

STAR Method Finally Explained (The Only Guide You Need)
If you’ve ever found yourself in a job interview, wracking your brain to deliver concise yet compelling responses, then this guide is for you.
We’re about to dive deep into the STAR Method – a tried and tested technique that’s your secret weapon to ace any interview.
The STAR method is a structured technique used to answer behavioral interview questions. It stands for Situation, Task, Action, and Result. This approach allows the interviewee to provide clear, concise, and thoughtful answers based on real-life examples from their own experiences.
Let’s dive in and discover how this powerful technique can transform your interviewing skills.
Understanding the STAR Method: The Basics
The STAR method is not just an interview response strategy; it’s a structured approach that helps you present your experiences and skills in a way that leaves a lasting impression on your potential employer.
Here are some key aspects of the STAR method that further illuminate its importance:
- Specificity : The STAR method encourages you to focus on specific situations rather than generalities. This allows interviewers to see exactly how you apply your skills in real-world scenarios.
- Structure : By following the Situation, Task, Action, Result framework, you ensure your responses are organized and coherent. It also ensures you don’t miss out on any critical details.
- Relevance : With STAR, you can tailor your answers to demonstrate how your past experiences directly align with the job requirements.
- Evidence-Based : Rather than simply stating that you have certain skills, the STAR method enables you to provide concrete examples where these skills have been put into action.
However, while the STAR method is an excellent tool for answering behavioral interview questions effectively, it’s not always applicable.
For instance:
- Not all interview questions require a detailed story or example. Some may simply need direct answers.
- In some instances, there might be more emphasis on future actions (e.g., “How would you handle…?”) rather than past situations.
Historical Origins: The Genesis Of The STAR Method

The STAR technique, a renowned method for answering behavioral interview questions, didn’t just appear out of the blue.
Its roots can be traced back to the 1980s when it was developed by psychologists as part of the structured behavioral interview methodology.
The goal was to create an approach that would allow employers to objectively assess a candidate’s potential based on their past experiences and behaviors.
In its early days, the STAR concept was primarily used within large corporations with dedicated human resources departments. These organizations saw value in a standardized approach that could help them sift through numerous applicants while minimizing bias.
Over time, however, the technique gained wider acceptance beyond corporate walls. It started being adopted by small businesses, non-profit organizations, educational institutions, and even individuals preparing for job interviews. Today, it’s considered a gold standard in behavioral interviewing across industries worldwide.
While it has evolved over time with variations like STAR-L (where L stands for Learning), at its core remains the same principle: using past behavior as the best predictor of future performance .
This focus on concrete examples rather than hypothetical scenarios sets it apart from other interviewing techniques and contributes significantly to its ongoing popularity among hiring professionals around the globe.
Breaking Down The STAR Method (A Step-By-Step Guide)

