Home — Essay Samples — Sociology — Citizenship — Qualities of a Good Citizen: Characteristics and Examples

Qualities of a Good Citizen: Characteristics and Examples
- Categories: Citizenship
About this sample

Words: 623 |
Published: Sep 12, 2023
Words: 623 | Page: 1 | 4 min read
Table of contents
Introduction, responsibility: a pillar of good citizenship, respect: fostering harmony and unity, active participation: the engine of change, examples of good citizenship.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Karlyna PhD
Verified writer
- Expert in: Sociology

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
3 pages / 1313 words
2 pages / 1019 words
5 pages / 2476 words
3 pages / 1209 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Citizenship
European Commission. (2019). Voting and standing as a candidate in another EU country. Retrieved from 127-141.
Learning about other cultures is a profound and transformative journey that goes beyond acquiring knowledge; it is a gateway to personal growth and global citizenship. This essay delves into the significance of learning about [...]
Joppke, Christian. 'The Content of Citizenship Tests: How Liberal?' Citizenship Studies, vol. 16, no. 2, 2012, pp. 179-193.Groenendijk, Kees, and Monique Kremer. 'A Touchstone of Belonging or a Barrier to Entry? The Role of [...]
Throughout history, women have been oppressed and marginalized in society. This is evident in Jamaica Kincaid's short story "Girl," which describes the cultural expectations and limitations placed upon young women. Kincaid's [...]
The Cambridge dictionary defines citizenship as the state of being a member of a particular country and having rights because of it. It is also the state of living in a particular area of town and behaving responsibly. To me a [...]
Citizenship bestows upon individuals legal, political and social dimensions. Access to citizenship was illustrated by how membership was determined. Ancient society witnessed the restriction of the access to citizenship as [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Good Citizenship and Global Citizenship Essay
Introduction, good citizen needed to make a global citizen, global citizenship needed to make a good citizen, works cited.
The 21st Century has witnessed integration and increased cultural interaction among people on a previously unprecedented scale. This frequent interaction between people from varied countries and cultures has risen mostly as a result of the advances that have been made in transport and communication technologies.
As a result of this interaction, there has been the major integration of economies and cultures in a process known as globalization. As a result of globalization, governments are increasingly being required to link together different levels of their activities: national and global. This has resulted in the building of a global citizenry which sees the world as their “country”.
However, the global citizen continues to be heavily influenced by the traditional notion of citizen, a term that is “wrapped up in rights and obligations and in owing allegiance to a sovereign state” (Lagos 1). This paper shall argue that it is hugely necessary for one to be a good citizen so as to become a global citizen. To reinforce this claim, this paper shall analyze the extent to which it is necessary to be a “good citizen” in order to be a “global citizen”, and vice versa.
The world is full of social injustices mostly perpetrated by the stronger members of the society against the weaker ones. A defining characteristic of a good national citizen in such an environment is his/her concern about the injustices that occur within their boundaries.
This concern normally manifests itself in protests and public demonstrations calling for action by the government in place to counter the perceived injustices. A report by the World Bank demonstrates that the global citizen shows the same concern for the welfare of the globe and is moved to free their fellow men from dehumanizing conditions (1). As such, it takes a good citizen to make the global citizen who will be keen to decry social injustices against other human beings.
Core to the agendas of the good citizen is the preservation of peace in his country. A good citizen will strive to preserve peace especially within the boundaries of his/her country. This is mostly because the citizen recognizes the destruction and loss that war culminates in. For this reason, the good citizen seeks to mobilize against all wars through peaceful demonstrations and advocacy against wars.
The United Nations declares that peace is a precondition of global citizenship. The global citizen views war and strife as being contrary to his/her agenda. A good citizen who is committed to preserving peace is therefore needed to make a global citizen.
One of the attribute that a good citizen in any democratic society should possess is an understanding of public policies in his/her country. An understanding of this policies will result in enlightenment on one’s country position on issues such as energy, free trade, agriculture and the environment to name but a few.
It is only by understanding the public policies adopted by one’s country that a person can act so as to shape certain conditions such as protection of natural habitat. A global citizen is also concerned with the protection of the environment and establishment of free trade. It would therefore take a good citizen who is well versed with public policies to make a global citizen.
A good citizen is concerned about the impact that his individual actions and daily personal choices have on the country. This is an ideal that is also desirable in the global citizen since as a global citizen should make his/her decisions bases on an awareness of the impact that the decisions will have on the planet. A good citizen who is aware and conscious of the impact that his actions have on a larger scale is therefore needed to make a global citizen.
The international community is characterized by a rich diversity of cultures among its people. The global citizen is therefore prepared to operate amicably in this intercultural environment. The global citizen realizes that there should be unity in diversity and nobody has the right to impose their ideology on anybody or any group of persons.
An ideal citizen should also demonstrate this values and pay respect to people from different cultures and strives to live harmoniously with them. The good citizen should recognize that differences may exist within members of the country and this should not be a cause of strive. By acting as a global citizen who operates in a multicultural sphere, a person can be a good citizen and exist harmoniously with other citizens of varied backgrounds.
Lagos documents that while globalization is acclaimed for having opened up the world and led to the emergence of a “global village”, the same force has paradoxically resulted in localization and local communities have taken greater and greater importance (9). In such an environment, it is the global citizen who holds the separate entities together and seeks to iron out the differences that the various local communities seek to advance.
For a citizen to pass for a good citizen in such an environment (the environment where local communities have taken great importance), he must have the global perspective of the global citizen. It is only by taking the global perspective that a citizen can give fair consideration to ideas with which they disagree.
Global citizenship is increasingly working towards making the planet sustainable for all people. The efforts directed to this end are mostly in the form of advocacy for conservation of the environment, reduction of pollution and the reliance on renewable sources of power. A good citizen is supposed to work towards the preservation of the country’s resources for future resources. As such, the good citizen has to be a global citizen who is concerned with making the planet sustainable.
As a global citizen, one is expected to be non judgmental and overlook the religious differences that divide humanity. The UN states that the global citizen should have values such as “rights to freedom of thought, conscience and religion”. A good citizen should also have these values enshrined in them. A good citizen should avoid engaging in religious discrimination since this threatens unity among the citizens of the nation.
This paper has demonstrated that being a global citizen is intrinsically connected to being a good citizen. As such, being a global citizenship implies a responsibility to be a good citizen. However, there are instances where being a global citizen may cause one to be a “bad citizen”.
For example, a global citizen is not expected to advocate for war or side with any party during war. Good citizenship calls for one to back their country when it is involved in a war. Acting as a global citizen in such instances can therefore prevent one from being an ideal citizen.
Lagos indicates that a citizen obtains a certain amount of protection from his/her country in return for abiding to some restrictions that the government may impose on him/her (3). A good citizen is therefore required to abide by some laws and allow some bureaucratic control from his/her nation.
A global citizen on the other hand does not have any kind of protection and has some amount of degree from bureaucratic control. Lagos states that the hallmark of global citizen is the lack of allegiance to any body of laws to control the individual. In this light, being a global citizen goes contrary to what being a good citizen entails.
This paper set out to argue that to a large extent, it is necessary to be a “good citizen” in order to be a “global citizen” and vice versa. The paper performed a detailed analysis of how a person may be obligated to be a good citizen so as to qualify as a global citizen and vise versa.
This paper has shown that global citizens borrow most of their rights and obligations from the traditional “citizen” who is defined by a civic engagement to a nation existing in a particular geography. In particular, the paper demonstrates that values such as tolerance, civic education are innate in both the good citizen and the global citizen. However, the paper has also shown that global citizen differs significantly from the citizen and in some instances, being a global citizen may cause one not to fulfill his role as a good citizen.
Lagos, Taso. Global Citizenship- Towards a Definition . 2002. Web.
The World Bank. “Global Citizenship- Ethical Challenges Ahead”. Conference on Leadership and Core Values . 2002. Web.
UN. The Universal Declaration of Human Rights. 2010. Web.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, January 31). Good Citizenship and Global Citizenship. https://ivypanda.com/essays/good-citizenship-and-global-citizenship/
"Good Citizenship and Global Citizenship." IvyPanda , 31 Jan. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/good-citizenship-and-global-citizenship/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'Good Citizenship and Global Citizenship'. 31 January.
IvyPanda . 2024. "Good Citizenship and Global Citizenship." January 31, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/good-citizenship-and-global-citizenship/.
1. IvyPanda . "Good Citizenship and Global Citizenship." January 31, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/good-citizenship-and-global-citizenship/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Good Citizenship and Global Citizenship." January 31, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/good-citizenship-and-global-citizenship/.
- Social, Economic and Environmental Challenges of Urbanization in Lagos
- "The Street Life in Lagos": Film Analysis
- Noise Pollution: Environmental Issue in Lagos, Nigeria
- How Is Globalization Impacting Citizenship?
- Humanizing Globalization’ Professional Analysis of Speech
- Defining of Citizenship and Its Aspects
- Dual Citizenship Pros and Cons
- Citizenship History and Development
- Maritime Security in East and West Africa by Siebels
- Fela Kuti: Music Is the Weapon
- Factors of the $787 Economic Stimulus Package
- Medical Marijuana Policy in the United States
- Food and Environmental Hygiene Department
- Why Are Political Parties So Strong in the United Kingdom
- Third World Countries and the Barriers Stopping Them to Escape Poverty

