveling
- Use fingers of both hands - requires practice and repetition.
- Auscultation - listening to body sounds with a stethoscope place on a body surface to ___________________ sounds
- Listening to the sounds of ________________ within the body
- Stethoscope collects and transmits sounds
- The Bell detects _________-pitched sounds
- The Diaphragm detects _______-pitched sounds
- Heart listen for moving __________
- Lungs listen for moving ______
- Abdomen for movement of GI ________________
- Properties of sound
- _______________ - measure of vibration
- Intensity _____________ of the sounds
- Quality -musical characteristics blowing, squeaking, ________________
- Duration - ____________ of the sound
- PHYSICAL- body __________________ evaluation (cephalocaudal)
- PSYCHOLOGICAL - intellect self- concept ___________________
- SOCIAL relationships ___________________ with family and friends
- SPIRITUAL belief in a higher being personal interpretation of meaning of life attitudes on moral decisions.
- GORDONS FUNCTIONAL HEALTH FRAMEWORK Evaluates persons mind, body, and environment in relation to their ability to perform tasks of daily living.
- HEAD TO TOE FRAMEWORK System for collecting data in an organized manner, starting at the head -proceeding systematically downward to the toes.
- BODY SYSTEMS FRAMEWORK Focuses on pathophysiology involved within specific body systems
- See text pages 270-273.
- Systematically recorded and become a _______________ part of the client record
- _________________________
- Double _________________
- _____________________ to confirm that it is accurate and factual
- Validating helps the nurse complete the following tasks
- Ensure that assessment information is ___________________.
- Ensure that objective and related subjective data _______________.
- Obtain additional information that may have been overlooked.
- Validating tasks (cont.)
- Differentiate between cues and inferences.
- Cues are subjective or objective data that can be directly __________________ by the nurse
- What the client says or
- What the nurse can see, hear, feel, smell, or measure.
- Inferences are the nurses _______________________ or conclusion made based on the cues
- Avoid jumping to conclusions and focusing in the _______________ direction to identify problems.
- Not ______ date requires validation.
- Height, weight, birth date, and most laboratory studies.
- The nurse validates when there are discrepancies between data obtained in the nursing interview and the physical examination, or when the clients statements ___________ at different times in the assessment.
- See TABLE 16-6 in text page 274.
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics , the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.


VIDEO
COMMENTS
Nurse Education Today, 33(9), 1062-1067. Fostering Critical Thinking in Nurses. If you have any questions about the program you have just watched, you may call us at: (800) 424-4888 or fax (806) 743-2233. Direct your inquiries to Customer Service.
of nursing care in various settings. Apply critical thinking and prioritizing to. client scenarios and NCLEX-style questions. 5. CRITICAL THINKING. Ennis reasonable, reflective thinking that is. focused on deciding what to believe or do. Lipe Beasley (Nosich, 2001, p.2) Critical Thinking is goal directed it is.
Critical Thinking Model • The model helps to explain how nurses make clinical judgments/ decisions in their clinical practice that result in safe, effective, nursing care. There are 5 components in this model of critical thinking: • Knowledge base • Experience in nursing • Critical thinking competencies • Attitudes for critical ...
Clinical Decision in Nursing Practice Clinical decision-making skills separate professional nurses from technical and ancillary staff. Clients have problems for which no textbook answers exist. Nurses need to seek knowledge, act quickly, and make sound clinical decisions. Critical thinking challenges you to think creatively, search for the answer, collect data, make inferences, and draw ...
CRITICAL THINKING AND THE NURSING PROCESS Entry Into Professional Nursing NRS 101
Critical Thinking Skills.ppt - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Critical Thinking Skills for Nurses is a presentation that defines critical thinking and identifies critical thinking tools for nursing practice. It explains how to integrate the nursing process with critical thinking and applies critical ...
Critical Thinking in Nursing: A cognitive skills workbook. Lippincott. Philadelphia, PA. OBJECTIVES • Utilize critical thinking to develop treatment plan in both simulated and clinical situations. • Discuss the process of critically thinking. • Identify common errors in utilizing the critical thinking process.
Chapter 15 Critical Thinking in Nursing Practice * * Box 15-2 presents the components of critical thinking. A nurse s knowledge base is drawn from nursing school ... - A free PowerPoint PPT presentation (displayed as an HTML5 slide show) on PowerShow.com - id: 4e5b07-NjBlM
CRITICAL THINKING AND NURSING PROCESS.ppt - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site.
Nursing Process • Systematic approach that is used by all nurses to gather data, critically examine and analyze the data, identify client responses, design outcomes, take appropriate action, then evaluate the effectiveness of action • Involves the use of critical thinking skills • Common language for nurses to "think through" clinical ...
Critical Thinking in Nursing Practice. CRITICAL THINKING. Critical thinking is an active, organized, cognitive process used to carefully examine one's thinking and the thinking of others (Pg. 216) Recognize that an issue exists Analyzing information about the issue Evaluating information. Download Presentation.
Critical Thinking in Nursing Definition Critical thinking is an active, organized, cognitive process used to carefully examine one s thinking and the thinking of ... - A free PowerPoint PPT presentation (displayed as an HTML5 slide show) on PowerShow.com - id: 3c1829-NDAwM
Creative thinkers have the intellectual courage and capacity to think in a new and in a different way. Without creative thinking, nursing would become routine and habitual. 2. Critical Thinking Applied in Nursing Application of critical thinking is vital to each step of the nursing process. Critical thinkers develop a questioning attitude.
CRITICAL THINKING in Nursing Practice: active, organized, cognitive process used to carefully examine one s thinking and the thinking of others. - A free PowerPoint PPT presentation (displayed as an HTML5 slide show) on PowerShow.com - id: 586f51-Y2Q1O
Kindred Hospital Louisville Shannon Ash, RN, BSN. Objectives 1. Define critical thinking. 2. Identify critical thinking tools to use in nursing practice. 3. Explain how to integrate the nursing process with critical thinking. 4. Apply critical thinking processes to solve patient care situations.
Critical Thinking in The Nursing Process Separating the Professional from the Technical. Aspects of Critical Thinking • "the active, organized, cognitive process used to examine one's own thinking and the thinking of others" • Using reflection, intuition, and previous experiences to make sound decisions • Requires a habit of asking ...
The Nursing Process: Critical Thinking & Assessment. Amy C. Chavarria, RN, MSN, MBA, HCM, CCE ... Restrictive or blocking to conversation ... - A free PowerPoint PPT presentation (displayed as an HTML5 slide show) on PowerShow.com - id: 1389b4-ZDQ2M