Good Citizenship for the Next Generation pp 13–32 Cite as
What Is a “Good Citizen”? a Systematic Literature Review
- Cristóbal Villalobos 23 ,
- María Jesús Morel 23 &
- Ernesto Treviño 24
- Open Access
- First Online: 01 September 2021
10k Accesses
3 Citations
Part of the book series: IEA Research for Education ((IEAR,volume 12))
The concept of “good citizenship” has long been part of discussions in various academic fields. Good citizenship involves multiple components, including values, norms, ethical ideals, behaviors, and expectations of participation. This chapter seeks to discuss the idea of good citizenship by surveying the academic literature on the subject. To map the scientific discussion on the notion of good citizenship, a systematic review of 120 academic articles published between 1950 and 2019 is carried out. The review of the literature shows that good citizenship is broadly defined, incorporating notions from multiple fields, although these are mainly produced in Western countries with comparatively higher income levels. Additionally, although there is no single definition of good citizenship, the academic literature focuses on three components: the normative, active, and personal dimensions. This systematic review informs the estimation of citizenship profiles of Chap. 3 using the IEA International Civic and Citizenship Education Study (ICCS) 2016.
- Citizenship norms
- Good citizenship
- Systematic review
- International Civic and Citizenship Education Study (ICCS)
Download chapter PDF
1 Introduction
The concept of “good citizenship” is part of a long-standing discussion in various academic fields, such as political science, education, sociology, anthropology, evolution, and history, among others. In addition, good citizenship involves various components, including values, norms, ethical ideals, behaviors, and expectations of participation. Finally, the idea of good citizenship is related to diverse contemporary issues, such as patterns of political participation, the meaning of democracy and human rights, the notion of civic culture, equal rights, and the role of technology in the digital era (Bolzendahl and Coffé 2009 ; Dalton 2008 ; Hung 2012 ; Noula 2019 ).
In this regard, the notion of good citizenship can be considered as a concept with three basic characteristics: multidisciplinary, multidimensional, and polysemic. Therefore, the definition of good citizenship is a topic of constant debate and academic discussion. This chapter seeks to discuss the idea of good citizenship, with the aim of contributing to the understanding of this phenomenon and its social, political, and educational implications. In this way, this chapter aims to map the academic discussion and literature regarding the notion of good citizenship, presenting the key debates about the limits and possibilities of this concept in the framework of the International Association for the Evaluation of Educational Achievement (IEA) International Civic and Citizenship Education Study (ICCS) 2016.
In order to organize this complex debate, we start from the premise that any notion of good citizenship is composed of the interaction of two definitions. On the one hand, it involves a certain notion of membership, that is, of belonging to a community. As Stokke ( 2017 ) shows, the definition of who is (and who is not) a citizen is, in itself, a subject of debate, since the definition of citizenship implies political, social, cultural, and legal components. On the other hand, the definition of good citizenship always implies a conceptual position regarding how citizens are expected to act and what they are expected to believe (the “public good” component). In this sense, the debate focuses on the types of behaviors that should be promoted and their ethical-political basis, which is highly dynamic depending on the cultural and historical context (Park and Shin 2006 ). Finally, in order to answer the question about the meaning of good citizenship, it is necessary to first decide who qualifies as a citizen, and how they are expected to behave.
Considering these objectives, the chapter is structured into five sections, including this introduction. The second section describes the systematic review methodology used to select the literature and analyze the discussion regarding the concept of good citizenship. The third and fourth sections describe the results of the analysis, mapping the main trends and characteristics of the academic discussion on good citizenship and exploring its different meanings. Finally, the fifth section presents the conclusions, focusing on the conceptual challenges and methodological limitations to be considered in future research.
2 Methodology
2.1 the systematic review.
We conducted a systematic review to map the academic discussion on good citizenship. This review seeks to identify, evaluate, and analyze the publications in relevant fields of study, in order to determine what has already been written on this topic, what works and what does not, and where new studies are needed (Petticrew and Roberts 2006 ). Through the definition of eligibility criteria, the systematic review is an explicit and reproducible methodology that allows for both an evaluation of the validity of the results of the selected studies (Higgins and Green 2011 ) and the objective valuation of evidence by summarizing and systematically describing the characteristics and results of scientific research (Egger 1997 ). In this regard, the systematic review, unlike other forms of literature review, allows for recognizing “gray” spaces in the literature, describing trends in academic research, and analyzing conceptual and methodological aspects of studies.
2.2 Procedure
The systematic review was conducted using five academic databases, including the main journals in the fields of education, social science, and the humanities. These databases are: (i) Journal Storage, JSTOR ( https://www.jstor.org ); (ii) Educational Resource Information Center, ERIC ( https://eric.ed.gov ); (iii) Springerlink ( https://link.springer.com ); (iv) WorldWideScience ( https://worldwidescience.org ); and (v) Taylor & Francis Group ( https://www.tandfonline.com ). For each search engine, the keywords used were: “good citizen” and “good citizenship.” Additionally, each search engine was tested with other related concepts, such as “citizenship norms,” “citizenship identities,” or “citizen norms.” The results showed that articles containing these latter concepts represented no more than 10% of new articles. For this reason, we decided to concentrate on the two keywords described above.
Considering the importance of these key concepts, the search was limited to those articles that contain these terms in the title, abstract, and/or full text. Of the five search engines, only two had the full-text option in the advanced search and only one allowed searching by keywords, then all results were filtered manually. The search was conducted from May to July 2019, obtaining 693 academic articles.
The search was restricted to those academic articles written in English and published between 1950 and 2019, as a way to study contemporary conceptualizations of good citizenship. We discarded letters to the editor, responses to articles, and book reviews. As a result, we obtained 693 articles to which, based on a full-text review, we applied an additional criterion, excluding those articles about other subjects or from other disciplines. Included in the first search exclusively for having the word “citizenship” in the abstract, there is a wide range of articles including studies on biology, entomology, and film studies. Similarly, with this search strategy we retrieved articles on a related topic but not specifically about citizenship (e.g., leadership, public participation, social values, and immigration), articles on the concept of corporate or organizational citizenship, and articles on social studies in the school curriculum and its contribution to the education of citizens.
After applying the abovementioned selection criteria, we analyzed the abstracts of the articles to verify that they were related to the general objective of the study. As a result, all articles were selected that sought (directly or indirectly) to answer the question, “what is a good citizen?” Specifically, this involved incorporating studies that: (i) study or analyze citizen norms in conceptual, historical, political, educational, or social terms; (ii) generate models or analytic frameworks that define variables or dimensions that should make up the concept of a good citizen; (iii) explore factors on how good citizenship occurs, studying the educational, institutional, and cultural factors that would explain this phenomenon; (iv) relate the expectations (or definitions) of a good citizen with other dimensions or aspects of the political or social behavior of the subjects. The research team, which was comprised of two reviewers, held a weekly discussion (six sessions in total) during which the selection criteria were discussed and refined. This analysis resulted in the selection of a total of 120 articles (see list in Appendix A ).
2.3 Analytical Strategy
The data collected in a systematic review may allow for a wide variety of studies, but the analysis depends on the purpose and nature of the data. Given that the review included quantitative and qualitative studies, as well as both theoretical and demonstrative essays, such heterogeneous literature does not allow for statistical analysis. As a result, the recommended methodology is to carry out a narrative synthesis and an analysis that focuses on relationships between different characteristics and the identification of gaps (Grant and Booth 2009 ; Petticrew and Roberts 2006 ).
The narrative synthesis is a process that allows for extracting and grouping the characteristics and results of each article included in the review (Popay et al. 2006 ), and can be divided into three steps: (i) categorization of articles; (ii) analysis of the findings within each category; and (iii) synthesis of the findings in the selected studies (Petticrew and Roberts 2006 ). The first step towards the narrative synthesis consisted of reading, coding, and tabulating the selected documents in order to describe their main characteristics. A set of categories was designed to classify documents according to four dimensions: general characteristics, purpose, methodology, and results.
To analyze these categories, we transformed data into a common numeric rubric and organized it for thematic analysis, using the techniques proposed by Popay et al. ( 2006 ). The first category was used to summarize the quantity and characteristics of the published studies, while the thematic analysis focused on systematically identifying the main, recurrent, and/or most important concepts of good citizenship.
3 The Concept of Good Citizenship in Academia
Despite being a topic of interest for several decades, academic production on good citizenship tends to be concentrated in the second decade of the 21st century. Since 2009, there has been an explosive increase in the number of scientific papers published on this topic (Fig. 1 ). Although an important part of this growth may be due to the global pressures of academic capitalism to publish in academic journals (Slaughter and Rhoades 2009 ), it could also be the case that academic communities have cultivated a growing interest in studying this issue.
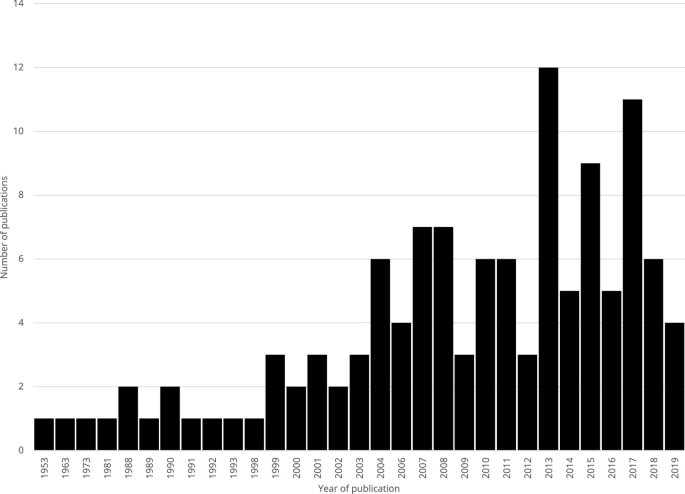
Academic papers by year of publication
Although few in number, the earliest articles published represent a landmark for the discussion. Thus, for example, the text of Almond and Verba ( 1963 ), which analyzes through interviews the perceptions of individuals in communities in five countries (United States, United Kingdom, Italy, Germany, and Mexico) and highlights their different participation profiles, has been repeatedly cited in the discussion with 263 references (as of August 2019), according to Google Scholar. Another classic text is Ichilov and Nave ( 1981 ), which aims at understanding the different dimensions of citizenship by surveying young Israelis. To this end, it generates the following five criteria, which have been widely used in academic discussions: (i) citizenship orientation (affective, cognitive, or evaluative); (ii) nature of citizenship (passive or active); (iii) object of citizenship (political or non-political); (iv) source of demand (mandatory or voluntary); and (v) type of guidance (support principles or behavior).
The selected articles are geographically concentrated in two aspects: by institutional affiliation and by the location of their studies. Considering the institutional affiliation of the authors, 32.77% of the articles were produced in the United States, a figure that rises to more than 60% when the countries of Western Europe and Australia are included. This bias is maintained, although to a lesser extent, when analyzing the countries where the studies were carried out. Moreover, more than 50% of the studies were carried out in the United States, England, and the democracies of Western Europe. Africa (4.24%) and Latin America (2.54%) were the regions least represented in the studies. These characteristics, which tend to be representative of global academic production in the social sciences (Connell 2007 ), may encourage certain notions of good citizenship that are anchored in Anglo-Saxon traditions, such as the liberal conception of citizenship studied by Peled ( 1992 ), or more recently, the conception of active citizenship (Ke and Starkey 2014 ), both of which have had an important influence on academic discussion about good citizenship.
Finally, the third characteristic of academic production is related to the multiple research fields and diverse purposes of the studies that deal with the concept of good citizenship. Research on good citizenship is published in multiple disciplines. Of the articles included in the review, 82.29% are concentrated in three disciplines: education, political science, and sociology. However, there are also articles associated with journals of history, philosophy, anthropology, and law. Additionally, we identified six main objectives from the articles reviewed (Table 1 ). The most common objectives are related to bottom-up research, which seeks to gather information on how diverse populations understand good citizenship, and top-down research, which seeks to conceptualize and/or define the idea of good citizens based on conceptual, historical, or political analysis. In addition, there are a wide variety of studies that seek to explain good citizenship, as well as studies that use the idea of a good citizen to explain other behaviors, skills, or knowledge. In other words, in addition to being multidisciplinary, research on good citizenship has multiple purposes.
In sum, although the academic discussion on good citizenship has been mainly developed during the last two decades in the most industrialized Western countries, the academic research is a field of ongoing and open debate.
4 Understanding the Meaning of “Good Citizenship”
As an academic field with a lively ongoing discussion, the notion of good citizenship is associated with different sets of ideas or concepts. Some keywords were repeated at least three times in the articles reviewed (Table 2 ). Only those articles that used a keyword format were included. The most frequent concepts are related to education, norms, social studies, political participation, and democracy.
This indicates that, first, studies tend to associate good citizenship with civic norms and citizen learning, highlighting the formative nature of the concept. Second, studies that associate good citizenship with other dimensions of citizenship (such as knowledge or civic attitudes) or contemporary global problems (such as migration) are comparatively scarcer.
Another way to approach the concept of good citizenship is by analyzing the definitions proposed by the authors in the articles studied. Most of the articles propose characteristics or aspects of good citizenship (in 43.8% of the cases) that, instead of creating new definitions, are often based on existing political, non-political, liberal, or philosophical concepts. In this regard, many papers define good citizenship based on specific behaviors. In contrast, other authors (18.6%) refer to citizenship rules when it comes to voting or participating in politics, thereby seeking to relate the concept of the good citizen with a specific civic attitude—participation in elections. Finally, a large group of studies define good citizenship in terms of the values, virtues, or qualities of a good citizen (22.6%). Within the group of studies that propose new definitions, it is possible to identify two main categories: studies that propose types of citizenship, such as Dalton ( 2008 ), distinguishing between “duty” and “engaged” citizenship, and works, such as Westheimer and Kahne ( 2004 ), which differentiate between “personal responsible citizenship,” “justice-oriented citizenship,” and “participatory citizenship.”
Finally, the meaning of good citizenship can be analyzed by studying the variables used in the studies. Among the quantitative studies included in the review, only 28.3% use international surveys such as ICCS, the Center for Democracy and Civil Society (CDACS), the International Social Survey Programme (ISSP), the United Citizenship, Involvement, Democracy (CID) Survey, and the European Social Survey (ESS). Each of these surveys contained a slightly different definition of good citizenship and the variables used to measure the concept (Table 3 ).
In general, the indicators used to measure citizenship in the different surveys share certain similarities. Variables associated with rules (such as obeying the law or paying taxes) are present in all surveys. Additionally, variables related to participation also have an important presence, especially (although not only) related to voting in national elections. To a lesser extent, surveys include variables related to solidarity (supporting people who are worse off than yourself) as well as attitudes related to critical thinking and civic culture (knowing the history of the country, thinking critically).
5 Discussion and Conclusions
The concept of good citizenship can be considered an umbrella term, which includes ethical, political, sociological, and educational aspects and discussions about who qualifies as a citizen and how they should act. The systematic review has shown that good citizenship is broadly defined, although these notions are mainly valued in Western countries with comparatively higher income levels.
For this reason, the definition of good citizenship used is, in large part, highly dependent on the research objective of the academic endeavor. In our case, the analysis is based on ICCS 2016, which defines good citizenship in relation to notions such as conventional citizenship, social movement citizenship, and personal responsibility citizenship (Köhler et al. 2018 ). The variables included in ICCS 2016 are related to the three main dimensions of good citizenship: normative, active, and personal. These three components of good citizenship have been essential in the academic discussion in the last seven decades, constituting the central corpus of the concept, although this definition does not incorporate current discussions on good citizenship, which focus, for example, on the notion of global citizenship (Altikulaç 2016 ) or the idea of digital citizenship (Bennett et al. 2009 ). These latter concepts are part of the ongoing debate on good citizenship, although it seems that more work is needed to better understand how these notions of citizenship are related to the ways in which individuals or groups in society relate to power and exercise it to shape the public sphere.
This systematic review has mapped the academic discussion to date on good citizenship. However, despite its usefulness, this review has a number of limitations. Firstly, it summarizes and analyzes the academic discussion, ignoring the gap between the scientific debate on good citizenship and the social discussion related to this subject. Secondly, it focuses on English-language literature, which may result in a bias towards publications produced in Western countries. In spite of these limitations, the review allows us to study the process of defining the concept of good citizenship, and to identify the main debates related to this notion, which is the central focus of this book.
Almond, G. A., & Verba, S. (1963). The civic culture. Political attitudes and democracy in five nations . Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Book Google Scholar
Altikulaç, A. (2016). Patriotism and global citizenship as values: A research on social studies teacher candidates. Journal of Education and Practice, 7 (36), 26–33.
Google Scholar
Bennett, W. L., Wells, C., & Rank, A. (2009). Young citizens and civic learning: Two paradigms of citizenship in the digital age. Citizenship Studies, 13 (2), 105–120. https://doi.org/10.1080/13621020902731116 .
Article Google Scholar
Bolzendahl, C., & Coffe, H. (2009). Citizenship beyond politics: The importance of political, civil and social rights and responsibilities among women and men. The British Journal of Sociology, 60 (4), 763–791.
Connell, R. W. (2007). Southern theory: The global dynamics of knowledge in social science . Sydney, Australia: Allen & Unwin.
Dalton, R. J. (2008). Citizenship norms and the expansion of political participation. Political Studies, 56 (1), 76–98. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9248.2007.00718.x .
Egger, M. (1997). Meta-analysis: Potentials and promise. BMJ, 315 (7119), 1371–1374.
Grant, M. J., & Booth, A. (2009). A typology of reviews: An analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Information and Libraries Journal, 26 (2), 91–108. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x .
Higgins, J., & Green, S. (2011). Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions . London, United Kingdom: The Cochrane Collaboration.
Hung, R. (2012). Being human or being a citizen? Rethinking human rights and citizenship education in the light of Agamben and Merleau-Ponty. Cambridge Journal of Education, 42 (1), 37–51.
Ichilov, O., & Nave, N. (1981). The Good Citizen as viewed by Israeli adolescents. Comparative Politics, 13 (3), 361–376.
Ke, L., & Starkey, H. (2014). Active citizens, good citizens, and insouciant bystanders: The educational implications of Chinese university students’ civic participation via social networking. London Review of Education, 12 (1), 50–62. https://doi.org/10.18546/LRE.12.1.06 .
Köhler, H., Weber, S., Brese, F., Schulz, W., & Carstens, R. (Eds.). (2018). ICCS 2016 user guide for the international database . Amsterdam, the Netherlands: International Association for the Evaluation of Educational Achievement (IEA).
Noula, I. (2019). Digital citizenship: Citizenship with a twist? Media@LSE Working Paper Series. London, United Kingdom: London School of Economics and Political Science.
Park, C.-M., & Shin, D. C. (2006). Do Asian values deter popular support for democracy in South Korea? Asian Survey, 46 (3), 341–361.
Peled, Y. (1992). Ethnic democracy and the legal construction of citizenship: Arab citizens of the Jewish state. The American Political Science Review, 86 (2), 432–443.
Petticrew, M., & Roberts, H. (2006). Systematic reviews in the social sciences: A practical guide . Oxford, United Kingdom: Blackwell Publishing.
Popay, J., Roberts, H., Sowden, A., Petticrew, M., Arai, L., Rodgers, M., et al. (2006). Guidance on the conduct of narrative synthesis in systematic reviews. A product from the ESRC Methods Programme . Lancaster, United Kingdom: Lancaster University.
Slaughter, S., & Rhoades, G. (2009). Academic capitalism and the new economy. Markets, state, and higher education . Baltimore, MD: The John Hopkins University Press.
Stokke, K. (2017). Politics of citizenship: Towards an analytical framework. Norsk Geografisk Tidsskrift, 71 (4), 193–207.
Westheimer, J., & Kahne, J. (2004). What kind of citizen? The politics of educating for democracy. American Educational Research Journal, 41 (2), 237–269. https://doi.org/10.3102/00028312041002237 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank their research sponsors, the Center for Educational Justice ANID PIA CIE160007, as well as the Chilean National Agency of Research and Development through the grants ANID/FONDECYT N° 1180667, and ANID/FONDECYT N° 11190198.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Centro de Estudios de Políticas y Prácticas en Educación (CEPPE-UC), Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Santiago, Chile
Cristóbal Villalobos & María Jesús Morel
Center UC for Educational Transformation, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Santiago, Chile
Ernesto Treviño
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Cristóbal Villalobos .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Center for Educational Justice, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Santiago, Chile
Centro de Medición MIDE UC, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Santiago, Chile
Diego Carrasco
Centre for Political Research, KU Leuven, Leuven, Belgium
Ellen Claes
University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg, South Africa
Kerry J. Kennedy
The following list of publications is the reviewed references for the systematic review conducted in this chapter.
Adler, S. A., & Kho, E. M. (2011). Educating citizens: A cross-cultural conversation. Journal of International Social Studies , 1 (2), 2–20.
Agbaria, A. K., & Katz-Pade, R. (2016). Human rights education in Israel: Four types of good citizenship. Journal of Social Science Education , 15 (2), 96–107. https://doi.org/10.4119/UNIBI/jsse-v15-i2-1455 .
Ahmad, I. (2017). Political science and the good citizen: The genealogy of traditionalist paradigm of citizenship education in the American school curriculum. Journal of Social Science Education , 16 (4), 38–48. https://doi.org/10.4119/UNIBI/jsse-v16-i4-1581 .
Ahmad, I. (2004). Islam, democracy and citizenship education: An examination of the social studies curriculum in Pakistan. Current Issues in Comparative Education , 7 (1), 39–49.
Ahrari, S., Othman, J., Hassan, S., Samah, B. A., & D’Silva, J. L. (2013). Role of social studies for pre-service teachers in citizenship education. International Education Studies , 6 (12), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.5539/ies.v6n12p1 .
Alazzi, K., & Chiodo, J. J. (2008). Perceptions of social studies students about citizenship: A study of Jordanian middle and high school students. The Educational Forum , 72 (3), 271–280.
Almond, G. A., & Verba, S. (1963). The obligation to participate. In The civic culture: Political attitudes and democracy in five nations (pp. 161–179). Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Altikulaç, A. (2016). Patriotism and global citizenship as values: A research on social studies teacher candidates. Journal of Education and Practice , 7 (36), 26–33.
Al-Zboon, M. S. (2014). Degree of student’s assimilation to the meaning of the term citizenships in the schools high grade basic level in Jordan. International Education Studies , 7 (2), 137–144. https://doi.org/10.5539/ies.v7n2p137 .
Angell, A. V. (1990). Civic attitudes of Japanese middle school students: Results of a pilot study [Paper presentation]. Paper presented at the Annual Meeting of the National Council for the Social Studies, Anaheim, CA.
Atkinson, L. (2012). Buying into social change: How private consumption choices engender concern for the collective. Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science , 644 (1), 191–206. https://doi.org/10.1177/0002716212448366 .
Avery, P. G. (2003). Using research about civic learning to improve courses in the methods of teaching social studies. In J. J. Patrick, G. E. Hamot, & R. S. Leming (Eds.), Civic learning in teacher education: International perspectives on education for democracy in the preparation of teachers (Vol. 2, pp. 45–65). Bloomington, IN: ERIC Clearinghouse for Social Studies/Social Science Education.
Baron, J. (2010). Cognitive biases in moral judgments that affect political behavior. Synthese , 172 (1), 7–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11229-009-9478-z .
Bass, L. E., & Casper, L. M. (2001). Differences in registering and voting between native-born and naturalized. Population Research and Policy Review , 20 (6), 483–511.
Bech, E. C., Borevi, K., & Mouritsen, P. (2017). A ‘civic turn’ in Scandinavian family migration policies? Comparing Denmark, Norway and Sweden. Comparative Migration Studies, 5 (1), 7.
Bickmore, K. (2001). Student conflict resolution, power. Curriculum Inquiry , 31 (2), 137–162. https://doi.org/10.1111/0362-6784.00189 .
Bolzendahl, C., & Coffé, H. (2009). Citizenship beyond politics: The importance of political, civil and social rights and responsibilities among women and men. British Journal of Sociology , 60 (4), 763–791. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-4446.2009.01274.x .
Bolzendahl, C., & Coffé, H. (2013). Are “good” citizens “good” participants? Testing citizenship norms and political participation across 25 nations. Political Studies , 61 (SUPPL.1), 63–83. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-9248.12010 .
Boontinand, V., & Petcharamesree, S. (2018). Civic/citizenship learning and the challenges for democracy in Thailand. Education, Citizenship and Social Justice, 13 (1), 36–50.
Capers, I. B. (2018). Criminal procedure and the good citizen. Columbia Law Review , 118 (2), 653–712. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107415324.004 .
Chávez, K. R. (2010). Border (in)securities: Normative and differential belonging in LGBTQ and immigrant rights discourse. Communication and Critical/Cultural Studies , 7 (2), 136–155. https://doi.org/10.1080/14791421003763291 .
Chimiak, G. (2004). NGO activists and their model of the good citizen empirical evidence from Poland. Polish Sociological Review , (1), 33–47.
Chipkin, I. (2003). ‘Functional’ and ‘dysfunctional’ communities: The making of national citizens. Journal of Southern African Studies, 29 (1), 63–82.
Clarke, M. T. (2013). The virtues of republican citizenship in Machiavelli’s Discourses on Livy. The Journal of Politics, 75 (2), 317–329.
Coffé, H., & Van Der Lippe, T. (2010). Citizenship norms in Eastern Europe. Social Indicators Research, 96 (3), 479–496.
Conger, K. H., & McGraw, B. T. (2008). Religious conservatives and the requirements of citizenship: Political autonomy. Perspectives on Politics, 6 (2), 253–266.
Connell, J. (2007). The Fiji Times and the good citizen: Constructing modernity and nationhood in Fiji. The Contemporary Pacific, 19 (1), 85–109.
Conover, P. J., Crewe, I. M., & Searing, D. D. (1991). The nature of citizenship in the United States and Great Britain: Empirical comments on theoretical themes. The Journal of Politics , 53 (3), 800–832. https://doi.org/10.2307/2131580 .
Cook, B. L. (2012). Swift-boating in antiquity: Rhetorical framing of the good citizen in fourth-century Athens. Rhetorica - Journal of the History of Rhetoric , 30 (3), 219–251. https://doi.org/10.1525/RH.2012.30.3.219 .
Costa, M. V. (2013). Civic virtue and high commitment schools. Theory and Research in Education , 11 (2), 129–134. https://doi.org/10.1177/1477878513485184 .
Crick, B. (2007). Citizenship: The political and the democratic author. British Journal of Educational Studies , 55 (3), 235–248.
Dalton, R. J. (2008). Citizenship norms and the expansion of political participation. Political Studies , 56 (1), 76–98. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9248.2007.00718.x .
Damrongpanit, S. (2019). Factors affecting self-discipline as good citizens for the undergraduates of Chiang Mai University in Thailand: A multilevel path analysis. Universal Journal of Educational Research , 7 (2), 347–355. https://doi.org/10.13189/ujer.2019.070206 .
Damrongpanit, S. (2019). Factor structure and measurement invariance of the self-discipline model using the different-length questionnaires: Application of multiple matrix sampling. Universal Journal of Educational Research , 7 (1), 133–145. https://doi.org/10.13189/ujer.2019.070118 .
Davidovitch, N., & Soen, D. (2015). Teaching civics and instilling democratic values in Israeli high school students: The duality of national and universal aspects. Journal of International Education Research (JIER) , 11 (1), 7–20. https://doi.org/10.19030/jier.v11i1.9093 .
Dekker, P. (2019). From pillarized active membership to populist active citizenship: The Dutch do democracy. Voluntas , 30 (1), 74–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11266-018-00058-4 .
Denters, B., Gabriel, O. W., & Torcal, M. (2007). Norms of good citizenship. In J. W. van Deth, J. R. Montero, & A. Westholm (Eds.), Citizenship and involvement in European democracies: A comparative analysis (pp. 112–132). London, United Kingdom: Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203965757 .
Develin, R. (1973). The good man and the good citizen in Aristotle’s “Politics.” Phronesis , 18 (1), 71–79.
Dynneson, T. L., Gross, R. E., & Nickel, J. A. (1989). An exploratory survey of four groups of 1987 graduating seniors’ perceptions pertaining to (1) the Qualities of a Good Citizen, (2) the Sources of Citizenship Influence, and (3) the Contributions of Social Studies Courses and Programs of Study to Citizens . Stanford University, California: Citizenship Development Study Center. ERIC Document Reproduction Service No. 329481.
Eder, A. (2017). Cross-country variation in people’s attitudes toward citizens’ rights and obligations: A descriptive overview based on data from the ISSP Citizenship Module 2014. International Journal of Sociology , 47 (1), 10–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207659.2017.1265309 .
Enu, D. B., & Eba, M. B. (2014). Teaching for democracy in Nigeria: A paradigm shift. Higher Education Studies , 4 (3), 64–71. https://doi.org/10.5539/hes.v4n3p64 .
Ersoy, A. F. (2012). Mothers’ perceptions of citizenship, practices for developing citizenship conscience of their children and problems they encountered. Kuram ve Uygulamada Egitim Bilimleri , 12 (3), 2120–2124.
Fernández, C., & Jensen, K. K. (2017). The civic integrationist turn in Danish and Swedish school politics. Comparative Migration Studies , 5 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40878-017-0049-z .
Garver, E. (2010). Why can’t we all just get along: The reasonable vs. the rational according to Spinoza. Political Theory , 38 (6), 838–858. https://doi.org/10.1177/0090591710378577 .
Goering, E. M. (2013). Engaging citizens: A cross cultural comparison of youth definitions of engaged citizenship. Universal Journal of Educational Research , 1 (3), 175–184. https://doi.org/10.13189/ujer.2013.010306 .
Green, J., Steinbach, R., & Datta, J. (2012). The travelling citizen: Emergent discourses of moral mobility in a study of cycling in London. Sociology , 46 (2), 272–289. https://doi.org/10.1177/0038038511419193 .
Gutierrez, R. (2002). What can happen to auspicious beginnings: Historical barriers to ideal citizenship. The Social Studies , 93 (5), 202–208. https://doi.org/10.1080/00377990209600166 .
Haas, M. E., Laughlin, M. A., Wilson, E. K., & Sunal, C. S. (2003, April). Promoting enlightened political engagement by using a citizenship scenario with teacher candidates and experienced teachers [Paper presentation]. Paper presented at the Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association, Chicago, IL.
Hammett, D. (2018). Engaging citizens, depoliticizing society? Training citizens as agents for good governance. Geografiska Annaler, Series B: Human Geography , 100 (2), 64–80. https://doi.org/10.1080/04353684.2018.1433961 .
Hébert, M., & Rosen, M. G. (2007). Community forestry and the paradoxes of citizenship in Mexico: The cases of Oaxaca and Guerrero. Canadian Journal of Latin American and Caribbean Studies , 32 (63), 9–44. https://doi.org/10.1080/08263663.2007.10816914 .
Hoekstra, M. (2015). Diverse cities and good citizenship: How local governments in the Netherlands recast national integration discourse. Ethnic and Racial Studies , 38 (10), 1798–1814. https://doi.org/10.1080/01419870.2015.1015585 .
Hooghe, M., Oser, J., & Marien, S. (2016). A comparative analysis of ‘good citizenship’: A latent class analysis of adolescents’ citizenship norms in 38 countries. International Political Science Review , 37 (1), 115–129. https://doi.org/10.1177/0192512114541562 .
Hoskins, B., Saisana, M., & Villalba, C. M. H. (2015). Civic competence of youth in Europe: Measuring cross national variation through the creation of a composite indicator. Social Indicators Research , 123 (2), 431–457. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-014-0746-z .
Hunter, E. (2013). Dutiful subjects, patriotic citizens, and the concept of “good citizenship” in Twentieth-Century Tanzania. Historical Journal , 56 (1), 257–277. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0018246X12000623 .
Ibrahimoğlu, Z. (2018). Who are good and bad citizens ? A story-based study with seventh graders. Innovation: The European Journal of Social Science Research , 0 (0), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/13511610.2018.1523709 .
Ichilov, O. (1988). Citizenship orientation of two Israeli minority groups: Israeli-Arab and Eastern-Jewish youth. Ethnic Groups , 7 (2), 113–135. https://doi.org/10.1109/ultsym.1996.584088 .
Ichilov, O. (1988). Family politicization and adolescents’ citizenship orientations. Political Psychology , 431–444.
Ichilov, O., & Nave, N. (1981). “The good citizen” as viewed by Israeli adolescents. Comparative Politics , 13 (3), 361–376.
Jarrar, A. G. (2013). Positive thinking & good citizenship culture: From the Jordanian Universities students’ points of view. International Education Studies , 6 (4), 183–193. https://doi.org/10.5539/ies.v6n4p183 .
Kariya, T. (2012). Is everyone capable of becoming a ‘Good Citizen’ in Japanese society? Inequality and the realization of the ‘Good Citizen’ Education. Multicultural Education Review , 4 (1), 119–146. https://doi.org/10.1080/23770031.2009.11102891 .
Ke, L., & Starkey, H. (2014). Active citizens, good citizens, and insouciant bystanders: The educational implications of Chinese university students’ civic participation via social networking. London Review of Education , 12 (1), 50–62. https://doi.org/10.18546/LRE.12.1.06 .
Kennelly, J. (2009). Good citizen/bad activist: The cultural role of the state in youth activism. Review of Education, Pedagogy, and Cultural Studies , 31 (2–3), 127–149. https://doi.org/10.1080/10714410902827135 .
Kennelly, J. (2011). Policing young people as citizens-in-waiting: Legitimacy, spatiality and governance. British Journal of Criminology , 51 (2), 336–354. https://doi.org/10.1093/bjc/azr017 .
Kuang, X., & Kennedy, K. J. (2018). Alienated and disaffected students: Exploring the civic capacity of ‘Outsiders’ in Asian societies. Asia Pacific Education Review , 19 (1), 111–135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12564-018-9520-2 .
Kwan Choi Tse, T. (2011). Creating good citizens in China: Comparing grade 7–9 school textbooks, 1997–2005. Journal of Moral Education , 40 (2), 161–180. https://doi.org/10.1080/03057240.2011.568098 .
Lefrançois, D., Ethier, M. -A., & Cambron-Prémont, A. (2017). Making “good” or “critical” citizens: From social justice to financial literacy in the Québec Education Program. Journal of Social Science Education , 16 (4), 84–96. https://doi.org/10.4119/UNIBI/jsse-v16-i4-1698 .
Lehning, P. B. (2001). European citizenship: Towards a European identity? Law and Philosophy, 20 (3), 239–282.
Leung, Y. W., Yuen, T. W. W., Cheng, E. C. K., & Chow, J. K. F. (2014). Is student participation in school governance a “mission impossible”?. Journal of Social Science Education , 13 (4), 26–40. https://doi.org/10.2390/jsse-v13-i4-1363 .
Li, H., & Tan, C. (2017). Chinese teachers’ perceptions of the ‘good citizen’: A personally-responsible citizen. Journal of Moral Education , 46 (1), 34–45. https://doi.org/10.1080/03057240.2016.1277341 .
Liem, G. A. D., & Chua, B. L. (2013). An expectancy-value perspective of civic education motivation, learning and desirable outcomes. Educational Psychology , 33 (3), 276–306. https://doi.org/10.1080/01443410.2013.776934 .
Long, D. H. (1990). Continuity and change in Soviet education under Gorbachev. American Educational Research Journal, 27 (3), 403–423.
Mara, G. M. (1998). Interrogating the identities of excellence: Liberal education and democratic culture in Aristotle’s “Nicomachean Ethics”. Polity, 31 (2), 301–329.
Martin, L. A., & Chiodo, J. J. (2007). Good citizenship: What students in rural schools have to say about it. Theory and Research in Social Education , 35 (1), 112–134. https://doi.org/10.1080/00933104.2007.10473328 .
Martin, L. A., & Chiodo, J. J. (2008). American Indian students speak out: What’s good citizenship? International Journal of Social Education , 23 (1), 1–26.
McGinnis, T. A. (2015). “A good citizen is what you’ll be”: Educating Khmer Youth for citizenship in a United States Migrant Education Program. Journal of Social Science Education , 14 (3), 66–74. https://doi.org/10.2390/jsse-v14-i3-1399 .
Meltzer, J. (2013). “Good citizenship” and the promotion of personal savings accounts in Peru. Citizenship Studies , 17 (5), 641–652. https://doi.org/10.1080/13621025.2013.818382 .
Mills, S. (2013). “An instruction in good citizenship”: Scouting and the historical geographies of citizenship education. Transactions of the Institute of British Geographers , 38 (1), 120–134. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-5661.2012.00500.x .
Morris, P., & Morris, E. (2000). Constructing the good citizen in Hong Kong: Values promoted in the school curriculum. Asia Pacific Journal of Education , 20 (1), 36–52. https://doi.org/10.1080/0218879000200104 .
Mosher, R. (2015). Speaking of belonging: Learning to be “good citizens” in the context of voluntary language coaching projects in Amsterdam, the Netherlands. Journal of Social Science Education , 14 (3), 20–30. https://doi.org/10.2390/jsse-v14-i3-1395 .
Murphy, M. (2004, April). Current trends in civic education: An American perspective [Paper presentation]. Paper presented at the philosophy of Education Society of Great Britain Annual Meeting, Oxford, England.
Niemi, R. G., & Chapman, C. (1999). The civic development of 9th- through 12th-grade students in the United States: 1996. The National Center For Education Statistics , 1 (1), 39–41.
Nieuwelink, H., Ten Dam, G., & Dekker, P. (2019). Adolescent citizenship and educational track: a qualitative study on the development of views on the common good. Research Papers in Education , 34 (3), 373–388. https://doi.org/10.1080/02671522.2018.1452958 .
Nurdin, E. S. (2015). The policies on civic education in developing national character in Indonesia. International Education Studies , 8 (8), 199–209. https://doi.org/10.5539/ies.v8n8p199 .
Orton, M. (2006). Wealth, citizenship and responsibility: The views of “better off” citizens in the UK. Citizenship Studies , 10 (2), 251–265. https://doi.org/10.1080/13621020600633218 .
Peled, Y. (1992). Ethnic democracy and the legal construction of citizenship: Arab citizens of the Jewish state. American Political Science Review, 86 (2), 432–443.
Perlmutter, O. W. (1953). Education, the good citizen, and civil religion. The Journal of General Education, 7 (4), 240–249.
Phillips, J. (2004). The relationship between secondary education and civic development: Results from two field experiments with inner city minorities. CIRCLE Working Papers , 14 (14), 1–8.
Prior, W. (1999). What it means to be a “good citizen” in Australia: Perceptions of teachers, students, and parents. Theory and Research in Social Education , 27 (2), 215–247. https://doi.org/10.1080/00933104.1999.10505879 .
Reichert, F. (2017). Young adults’ conceptions of ‘good’ citizenship behaviours: A latent class analysis. Journal of Civil Society , 13 (1), 90–110. https://doi.org/10.1080/17448689.2016.1270959 .
Reichert, F. (2016). Who is the engaged citizen? Correlates of secondary school students’ concepts of good citizenship. Educational Research and Evaluation , 22 (5–6), 305–332. https://doi.org/10.1080/13803611.2016.1245148 .
Russell, S. G., & Quaynor, L. (2017). Constructing citizenship in post-conflict contexts: The cases of Liberia and Rwanda. Globalisation, Societies and Education , 15 (2), 248–270. https://doi.org/10.1080/14767724.2016.1195723 .
Sasson-Levy, O. (2002). Constructing identities at the margins: Masculinities and citizenship in the Israeli army. The Sociological Quarterly , 43 (3), 357–383. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1533-8525.2002.tb00053.x .
Schoeman, S. (2006). A blueprint for democratic citizenship in South African public schools: African teacher’s perceptions of good citizenship. South African Journal of Education , 26 (1), 129–142.
Sim, J. B. Y. (2011). Social studies and citizenship for participation in Singapore: How one state seeks to influence its citizens. Oxford Review of Education , 37 (6), 743–761. https://doi.org/10.1080/03054985.2011.635103 .
Siphai, S. (2015). Influences of moral, emotional and adversity quotient on good citizenship of Rajabhat Universitys Students in the Northeast of Thailand. Educational Research and Reviews , 10 (17), 2413–2421. https://doi.org/10.5897/err2015.2212 .
Stokke, K. (2017). Politics of citizenship: Towards an analytical framework. Norsk Geografisk Tidsskrift , 71 (4), 193–207. https://doi.org/10.1080/00291951.2017.1369454 .
Stuteville, R., & Johnson, H. (2016). Citizenship education in the United States: Perspectives reflected in state education standards. Administrative Issues Journal: Education, Practice, and Research , 6 (1), 99–117. https://doi.org/10.5929/2016.6.1.7 .
Sumich, J. (2013). Tenuous belonging: Citizenship and democracy in Mozambique. Social Analysis, 57 (2), 99–116.
Sweeney, E. T. (1972). The A.F.L’.s good citizen, 1920–1940. Labor History , 13 (2), 200–216. https://doi.org/10.1080/00236567208584201 .
Tan, C. (2008). Creating “good citizens” and maintaining religious harmony in Singapore. British Journal of Religious Education , 30 (2), 133–142. https://doi.org/10.1080/01416200701830921 .
Terchek, R. J., & Moore, D. K. (2000). Recovering the political Aristotle: A critical response to Smith. American Political Science Review , 94 (4), 905–911. https://doi.org/10.2307/2586215 .
Thapan, M. (2006). ‘Docile’ bodies, ‘good’ citizens or ‘agential’ subjects? Pedagogy and citizenship in contemporary society. Economic and Political Weekly , 4195–4203.
Theiss-morse, E. (1993). Conceptualizations of good citizenship and political participation. Political Behavior , 15 (4), 355–380.
Thompson, L. A. (2004). Identity and the forthcoming Alberta social studies curriculum: A postcolonial reading. Canadian Social Studies , 38 (3), 1–11.
Tibbitts, F. (2001). Prospects for civics education in transitional democracies: Results of an impact study in Romanian classrooms. Intercultural Education , 12 (1), 27–40. https://doi.org/10.1080/14675980124250 .
Tonga, D., & Keles, H. (2014). Evaluation of the citizenship consciousness of the 8th year students. Online Submission , 4 (2), 59–72. https://doi.org/10.13054/mije.14.10.4.2 .
Torres, M. (2006). Youth activists in the age of postmodern globalization: Notes from an ongoing project. Chapin Hall Working Paper. Chicago, IL: Chapin Hall Center for Children at the University of Chicago.
Tupper, J. A., Cappello, M. P., & Sevigny, P. R. (2010). Locating citizenship: Curriculum, social class, and the “good” citizen. International Education Studies , 38 (3), 336–365. https://doi.org/10.5539/ies.v8n8p199 .
Van Deth, J. W. (2009). Norms of citizenship. The Oxford Handbook of Political Behavior , (June 2018), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199270125.003.0021 .
Westheimer, J., & Kahne, J. (2004). What kind of citizen? The politics of educating for democracy. American Educational Research Journal , 41 (2), 237–269. https://doi.org/10.3102/00028312041002237 .
White, M. (2006). The dispositions of ‘good’ citizenship: Character, symbolic power and disinterest. Journal of Civil Society , 2 (2), 111–122. https://doi.org/10.1080/17448680600905882 .
Wilkins, C. (1999). Making ‘good citizens’: The social and political attitudes of PGCE students. Oxford Review of Education , 25 (1&2). https://doi.org/10.1080/030549899104224 .
Wong, K. L., Lee, C. K. J., Chan, K. S. J., & Kennedy, K. J. (2017). Constructions of civic education: Hong Kong teachers’ perceptions of moral, civic and national education. Compare , 47 (5), 628–646. https://doi.org/10.1080/03057925.2016.1262756 .
Woolf, M. (2010). Another mishegas: Global citizenship. Frontiers. The Interdisciplinary Journal of Study Abroad , 19 , 47–60.
Worku, M. Y. (2018). Perception of Ethiopian students and educators on the responsibility for good citizenship. Journal of International Social Studies , 8 (2), 103–120.
Yesilbursa, C. C. (2015). Turkish pre-service social studies teachers perceptions of “Good” citizenship. Educational Research and Reviews , 10 (5), 634–640. https://doi.org/10.5897/err2014.2058 .
Zamir, S., & Baratz, L. (2013). Educating “good citizenship” through bilingual children literature Arabic and Hebrew. Journal of Education and Learning (EduLearn) , 7 (4), 223. https://doi.org/10.11591/edulearn.v7i4.197 .
Rights and permissions
Open Access This chapter is licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ ), which permits any noncommercial use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license and indicate if changes were made.
The images or other third party material in this chapter are included in the chapter's Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the chapter's Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 International Association for the Evaluation of Educational Achievement (IEA)
About this chapter
Cite this chapter.
Villalobos, C., Morel, M.J., Treviño, E. (2021). What Is a “Good Citizen”? a Systematic Literature Review. In: Treviño, E., Carrasco, D., Claes, E., Kennedy, K.J. (eds) Good Citizenship for the Next Generation . IEA Research for Education, vol 12. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-75746-5_2
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-75746-5_2
Published : 01 September 2021
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-75745-8
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-75746-5
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
Student Essays
Essays-Paragraphs-Speeches
Essay on Responsibilities of a Good Citizen
Leave a Comment
A good citizen is one who is responsible for his own actions and also for the well-being of the society. He abides by the laws of the country and does everything in his power to make his society a better place to live in. The following Essay talks about the chief responsibilities of a good citizen and how a good citizen is a valuable asset of the state in its prosperity, progress and peace.
List of Topics
Essay on Responsibilities of a Good Citizen for the Progress a State
A good citizen should always be aware of the happenings in his society and should try to do his bit to improve things. He should be vocal about his views and stand up for what he believes in, even if it means going against the mainstream opinion. He should also be ready to help those who are in need and work towards creating a society that is based on empathy and compassion.
What are Chief Responsibilities of a Good Citizen:
A good citizen has a number of responsibilities. Some of the most important ones are mentioned below.
1. To Obey the Law:
This is perhaps the most important responsibility of a good citizen. A good citizen always obeys the laws of his country and does not try to break them. He knows that breaking the law can lead to chaos and disorder in society and so, he always tries to uphold the law.
>>>> Read Also : “Paragraph On Cleanliness & Its Importance”
2. To Respect the Rights of Others:
A good citizen always respects the rights of others. He knows that every individual has certain basic rights which need to be respected. He does not try to infringe upon the rights of others and always tries to create an atmosphere of mutual respect.
3. To Pay Taxes:
A good citizen always pays his taxes properly. He knows that taxes are essential for the development of the country and so, he does not try to avoid them. He also tries to pay his taxes on time so that the government can use them for the benefit of society.
4. To Be Honest:
A good citizen is always honest. He does not try to mislead others or cheat them in any way. He knows that honesty is the best policy and so, he always tries to be truthful in his dealings with others.
5. To Help Others:
A good citizen always tries to help those who are in need. He knows that it is his responsibility to make sure that everyone in society has a fair chance at success. He also tries to lend a helping hand to those who are less fortunate than him.
6. To Maintain Public Property:
A good citizen always takes care of public property. He does not litter or vandalize public property and always tries to keep it clean and tidy. He knows that if everyone takes care of public property, it will be a much better place to live in.
7. To Promote National Values:
A good citizen always tries to promote national values. He knows that these values are essential for the development of the country and so, he tries to inculcate them in others as well. He also tries to spread awareness about these values so that more and more people can follow them.
>>>> Read Also : ” Essay On Our National Flag “
In conclusion, it can be said that being a good citizen is not just about following the rules and regulations of the land. It is also about being a voice for the voiceless and working towards making your society a better place for all. It is an ongoing process and something that we should all strive for. We all have a role to play in making our world a better place and it starts with each one of us doing our bit to be good citizens.
Essay on Duties of a Good Citizen:
As citizens of our country, we have certain responsibilities towards the society. These duties are not just limited to voting in elections or paying taxes, but they extend to various aspects of our daily lives. Being a good citizen means actively participating in the betterment of our community and being aware of our impact on others.
One of the most important duties of a good citizen is to follow the laws of their country. Laws are put in place to maintain order and ensure that everyone’s rights are protected. This means following traffic rules, paying attention to zoning regulations, and respecting property rights. By obeying the law, we contribute to a safe and harmonious society.
A good citizen also takes an active role in their community. This can involve volunteering for local events, participating in neighborhood cleanups, or even just being a good neighbor. By taking care of our surroundings, we create a better environment for everyone to live in.
Another duty of a good citizen is to be politically aware and exercise their right to vote. In order for democracy to function properly, citizens need to be informed about current issues and use their votes wisely. This not only ensures that the best leaders are elected, but also holds them accountable for their actions.
Moreover, being a good citizen means respecting and valuing diversity. Our society is made up of people from different backgrounds, cultures, and beliefs. It is our duty to promote inclusivity and respect towards all individuals. By doing so, we create a more tolerant and accepting community.
In addition to these duties, a good citizen also takes care of the environment. We have a responsibility towards Mother Earth and must do our part in preserving it for future generations. This can involve recycling, conserving energy, using sustainable resources, and raising awareness about environmental issues.
Last but not least, good citizens pay their taxes on time and contribute to the economy. Taxes fund important government services such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure. By fulfilling our tax obligations, we help build a better society for ourselves and others.
In conclusion, being a good citizen is more than just following rules and paying taxes. It involves active participation in the community, political awareness, respect for diversity and the environment. As individuals, we all have a role to play in making our society a better place to live in. Let us strive to fulfill our duties as responsible citizens and contribute towards a brighter future for all.
Duties of Good Citizen Essay 100-150-250 words :
Being a good citizen is not just about following rules and paying taxes. It’s about taking responsibility for the society we live in and doing our part to make it a better place. As citizens, we have certain duties that we need to fulfill towards our country and fellow humans.
Firstly, it is important to respect and obey the laws of the land. This means abiding by the rules and regulations set by the government for the betterment of society.
Secondly, we must actively participate in our democracy. This includes exercising our right to vote, staying informed about current events, and voicing our opinions on important issues.
Moreover, as good citizens, we should also contribute to the community through acts of kindness, volunteering, or simply being a good neighbor.
It is also our duty to protect the environment and conserve natural resources for future generations.
Lastly, we must uphold the values of equality, tolerance, and respect for diversity. We should treat everyone with dignity and stand up against discrimination and injustice.
In conclusion, being a good citizen requires more than just fulfilling legal obligations. It means being an active member of society and making a positive impact in our own small ways. Each one of us has a role to play in creating a better world for ourselves and future generations, and it all starts with fulfilling our duties as good citizens
Q: What are the good responsibilities of a good citizen?
A: Good responsibilities of a citizen include obeying the law, voting, paying taxes, volunteering, and participating in their community.
Q: How to be a responsible citizen essay?
A: An essay on how to be a responsible citizen should discuss actions like civic engagement, respect for others, environmental stewardship, and adherence to laws and social norms.
Q: What is our responsibility as a good citizen paragraph?
A: Our responsibility as good citizens is to contribute positively to society by following the law, respecting others, participating in the democratic process, and engaging in community service.
Q: What are the responsibilities of a citizen?
A: Citizen responsibilities typically include obeying the law, paying taxes, voting, defending the country if required, and participating in civic life

Related Posts:

Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Skip to main content
India’s Largest Career Transformation Portal
Essay on Responsibilities of a Good Citizen for Students [500+ Words]
December 10, 2020 by Sandeep
Essay on Responsibilities of a Good Citizen: Responsibility of a good citizen is to sacrifice everything for the motherland. Respecting the culture & heritage of their own country is one of the duties of a citizen. He or She must always keep in mind to raise the future of his country. Unity & prosperity must be the priorities of a good citizen.
Essay on Good Citizen 500 Words in English
Below we have provided the responsibilities of a good citizen essay, written in easy and simple words for class 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10 school students.
We are born and raised in a single country, sometimes different countries., regardless of location, we incorporate the values of our respective cultures in the way we act and treat other people. Being a citizen of a country, however, is much more than some words and a stamp on endless paperwork. Along with it, one bears an ideology that connects them to other citizens of that country, regardless of their race, religion, or gender. Being a citizen gives a person all the rights to which the constitution says they are entitled.
This is why the process of citizenship of any country is a long and complicated one since it means that the person will legally have a voice in matters of the country. It also means that they will have to abide by the laws of that country, out of respect for the nation as a whole, as well as to uphold law and order. To be a responsible citizen, the person must educate themselves about their country and culture. This begins by conversing with people and understanding their way of life. It also involves an awareness of the country’s history and heritage.
This would mean reading about important figures in the country’s history, crucial events that led the country to where it currently stands, and other aspects such as the history of art and literature. It is also crucial that people who want to be responsible citizens know the diversity of different socioeconomic groups in the country. They must learn about the situation in the country in regard to equality in terms of race, religion, gender, and several other factors. One must learn about how minority groups are treated in the country, and if they are discriminated against, then the person must be an advocate to protect their rights.
A responsible citizen must always stay updated with the news. This does not mean simply reading the headlines on the front page of a newspaper- it means reading the articles thoroughly to understand the state of the nation. In an age where fake news is rampant, one must also not limit themselves to a single news source. They should try understanding an issue by learning about it from different news channels and articles by different newspapers. They will always provide different perspectives on the same issue, and this knowledge will allow the person to gain a better understanding of what their stance ought to be.
One must also learn about their own purchases- in an age of globalization, the products we use can be made in one country with materials from another. As a responsible citizen, one must not completely boycott products from other countries but should try to use local goods and services as much as possible. By doing so, the person is helping the economy of the country as well as financing local households. Volunteering and contributing to community development efforts is an important step in helping the country progress. One does not have to have widespread connections with major NGOs to volunteer- simply helping a disabled neighbour with their groceries also counts.
One can volunteer in local homeless shelters, orphanages, animal shelters, retirement homes, as well as other educational institutions like struggling schools and nurseries. If one does not have the time in their schedule to volunteer physically, they can instead choose to donate to charity. However, one must always donate wisely, because some charities are dishonest and lack transparency in terms of what actually happens with the funds from the donation. Therefore, always research the charity before donating to it.
However, supporting the community isn’t limited merely to volunteering with organizations or donating- it also involves supporting art, music, and cultural activities. One should support local artists by promoting their work and also stay on the lookout for shows, exhibitions, and other cultural events. By attending and promoting them, the person will not only develop a healthy sense of what truly constitutes entertainment but also allow the culture of the country to flourish in all areas truly. Being a good citizen involves being cooperative, friendly, considerate, and dedicated to fostering a positive environment in the community.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to conclude an essay | Interactive example
How to Conclude an Essay | Interactive Example
Published on January 24, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on July 23, 2023.
The conclusion is the final paragraph of your essay . A strong conclusion aims to:
- Tie together the essay’s main points
- Show why your argument matters
- Leave the reader with a strong impression
Your conclusion should give a sense of closure and completion to your argument, but also show what new questions or possibilities it has opened up.
This conclusion is taken from our annotated essay example , which discusses the history of the Braille system. Hover over each part to see why it’s effective.
Braille paved the way for dramatic cultural changes in the way blind people were treated and the opportunities available to them. Louis Braille’s innovation was to reimagine existing reading systems from a blind perspective, and the success of this invention required sighted teachers to adapt to their students’ reality instead of the other way around. In this sense, Braille helped drive broader social changes in the status of blindness. New accessibility tools provide practical advantages to those who need them, but they can also change the perspectives and attitudes of those who do not.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: return to your thesis, step 2: review your main points, step 3: show why it matters, what shouldn’t go in the conclusion, more examples of essay conclusions, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about writing an essay conclusion.
To begin your conclusion, signal that the essay is coming to an end by returning to your overall argument.
Don’t just repeat your thesis statement —instead, try to rephrase your argument in a way that shows how it has been developed since the introduction.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Next, remind the reader of the main points that you used to support your argument.
Avoid simply summarizing each paragraph or repeating each point in order; try to bring your points together in a way that makes the connections between them clear. The conclusion is your final chance to show how all the paragraphs of your essay add up to a coherent whole.
To wrap up your conclusion, zoom out to a broader view of the topic and consider the implications of your argument. For example:
- Does it contribute a new understanding of your topic?
- Does it raise new questions for future study?
- Does it lead to practical suggestions or predictions?
- Can it be applied to different contexts?
- Can it be connected to a broader debate or theme?
Whatever your essay is about, the conclusion should aim to emphasize the significance of your argument, whether that’s within your academic subject or in the wider world.
Try to end with a strong, decisive sentence, leaving the reader with a lingering sense of interest in your topic.
The easiest way to improve your conclusion is to eliminate these common mistakes.
Don’t include new evidence
Any evidence or analysis that is essential to supporting your thesis statement should appear in the main body of the essay.
The conclusion might include minor pieces of new information—for example, a sentence or two discussing broader implications, or a quotation that nicely summarizes your central point. But it shouldn’t introduce any major new sources or ideas that need further explanation to understand.
Don’t use “concluding phrases”
Avoid using obvious stock phrases to tell the reader what you’re doing:
- “In conclusion…”
- “To sum up…”
These phrases aren’t forbidden, but they can make your writing sound weak. By returning to your main argument, it will quickly become clear that you are concluding the essay—you shouldn’t have to spell it out.
Don’t undermine your argument
Avoid using apologetic phrases that sound uncertain or confused:
- “This is just one approach among many.”
- “There are good arguments on both sides of this issue.”
- “There is no clear answer to this problem.”
Even if your essay has explored different points of view, your own position should be clear. There may be many possible approaches to the topic, but you want to leave the reader convinced that yours is the best one!
- Argumentative
- Literary analysis
This conclusion is taken from an argumentative essay about the internet’s impact on education. It acknowledges the opposing arguments while taking a clear, decisive position.
The internet has had a major positive impact on the world of education; occasional pitfalls aside, its value is evident in numerous applications. The future of teaching lies in the possibilities the internet opens up for communication, research, and interactivity. As the popularity of distance learning shows, students value the flexibility and accessibility offered by digital education, and educators should fully embrace these advantages. The internet’s dangers, real and imaginary, have been documented exhaustively by skeptics, but the internet is here to stay; it is time to focus seriously on its potential for good.
This conclusion is taken from a short expository essay that explains the invention of the printing press and its effects on European society. It focuses on giving a clear, concise overview of what was covered in the essay.
The invention of the printing press was important not only in terms of its immediate cultural and economic effects, but also in terms of its major impact on politics and religion across Europe. In the century following the invention of the printing press, the relatively stationary intellectual atmosphere of the Middle Ages gave way to the social upheavals of the Reformation and the Renaissance. A single technological innovation had contributed to the total reshaping of the continent.
This conclusion is taken from a literary analysis essay about Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein . It summarizes what the essay’s analysis achieved and emphasizes its originality.
By tracing the depiction of Frankenstein through the novel’s three volumes, I have demonstrated how the narrative structure shifts our perception of the character. While the Frankenstein of the first volume is depicted as having innocent intentions, the second and third volumes—first in the creature’s accusatory voice, and then in his own voice—increasingly undermine him, causing him to appear alternately ridiculous and vindictive. Far from the one-dimensional villain he is often taken to be, the character of Frankenstein is compelling because of the dynamic narrative frame in which he is placed. In this frame, Frankenstein’s narrative self-presentation responds to the images of him we see from others’ perspectives. This conclusion sheds new light on the novel, foregrounding Shelley’s unique layering of narrative perspectives and its importance for the depiction of character.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Your essay’s conclusion should contain:
- A rephrased version of your overall thesis
- A brief review of the key points you made in the main body
- An indication of why your argument matters
The conclusion may also reflect on the broader implications of your argument, showing how your ideas could applied to other contexts or debates.
For a stronger conclusion paragraph, avoid including:
- Important evidence or analysis that wasn’t mentioned in the main body
- Generic concluding phrases (e.g. “In conclusion…”)
- Weak statements that undermine your argument (e.g. “There are good points on both sides of this issue.”)
Your conclusion should leave the reader with a strong, decisive impression of your work.
The conclusion paragraph of an essay is usually shorter than the introduction . As a rule, it shouldn’t take up more than 10–15% of the text.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, July 23). How to Conclude an Essay | Interactive Example. Scribbr. Retrieved March 22, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/conclusion/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, example of a great essay | explanations, tips & tricks, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

Essay on Duties of a Good Citizen
Students are often asked to write an essay on Duties of a Good Citizen in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Duties of a Good Citizen
Understanding citizenship.
Being a good citizen means to contribute to society and the community. Good citizenship is about following rules, respecting others, and actively participating in the community.
Respecting Laws
A good citizen respects the law. This means following rules and regulations, and not engaging in illegal activities.
Participation in Community
Active participation in the community is another duty. This can be through voting, volunteering, or helping neighbors.
Respecting Others
Good citizens respect others. They treat everyone equally, regardless of their race, religion, or gender.
In conclusion, being a good citizen involves respect for laws, active participation, and treating others equally.

250 Words Essay on Duties of a Good Citizen
Introduction.
A good citizen is a cornerstone of a healthy society, contributing to its development, prosperity, and stability. Their responsibilities extend beyond mere law-abiding behavior, encompassing a broad spectrum of duties and obligations.
Moral and Legal Obligations
Primarily, a good citizen abides by the law, respecting the rights and freedoms of others. They uphold moral values, demonstrating honesty, integrity, and respect in their daily interactions. Their commitment to justice ensures they act as a moral compass, fostering a sense of community and mutual respect.
Political Participation
Active participation in political processes is another vital duty. Good citizens stay informed about national and global issues, exercising their right to vote responsibly. They engage in constructive criticism, voicing their opinions and advocating for change when necessary.
Social Responsibility
Good citizens also shoulder social responsibilities, contributing to societal welfare. They volunteer, assist the less fortunate, and strive for environmental sustainability. Their actions reflect a deep understanding of the interconnectedness of society and the environment.
In essence, the duties of a good citizen are multifaceted, intertwining legal, moral, political, and social dimensions. By fulfilling these duties, citizens not only enhance their personal growth but also contribute to societal progress. The collective efforts of good citizens are the bedrock upon which thriving societies are built.
500 Words Essay on Duties of a Good Citizen
A good citizen is an integral part of a society who contributes to its growth and development. The concept of citizenship goes beyond merely living in a country; it involves actively participating in societal affairs and upholding the values and laws of the land.
Upholding the Law
The first duty of a good citizen is to respect and adhere to the laws of the country. Laws are designed to maintain order and protect the rights and freedoms of all citizens. Disregarding these laws not only disrupts societal harmony but also infringes upon the rights of others. A good citizen understands the importance of these laws and follows them diligently.
Active Participation in Democratic Processes
In democratic societies, citizens have the right to vote and voice their opinion. It is the duty of every citizen to participate in these democratic processes. Voting is not merely a right, but a responsibility. A good citizen understands the power of their vote and utilizes it to elect leaders who they believe will best represent their interests and the interests of the society at large.
Respect for Diversity
A good citizen respects diversity and promotes tolerance. In today’s globalized world, societies are becoming increasingly diverse. A good citizen understands that diversity is not a threat, but an asset. They respect the rights of others to hold different beliefs and opinions, and they promote a culture of tolerance and acceptance.
Environmental Responsibility
A good citizen recognizes the importance of protecting the environment. They understand that their actions have an impact on the environment and strive to minimize their environmental footprint. This includes practicing sustainable living, recycling, and advocating for environmental policies.
Social responsibility is another crucial duty of a citizen. This involves contributing to the welfare of the society in whatever capacity one can. It could be through volunteering, donating to charities, or simply helping a neighbor in need. A good citizen understands that they are part of a larger community and that their actions can have a significant impact on the well-being of this community.
In conclusion, the duties of a good citizen are multifaceted and extend beyond mere law-abiding behavior. They involve active participation in democratic processes, respect for diversity, environmental responsibility, and social responsibility. By fulfilling these duties, citizens not only contribute to the betterment of their society but also promote a more just and equitable world.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on An Ideal Citizen
- Essay on American Diet
- Essay on American Democracy
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Essay on How Can We be Good Citizens

Every nation or society is known because of its people. It is required that every person living in the nation be a responsible and good citizen. How can we be good citizens? What qualities make us good citizens of the nation? I hope many of us have several answers to these questions and many of us would also be curious to know the qualities that make a person a good citizen of a nation.
Short and Long Essay on How can We be Good Citizens in English
This is a commonly asked topic in exams and competitive exams to write an essay on it. Many students find it difficult to understand that what things have to be included in writing an essay on this topic.
10 Lines Essay on How can We be Good Citizens (100-120 Words)
1) A good citizen is a person that understands his duty toward the nation.
2) A good citizen is responsible for a good and healthy nation.
3) We can be good citizens if we follow all the rules and regulations.
4) Helping the poor and needy makes us good citizens.
5) A good citizen will never misuse the rights provided to them.
6) We can be good citizens if we maintain peace and harmony in the nation.
7) A responsible person is considered a good citizen.
8) Good deeds towards other people and the country makes us good citizen.
9) A good citizen will never be a participant in violent activities.
10) Working for the progress of the country will make you a good citizen.
Short Essay – 250 Words
Introduction
The people living in any of the nations in the world are called its citizens. The nation provides rights and freedom to every citizen. Thus, it is the duty of every citizen to be a good and responsible citizen of the nation.
Being good citizens is the real service to the nation
The nation provides us with different types of rights that are essential for the growth and development of a person. It also expects us to be good citizens of the nation. The work of the good citizens is to fulfill the duties and responsibilities that they have towards the nation. If we want to do something for our nation we must become the good citizens of the nation. It will enable us to do the right things, respect and care for other people’s rights, abide by the rules and regulations of the nation, help the old, poor, and needy people, and make the right use of the freedom granted to us. The act of doing good things for the nation will make us good citizens and will be the real service to the nation.
Good citizens are the real strength of the nation
The progress and development of every nation depend upon the deeds of its citizens. If the percentage of good citizens is higher in a nation the country will have good progress and development. We must always try to work in unity, live with peace and harmony, treat everyone equally, foster the understanding of education among people, and be ready to help the nation in its need. When we develop these qualities in us we can be good citizens and the strength of the nation.
Good citizens are those who give priority to the nation and never try to hurt anyone by their words or deeds.
In the same reference, I have also provided a long essay on this topic. I hope it might ease the difficulty of students and give them an idea to write an essay, project, or assignment on this topic.
How can You be a Good Citizen – Long Essay (1100 Words)
There are many people residing in any of the nations in the world. They all are called the citizens of that particular nation in which they live. We get recognition in our society because of our deeds. Every person born in the nation has some duties and responsibilities towards the nation. This act of being a responsible person and doing good deeds make us good citizens of the nation.
What is Meant by a Good Citizen?
Citizens are the real wealth of any of the nations in the world. In democratic countries, every single citizen holds equal importance. For example- India is the biggest democracy in the world. Every Indian citizen’s contribution is important for the development and progress of the nation. As a citizen, every person in India has their liabilities towards the nation. The person who serves the nation by caring about the people of the nation and abides with every rule and regulation in life is stated as a good citizen of the nation. Everybody can be a citizen of any of the nations in the world but to be a good citizen requires doing good deeds and caring about everyone’s rights.
Qualities Required for being a Good Citizen
The people who are good as a person by their deeds help in the formation of a good society and nation. They are called the good citizens of the nation. The special qualities required for becoming a good citizen are enlisted below:
Enjoy the Right and Freedom Sensibly – As a citizen of the nation, every one of us enjoys some rights and freedom. These rights are granted to us by birth and are meant for our development and progress. A good citizen should understand the limitation of freedom and rights and never misuse them.
Respect for others – A good citizen should have respect for everyone in the society either it is rich or poor. He/she must respect and help the older people of the society and take advice from them when needed. He/she must be polite to everyone. He should not hurt anyone because of their look or status. In a democratic country like India, there is the freedom to practice any religion according to our faith. Therefore a good citizen must have respect for every culture and region in the society. He/she must do anything that might create violence or hurt the feeling of other communities.
Help People in Need – If we are born in any of the nations we are ultimately called the citizens of that nation. As the citizens of any nation, it is our duty to helps people in their needs. When we help others in their needs other people also help us in our needs. This makes us a good citizen of society.
Participate in Healthy Politics – A good citizen must give a vote during the elections in the nation. Every single vote is of immense value. This also confirms the views and opinions of every single person. We know that the existence of any nation is only because of its citizens. Therefore it is the responsibility of a good citizen to participate in the political, social, judicial activities of the nation. A good citizen does not give the vote to support a particular party or a group of people but for the welfare of the entire nation and its people.
Abide by Rules and Regulations – A good citizen should follow all the rules and regulations made by the nation. He/she should never break any rule or perform any act by going against the laws. They must understand the importance of the judiciary and laws made by the nation and must pay tax. A good citizen must go through proper procedure meant in the nation for seeking justice for any injustice or crime.
Work for the Betterment of the Nation – A good citizen is only the one who thinks about the progress of the nation. He/she instead of being indulged in nonsense activities should think about some new ideas and ways that might benefit the nation and people. He/she must make others aware of pollution by giving speeches and conducting cleanliness drives. Moreover, a good citizen should make people understand the need for education in their lives.
Never Participate in Violence – A good citizen teaches people in the society to live with peace and harmony. He/she does this by not involving in any of the violent acts that might give rise to fight. In this way, a good citizen becomes an example for other people living in society. A good citizen always tries to make every people in the society become a good person and act in a wise way.
Always be Ready to Serve the Nation – A good citizen must be a true patriot and always be ready to serve the country in need. He/she should be ready for any type of sacrifice for the nation and its people.
Are we Seriously Performing our Duties as Good Indian Citizens?
India is a democratic nation and every Indian is a citizen of this nation. Every citizen of the nation is granted some rights and freedom from birth. This right is granted to every citizen for their progress and development that in turn would benefit the entire nation. Now the great question arises that’ Are we seriously performing our duties as a good citizen?’ Every day we notice different types of heinous crimes, corruption, violent acts, happening in our nation. If we Indians are performing our duties as good citizens then why are these things happening.
We all need to understand our duties and responsibilities as the citizen of India. We must try our best to be a good citizen instead of just being a citizen of the nation. The honest answer to the question stated above is “No”. The fault lies among us as we are not fulfilling our duties as good citizens. Unless and until every citizen understands their duty and responsibility towards the nation it is difficult to bring the change. It is never too late for starting anything and we all know that citizens are the real wealth of any nation. Therefore it is only we who can change the present scenario by acting wisely and understanding our responsibility for the nation.
The citizens are smallest units of the nations that organize to form a family, society, and further a nation. A good citizen will surely give rise to a good family. Several good families will make a good society and finally a good nation. We all must try to become good people in our life. The good person only becomes a good citizen for the nation.
FAQs: Frequently Asked Questions
Ans . Bhutan is the country in the world having the toughest procedure of giving citizenship.
Ans . The virtue of being honest, respectful, responsible, and true love for the nation makes a person to be called a good citizen.
Ans . Educated people can participate in decision making and that is the duty of a good citizen.
Ans . The minimum age of voting is 18 years for a citizen in India.
Related Posts
Essay on digital india, cashless india essay, essay on child is father of the man, essay on causes, effects and prevention of corona virus, essay on dr. sarvepalli radhakrishnan, durga puja essay, essay on summer vacation, essay on my plans for summer vacation, essay on holiday.

Good Citizen Paragraph & Composition

Table of Contents
Duties of a Citizen Essay 300 Words
By: Haque , Words: 300, For class 9-10/SSC
Write an essay/composition about the duties of a citizen. Use the following hints: “meaning of citizen”, “rules and laws”, “lacking in a civic sense”, “your expectation”.
Citizen primary means one who lives in a city. But the term is usually used to mean belonging to a state in a broad sense.
There are certain rules of conduct for the members of every society so that there is peace and harmony among them. Some of these rules are written laws, and anyone who breaks them is punished by the court. But there are many unwritten rules which are no less binding on every member of society. The peace and happiness of the society depend a good deal upon the proper observance of these rules too. A good citizen follows these unwritten rules of conduct in the way he obeys written laws.
It is a pity that many in our country are indifferent to these unwritten rules of humane and social behavior. We often throw banana peels on the road, which can cause serious injuries to anyone who slips. We spit and throw garbage whenever we want. This makes the roads and the environment dirty. We waste filtered water by leaving the taps open. We have also a bitter experience of the use made of loudspeakers without any thought of the sufferings of people nearby.
All these common experiences show that we are lacking in a civic sense. A good citizen not only avoids breaking the rules himself but also tries to make sure that the rules are not broken by others. We wish to see our society peaceful. But we do not fulfill our responsibility to build a peaceful society. Society cannot do much unless we allow it. So, it is our duty to try to correct people whenever we see them doing something wrong. We will encourage everyone to be polite, courteous and to follow social and state norms.
Qualities of a Good Citizen Essay
Words: 330 | for Class 9-10/SSC
A good citizen is someone who actively participates in the community and works to make it a better place. They are responsible, respectful, and engaged members of society who take an active role in the civic life of their community.
One of the most important qualities of a good citizen is responsibility. This means taking ownership of one’s actions and being accountable for their impact on the community. A responsible citizen pays their taxes, follows the laws, and participates in the democratic process by voting in elections. They also take care of the environment and actively work to improve it.
Respect is another crucial quality of a good citizen. This means treating others with kindness and courtesy, and valuing their opinions and perspectives. A respectful citizen listens to and considers the views of others, and actively works to promote understanding and unity in the community.
Engagement is also an important quality of a good citizen. This means actively participating in the community and working to make it a better place. Engaged citizens volunteer in their community, participate in local government, and work to address issues that affect their community. They also stay informed about local and national issues and use their voices to advocate for positive change.
To be a good citizen, one must also possess a sense of civic duty. This means recognizing the importance of contributing to the well-being of the community and working to make it a better place. A good citizen actively participates in the civic life of their community and takes an active role in making it a better place for all.
In conclusion, a good citizen is someone who is responsible, respectful, engaged, and possesses a sense of civic duty. These qualities are essential for promoting the well-being of the community and working towards a better future for all. By actively participating in the community, being responsible and respectful to others, and staying informed and engaged, anyone can strive to be a good citizen.
A Paragraph about a Good Citizen
In 200 words, for class 8 to 12
A good citizen is a person who abides by the rules of his society and country, and fulfills his responsibilities as a citizen. A good citizen is first and foremost a good person. He wants peace for all and never harms others. He doesn’t quarrel with others, but always tries to resolve the conflicts of others. A good citizen wishes good for his country and loves it. If he is eligible to pay taxes, he pays it regularly, and works as hard as he can for the development of the country. He himself doesn’t waste state resources and doesn’t allow others to do so. A good citizen never thinks of earning in a dishonest way. He makes his living honestly . He tries his best to remove bribery and corruption from the society. To build a better society, he tries to help law enforcement agencies prevent drug addiction. After all, a good citizen is a patriot, he never does anything that degrades the dignity of his country. Thus a good citizen is the main asset of a country. Good citizens are very important in building a developed and peaceful society. Therefore, we should all strive to be good citizens.
A Paragraph on a Good Citizen
In 150 words, for class 5 to 10
Write a paragraph about your idea of A Good Citizen. Think of a particular citizen you have known. Describe some of rights and duties to the state.
A citizen is a member of state in which he lives and enjoys some rights. I have known a citizen who is my neighbor . His name is Mr. N. Islam. He lives in the country. He is loyal to the country. He never does anything as against the interest of the country. He obeys the law of the country. He exercises his vote in election honestly. Above all, he is patriotic. He loves his country and his countrymen from the core of his heart. His love is not narrow-minded and selfish. He pays his taxes regularly. He also does some other duties. During the natural calamities, he stands by the people. He has set up a night school to teach the illiterate people. He lives in peace and good understanding with others in the society. He is physically healthy. In fact, he is an asset of our country.
A Good Citizen Paragraph
In 130 words, for class 5 to 8
The prerequisite for building a peaceful country is to create good citizens. The identity of a good citizen is that he is a good man. He is honest and kind. He abides by the rules of religion and the laws of the state. He is an educator because he knows that through education people become aware of their responsibilities and rights. A good citizen wants peace and order in the society. That is why when he sees injustice or irregularity somewhere, he tries to resist and protest. He did his best to promote education, health and justice in his area and protect the environment . As a good citizen, he is always vigilant against corruption and waste of government resources. Indeed, a good citizen is the most valuable asset of a society and country.
Check out: 300+ Essays & Paragraphs in English
About the Author
A teacher, writer and blogger, started allparagraph noting students search online for paragraphs on various topics, short and simple essays , edifying stories and other materials of study . In composing these lessons we have tried to use as simple language as possible, keeping young students in mind. If you find any text inappropriate, please let us know so we can make it more useful through necessary corrections and modifications. Thank you!
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Adblock Detected!
Please help us run the website by disabling your ad blocker..
- Call us Topics in English
- Privacy Policy
- terms of use
Topics in English Topics in english to learn and fluent pronunciation and writing and facilitate conversation between you and others, whether in school, work or daily life

A good citizen paragraph 8 Models
Last updated Friday , 15-03-2024 on 11:25 am
A good citizen paragraph , It is important to know how to write a graph about a good citizen, or an essay about the characteristics of a good citizen, because this topic is asked in all grades, and you can write an article about the importance of a good citizen for the progress of the country, or a short essay summarizing the most important qualities of a good citizen from your point of view, and what are the duties of a citizen and what are his rights?. Because if you know your duties towards your country, it will be easy for you to perform these duties, and thus you will be a good citizen.
We live in a society and we must abide by the laws without regard to personal interests only, because these laws are in the interest of everyone.
A good citizen paragraph
Undoubtedly, the well-being of society depends on the well-being of the citizens. This is because the individual is the basis for the formation of society. If the citizens are good, the society will advance.
Society consists of a group of individuals who live in a specific geographical place, have the same customs and traditions, the same language and the same beliefs, and they have a common culture and a long history written by their ancestors. All this makes the individual linked to his homeland with a strong bond that nothing can affect.
He carries the love of his homeland within him, so that his departure from his homeland does not change that strong emotion, but he remains longing for his homeland and dreams of returning to it.
Therefore, the citizen must have some good qualities that make him a good citizen, such as following the laws regulating the society, having decent morals in dealing with others, loving the homeland and belonging to it, and being ready to defend it and sacrifice for it.
All these qualities make you worthy of being called a good citizen.
Undoubtedly, if individuals reconcile, it will be reflected in society as a whole.
Therefore, we must take care of teaching students what they have to do towards their country, in addition to providing them with good moral qualities.
One of the important qualities that makes you a good citizen is to follow the laws that regulate life in your community.
Because not following these laws is detrimental to the public interest, you must abandon the idea of achieving personal gains without respecting the rights of others. You must also be loyal to your country so that you work for its progress and prosperity in peacetime, and defend it against its enemies in time of war.
The simplest example of this is paying the tax you owe. It is possible for a person to find a method that enables him to evade paying the tax, thus achieving a personal interest for himself, but at the same time it is detrimental to the interest of the society in which he lives, because these taxes will be used by the government in making projects or services that benefit all citizens.
Therefore, we must raise our children with love and loyalty to the homeland.
There are many good qualities that we must teach our children to be good citizens, including the preservation of public property.
We see many people do not maintain public property and spoil it.
These people are unaware that this public property was established from tax money paid by the citizens, which means that this public property is their property as well and they must preserve it by using it properly and not destroying it.
These qualities will not be acquired by a person except when there is awareness for the children in the school and the family to realize the importance of preserving public properties such as parks, transportation, schools, hospitals and other facilities that provide services to citizens.
Given the importance of the citizen and his influence in society, great attention must be given to the citizens’ ability to belong to the homeland.
This can be done through several methods, namely the family, the school, and the various media.
The family must cultivate in the young people a love of the homeland and the preservation of the environment in which we live.
When a mother directs her children to maintain public property, such as maintaining the cleanliness of gardens, streets, or schools, she instills in them a love of the environment in which they live.
Likewise, the school should play a major role in instilling a sense of belonging to the homeland in the hearts of students by preparing curricula to educate them about the importance of preserving the environment and others.
There must be a major role for the media in educating citizens about the importance of preserving the homeland and what are the risks that may result from not preserving the homeland.
In conclusion, we can say that since the individual is the building block of society, it has become necessary for the citizen to be a good citizen in order to be a reason for the progress and prosperity of his country.
In order for the citizens to be good, there must be awareness among the citizens of the importance of being good, because this will work on the cohesion of the country and increase its strength.
Therefore, the family and the school must cooperate in raising young people, giving them good morals and patriotism, and preserving public and private property as well.
There is also a major role for the various media in educating citizens about the importance of preserving their homeland and its wealth.
A good citizen essay
Since the citizen is one of the building blocks that make up the society, if the citizen is righteous, the society will progress and prosper and the crime rate will decrease, and if the citizen is not righteous, then injustice, chaos and underdevelopment will prevail.
Hence the importance of forming strong ties between the citizen and other citizens, as well as between him and his homeland. This is done by spreading awareness of the importance of cooperation among the people, and that the interest of the country is sacred to all citizens.
One of the manifestations that indicates love and belonging to the homeland is the mastery of work. A good citizen must abide by labor laws, such as adherence to work schedules and number of hours, and try to develop his work to give the best production.
And do not forget the role of students in the development of their homeland, and this is through learning seriously, and trying to join the best international universities in order to learn there, and then transfer his experiences to his homeland. The role of young people is pivotal, as they are the ones who can develop and raise their country.
Qualities of a good citizen essay
There are many qualities that characterize a good citizen, such as love of the homeland and sacrifice for it, keenness to seek knowledge in order to develop the country for the better, and preserving public property.
One of the important characteristics of a good citizen is that he be a positive person, who fights corruption and reports the corrupt to the police.
In order for the citizen to be righteous, he must have decent morals such as honesty and trust, and not deceive or defraud people, so that peace and security prevail among the members of society. Because it is very important that peace and cooperation prevail among the citizens so that everyone can perform his duty towards the homeland.
We must respect the good citizen and present him in the media as a model that we must emulate. Because young people want to take for themselves a role model to follow in thinking and lifestyle.
There must be a focus from the media on examples of good citizens who have rendered great services to their country. This will encourage young people to take these good citizens as role models.
Duties of a good citizen essay
The responsibility of a good citizen is great, as it does not stop at following the laws regulating life only, but he must be a positive citizen with an effective influence in society, and be a reason for the progress of society.
The willingness of a citizen to defend his homeland, even if he loses his life, is the highest quality of a good citizen.
We can mention some of these responsibilities that a good citizen must have as follows:
- A good citizen respects and adheres to the laws of his country, because failure to follow the laws leads to the spread of chaos and corruption.
- A good citizen respects the cultural heritage of his country and preserves its monuments.
- The good citizen must respect the beliefs of his homeland and respect the prophets, sages and heroes who sacrificed themselves for the sake of the country.
- A good citizen respects the race to which he belongs, and tries to develop the positives. And eliminates the negative customs and traditions of his society.
- He must be ready to defend his homeland against the enemies, even if it would cost him his life.
- Works for the common good, such as paying taxes, maintaining public property, and cooperating in the dissemination of science and knowledge among citizens.
- The good citizen must also be positive in repelling injustice from the oppressed, fighting corruption and other things in which he can participate.
- A good citizen is a person responsible for his actions, who does not commit mistakes that harm his country, and he is a conscious person who is aware of the dangers facing his country.
- A good citizen must have decent morals such as honesty, cooperation and other good qualities.
Importance of being a good citizen essay
There is great importance to be a good citizen, because society consists of a group of individuals and the progress of that society depends on the progress and advancement of these individuals (citizens).
Citizens must be good and aware of their importance and effective influence in their country, as they are responsible for the progress and protection of their country.
Therefore, everyone should be working hard, and there should be brilliant scientists, distinguished engineers, distinguished doctors, skilled craftsmen, loyal teachers, loyal soldiers, and students who are diligent in acquiring knowledge.
Certainly, if every citizen does what he must, the country will advance and become stronger, and the enemies will never be able to defeat it.
Therefore, the state should care about educating citizens about the importance of loyalty to their homeland, and that the progress of the homeland depends on them.
A good citizen short essay
A good citizen is the main engine of the country towards progress and prosperity. The role of the good citizen is highlighted in all areas of life. The scientist who invents machines and works for the advancement of his country is a good citizen.
A soldier who fights for his country and may lose his life is a good citizen, and a doctor who works seriously to eradicate diseases and epidemics without caring that he may be exposed to infection is a good citizen.
A student who studies seriously and tries to excel in his studies in order to benefit his country in the future is also a good citizen, and a teacher who endures difficulties in order to educate students is a good citizen.
From the foregoing it becomes clear that every citizen who does his job in the best manner is indeed a good citizen.
I am a good citizen essay
I consider myself a good citizen, because my family taught me from my childhood to preserve public property. When I used to go with my family to the public garden, my mother used to ask us not to pick roses and not climb trees, and to keep the garden clean by throwing garbage in the designated bin.
Then when I joined school, my mother asked me to keep my school clean, just as I keep my house clean. She also asked me to respect the school’s rules in terms of appointments, uniform, and dealing with other students, in addition to respecting teachers and all school staff.
My mother also asked me to work hard in my studies, and she told me that you study in order to benefit your country, and this goal you must remember throughout the years of your studies.
Indeed, I carried out my mother’s directives until I became a good citizen, and I am appreciated and respected by everyone.
Being a good citizen essay
There is no doubt that a good citizen is a wealth for his country. Throughout history, we have read about citizens who changed their country’s life for the better. Some of them struggled for the independence of their country, some were keen to spread useful sciences among members of their community, and some of them challenged difficulties and worked hard to improve their country’s economy.
The good citizen model has many forms. Each of us can be a good citizen by performing his work seriously and being sincere in performing his work. The citizen must also have good morals in order for peace and cooperation to prevail among the members of society.
The role of the good citizen never stops. In peace, he works to advance his country economically, healthily, culturally and socially, and in war his role is greater, since defending the homeland and sacrificing for it, which is the highest goal that a citizen can offer to his homeland.
We have provided you with an A good citizen paragraph, and you can read more through the following link:
- Essay on self confidence
- Essay on spring season
- A friend in need is a friend indeed essay
Related Articles

Paragraph on morning walk 10 Models

short paragraph 2 models

Paragraph writing examples 2 models
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Tips for Writing an Effective Application Essay

How to Write an Effective Essay
Writing an essay for college admission gives you a chance to use your authentic voice and show your personality. It's an excellent opportunity to personalize your application beyond your academic credentials, and a well-written essay can have a positive influence come decision time.
Want to know how to draft an essay for your college application ? Here are some tips to keep in mind when writing.
Tips for Essay Writing
A typical college application essay, also known as a personal statement, is 400-600 words. Although that may seem short, writing about yourself can be challenging. It's not something you want to rush or put off at the last moment. Think of it as a critical piece of the application process. Follow these tips to write an impactful essay that can work in your favor.
1. Start Early.
Few people write well under pressure. Try to complete your first draft a few weeks before you have to turn it in. Many advisers recommend starting as early as the summer before your senior year in high school. That way, you have ample time to think about the prompt and craft the best personal statement possible.
You don't have to work on your essay every day, but you'll want to give yourself time to revise and edit. You may discover that you want to change your topic or think of a better way to frame it. Either way, the sooner you start, the better.
2. Understand the Prompt and Instructions.
Before you begin the writing process, take time to understand what the college wants from you. The worst thing you can do is skim through the instructions and submit a piece that doesn't even fit the bare minimum requirements or address the essay topic. Look at the prompt, consider the required word count, and note any unique details each school wants.
3. Create a Strong Opener.
Students seeking help for their application essays often have trouble getting things started. It's a challenging writing process. Finding the right words to start can be the hardest part.
Spending more time working on your opener is always a good idea. The opening sentence sets the stage for the rest of your piece. The introductory paragraph is what piques the interest of the reader, and it can immediately set your essay apart from the others.
4. Stay on Topic.
One of the most important things to remember is to keep to the essay topic. If you're applying to 10 or more colleges, it's easy to veer off course with so many application essays.
A common mistake many students make is trying to fit previously written essays into the mold of another college's requirements. This seems like a time-saving way to avoid writing new pieces entirely, but it often backfires. The result is usually a final piece that's generic, unfocused, or confusing. Always write a new essay for every application, no matter how long it takes.
5. Think About Your Response.
Don't try to guess what the admissions officials want to read. Your essay will be easier to write─and more exciting to read─if you’re genuinely enthusiastic about your subject. Here’s an example: If all your friends are writing application essays about covid-19, it may be a good idea to avoid that topic, unless during the pandemic you had a vivid, life-changing experience you're burning to share. Whatever topic you choose, avoid canned responses. Be creative.
6. Focus on You.
Essay prompts typically give you plenty of latitude, but panel members expect you to focus on a subject that is personal (although not overly intimate) and particular to you. Admissions counselors say the best essays help them learn something about the candidate that they would never know from reading the rest of the application.
7. Stay True to Your Voice.
Use your usual vocabulary. Avoid fancy language you wouldn't use in real life. Imagine yourself reading this essay aloud to a classroom full of people who have never met you. Keep a confident tone. Be wary of words and phrases that undercut that tone.
8. Be Specific and Factual.
Capitalize on real-life experiences. Your essay may give you the time and space to explain why a particular achievement meant so much to you. But resist the urge to exaggerate and embellish. Admissions counselors read thousands of essays each year. They can easily spot a fake.
9. Edit and Proofread.
When you finish the final draft, run it through the spell checker on your computer. Then don’t read your essay for a few days. You'll be more apt to spot typos and awkward grammar when you reread it. After that, ask a teacher, parent, or college student (preferably an English or communications major) to give it a quick read. While you're at it, double-check your word count.
Writing essays for college admission can be daunting, but it doesn't have to be. A well-crafted essay could be the deciding factor─in your favor. Keep these tips in mind, and you'll have no problem creating memorable pieces for every application.
What is the format of a college application essay?
Generally, essays for college admission follow a simple format that includes an opening paragraph, a lengthier body section, and a closing paragraph. You don't need to include a title, which will only take up extra space. Keep in mind that the exact format can vary from one college application to the next. Read the instructions and prompt for more guidance.
Most online applications will include a text box for your essay. If you're attaching it as a document, however, be sure to use a standard, 12-point font and use 1.5-spaced or double-spaced lines, unless the application specifies different font and spacing.
How do you start an essay?
The goal here is to use an attention grabber. Think of it as a way to reel the reader in and interest an admissions officer in what you have to say. There's no trick on how to start a college application essay. The best way you can approach this task is to flex your creative muscles and think outside the box.
You can start with openers such as relevant quotes, exciting anecdotes, or questions. Either way, the first sentence should be unique and intrigue the reader.
What should an essay include?
Every application essay you write should include details about yourself and past experiences. It's another opportunity to make yourself look like a fantastic applicant. Leverage your experiences. Tell a riveting story that fulfills the prompt.
What shouldn’t be included in an essay?
When writing a college application essay, it's usually best to avoid overly personal details and controversial topics. Although these topics might make for an intriguing essay, they can be tricky to express well. If you’re unsure if a topic is appropriate for your essay, check with your school counselor. An essay for college admission shouldn't include a list of achievements or academic accolades either. Your essay isn’t meant to be a rehashing of information the admissions panel can find elsewhere in your application.
How can you make your essay personal and interesting?
The best way to make your essay interesting is to write about something genuinely important to you. That could be an experience that changed your life or a valuable lesson that had an enormous impact on you. Whatever the case, speak from the heart, and be honest.
Is it OK to discuss mental health in an essay?
Mental health struggles can create challenges you must overcome during your education and could be an opportunity for you to show how you’ve handled challenges and overcome obstacles. If you’re considering writing your essay for college admission on this topic, consider talking to your school counselor or with an English teacher on how to frame the essay.
Related Articles

COMMENTS
Conclusion. Being a good citizen is not just a superficial label that a person can be proud of. It is about having a sense of responsibility towards the society that we live in and for the world we will leave behind. Being a good citizen is more than just voting every year. It's about being an active citizen.
In this essay, we will explore the characteristics that make up a good citizen and how these attributes can be harnessed to promote both personal growth and social progress. Key traits such as responsibility, respect, and active participation will be examined for their role in fostering civic engagement and advancing social justice.
Conclusion. In conclusion, a good citizen is a valuable asset to any country. They follow rules, respect others, participate actively in their community, behave responsibly, and promote education. They contribute positively to their society and inspire others to do the same. Being a good citizen is not just about enjoying rights but also about ...
17867. A good citizen is one who properly fulfills his or her role as a citizen. There are many opinions as to what constitutes a good citizen. Theodore Roosevelt said, "The first requisite of a good citizen in this Republic of ours is that he shall be able and willing to pull his weight." Education is sometimes viewed as a prerequisite to good ...
The Responsibilities of A Good Citizen essay 100, 150, 200, 250, 500 words in English help the students with their class assignments, comprehension tasks, and even for competitive examinations. You can also find more Essay Writing articles on events, persons, sports, technology and many more.
A good citizen also protects the environment. They recycle, conserve water, and promote sustainability. Conclusion. In conclusion, a good citizen is an active, respectful, and responsible member of society. 250 Words Essay on Responsibilities of a Good Citizen Introduction
Students are often asked to write an essay on Good Citizen in their schools and colleges. And if you're also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic. Let's take a look… 100 Words Essay on Good Citizen Defining a Good Citizen. A good citizen is someone who respects others and their property.
In this light, being a global citizen goes contrary to what being a good citizen entails. Conclusion. This paper set out to argue that to a large extent, it is necessary to be a "good citizen" in order to be a "global citizen" and vice versa. ... This essay, "Good Citizenship and Global Citizenship" is published exclusively on IvyPanda ...
Good citizenship involves multiple components, including values, norms, ethical ideals, behaviors, and expectations of participation. This chapter seeks to discuss the idea of good citizenship by surveying the academic literature on the subject. To map the scientific discussion on the notion of good citizenship, a systematic review of 120 ...
The first essay is a long essay on the Good Citizen of 400-500 words. This long essay about Good Citizen is suitable for students of class 7, 8, 9 and 10, and also for competitive exam aspirants. The second essay is a short essay on Good Citizen of 150-200 words. These are suitable for students and children in class 6 and below.
In conclusion, being a good citizen is more than just following rules and paying taxes. It involves active participation in the community, political awareness, respect for diversity and the environment. As individuals, we all have a role to play in making our society a better place to live in. ... Duties of Good Citizen Essay 100-150-250 words:
Paragraph Writing A GOOD CITIZENA citizen is the asset of a country. A good citizen has as many duties as he has rights. The basic rights of a citizen are his basic human rights. He has right to live, travel, work, and vote. He has the right to education, security and justice. He has also the right to die a normal death. He has many other rights which he can enjoy. Again a citizen has to ...
Essay on Responsibilities of a Good Citizen: Responsibility of a good citizen is to sacrifice everything for the motherland. Respecting the culture & heritage of their own country is one of the duties of a citizen. He or She must always keep in mind to raise the future of his country. Unity & prosperity must be the priorities of a good citizen.
PAGES 3 WORDS 918. Citizen in the Analects of Confucius. A good citizen ought to have a number of qualities and behave in a certain way. To determine what it means to be a good citizen, one could consult the Analects of Confucius and relate the teachings therein to current events and happenings. From the onset, it would be prudent to point out ...
Step 1: Return to your thesis. To begin your conclusion, signal that the essay is coming to an end by returning to your overall argument. Don't just repeat your thesis statement—instead, try to rephrase your argument in a way that shows how it has been developed since the introduction.. Example: Returning to the thesis Braille paved the way for dramatic cultural changes in the way blind ...
Conclusion. In conclusion, being a good citizen involves respect for laws, active participation, and treating others equally. 250 Words Essay on Duties of a Good Citizen Introduction. A good citizen is a cornerstone of a healthy society, contributing to its development, prosperity, and stability.
Pages • 2. Paper Type: 450 Word Essay Examples. 1.Explain what citizenship in the nation means and what it takes to be a good citizen of this country. Discuss the rights, duties, and obligations of a responsible and active American citizen. 2.Do TWO of the following: a.
Good Citizenship Essay. When dealing with such issues as equality and diversity, good citizenship between the society and public services is important because it allows tasks to run much more smoothly and efficiently. Good citizenship will allow all races/genders/cultures to coexist in a society peacefully without prejudice or discrimination.
10 Lines Essay on How can We be Good Citizens (100-120 Words) 1) A good citizen is a person that understands his duty toward the nation. 2) A good citizen is responsible for a good and healthy nation. 3) We can be good citizens if we follow all the rules and regulations. 4) Helping the poor and needy makes us good citizens.
A Good Citizen Paragraph. In 130 words, for class 5 to 8. The prerequisite for building a peaceful country is to create good citizens. The identity of a good citizen is that he is a good man. He is honest and kind. He abides by the rules of religion and the laws of the state.
A good citizen short essay. A good citizen is the main engine of the country towards progress and prosperity. The role of the good citizen is highlighted in all areas of life. The scientist who invents machines and works for the advancement of his country is a good citizen. A soldier who fights for his country and may lose his life is a good ...
Abigail Martin of Massac County High School reads her Good Citizens Award essay to the Fort Massac Chapter, National Society of the Daughters of the American Revolution, and guests during the organization's Feb. 24 meeting. Martin's essay was sent on to the district competition.
Spending more time working on your opener is always a good idea. The opening sentence sets the stage for the rest of your piece. The introductory paragraph is what piques the interest of the reader, and it can immediately set your essay apart from the others. 4. Stay on Topic. One of the most important things to remember is to keep to the essay ...