At its core, the STAR method is about storytelling.
It allows you to weave together narratives from your past experiences that not only answer an interviewer’s question but also highlight relevant skills and competencies.
Let’s break down the components:
- Situation : Set the scene
- Task : Define your responsibilities
- Action : Describe what steps you took
- Result : Highlight the outcomes
This four-step framework helps ensure that every example you give during an interview is easy to follow and highlights your abilities effectively.
It’s important to note that while the STAR method may seem straightforward on paper, its real-world application requires practice and finesse.
The aim isn’t just to structure responses but also to deliver them in a compelling manner that resonates with interviewers.
Situation: Defining And Setting The Scene
Diving straight into the first element of the STAR method, let’s explore ‘ Situation ‘.
This is where you set the stage for your story. But don’t just think of it as a simple backdrop; this is your chance to draw your interviewer – into your narrative.
Start by providing context .
What was the environment like? Was it a high-pressure sales team chasing ambitious targets, or an under-resourced non-profit struggling to meet community needs?
Perhaps it was a start-up on the verge of significant expansion, or a well-established corporation navigating a challenging market downturn?
Next, identify any key players involved.
Were there colleagues who played pivotal roles? Or maybe external stakeholders like clients, suppliers, or regulatory bodies that influenced the situation?
Remember, details are crucial here but be careful not to get lost in them.
Your goal is to provide enough information so that anyone listening can understand what you were up against without getting bogged down in unnecessary specifics.
This isn’t just about painting a picture of your past work environment. You’re laying out the particular circumstances surrounding the challenge you faced. So clearly define what made this situation unique or difficult.
For example, instead of saying, “I was working as a project manager at a software company”, add more context : “I was overseeing a critical software development project at XYZ Corp., one of our biggest clients had requested an advanced feature within an extremely tight deadline.”
This gives depth and adds complexity to your situation – showing you weren’t just performing routine tasks but dealing with demanding situations.
Task: Detailing Your Specific Responsibilities
In the STAR method, the ‘Task’ component is where you’ll outline your specific responsibilities in a given situation.
When detailing your task, clarity is crucial. You want the interviewer to understand exactly what was expected of you.
Start by describing any objectives or goals that were set for you at the outset. Were there targets or KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) that you had to meet? Did you have a deadline?
These details help paint a picture of the pressure or challenges involved in your task.
Next, consider any constraints or limitations that might have been present. For instance, did you have limited resources, such as time, budget, or manpower? Were there any particular rules or regulations that needed to be adhered to?
Mentioning these elements can highlight how demanding your task was and set up a compelling narrative for how you overcame these obstacles.
Also crucial in this section is demonstrating an understanding of who benefited from your tasks – whether it was clients, colleagues, stakeholders, or even broader society.
By doing this, not only are you showing awareness of your role within a larger context but also emphasizing its significance.
Avoid being too generic or vague. Instead of saying “I managed a team,” say something like “I was responsible for leading a five-person team tasked with developing a comprehensive marketing strategy within two weeks.” The latter gives more depth and provides a clearer picture of what exactly your task entailed.
Don’t shy away from using industry-specific jargon if it helps illustrate your point better. However, ensure it doesn’t cloud comprehension for those outside your field – balance technical language with layman terms when necessary.
Action: Describing The Steps You Took
Taking action is the critical core of the STAR Method.
It’s where you get to demonstrate your problem-solving skills, initiative, and ability to adapt in real-time situations.
Here’s how you can effectively describe the steps you took:
- Be Specific: Avoid vague descriptions. Instead, delve into the exact steps you undertook to address the situation or task at hand. Did you organize a team meeting? Implement a new software system? Develop a marketing strategy? The more specific, the better.
- Showcase Your Skills: This is your chance to highlight your unique abilities and strengths. Focus on actions that underline key competencies such as leadership, teamwork, creativity, resilience, or strategic thinking.
- Use Active Language: Frame your actions with dynamic verbs like ‘spearheaded’, ‘negotiated’, ‘engineered’, or ‘orchestrated’. This makes your actions more impactful and engaging for the reader.
- Sequence Your Actions: Detailing your actions in chronological order helps provide clarity and paints a vivid picture of how events unfolded.
- Quantify Where Possible: If you can attach numbers or percentages to illustrate your action’s impact – do it! For example: “I led a team of five members,” “We increased sales by 20%,” or “I reduced project delivery time by two weeks.”
- Highlight Challenges Overcome: If any obstacles arose during this phase and you successfully navigated them, be sure to include these details too—it adds depth and demonstrates resilience.
- Include Collaborative Efforts: If your action involved others (e.g., colleagues, stakeholders), mention their involvement to show your ability to work effectively within a team.
Result: Highlighting The Outcomes Of Your Actions
In the STAR method, the Result is your shining moment, your chance to highlight the outcomes of your actions.
The key here is to quantify your success whenever possible. Numbers speak volumes in an interview setting.
Did you increase sales by 20%? Reduce customer complaints by 50%? Or perhaps you streamlined a process that saved 10 hours of work each week? These are powerful statements that can establish you as a problem-solver who gets results.
But what if your result wasn’t quantifiable or didn’t end in absolute success? That’s okay too! What matters is that you show progress, learning, and growth.
Perhaps your action led to improved team morale or better communication within the department. Maybe it paved the way for future improvements or sparked new ideas for innovation.
Remember, not all results have to be earth-shattering successes. Sometimes, they’re stepping stones towards bigger victories down the line.
Another point worth noting is that results should ideally tie back to the company’s goals or values. This shows alignment with their mission and demonstrates how you could contribute if hired.
For instance, if applying for a role in a company known for its customer service excellence, highlighting a result where you resolved a complex client issue and retained their business would resonate well with interviewers.
Lastly, ensure your result answers this question: “What was different because of what I did?” This keeps you focused on showcasing the impact of your actions rather than just listing tasks completed.
Benefits Of Using The STAR Method

The STAR method stands out for a myriad of reasons, offering a multitude of benefits that make it an indispensable tool in your interview arsenal.
- Structured Responses : The STAR method offers a clear framework for detailing your experiences. By organizing your answer into the four key components – Situation, Task, Action, and Result – you give comprehensive insights into your past roles. This not only paints a full picture for the interviewer but also underscores your thorough understanding of your experiences.
- Showcase Soft Skills : Instead of merely narrating events, the STAR method emphasizes how you navigated those events. It lets you highlight vital skills such as problem-solving, leadership, initiative, and creativity—attributes employers are eager to see in potential candidates.
- Promote Specificity : With the STAR method, generic responses won’t cut it. This approach nudges you to share specific instances where you’ve demonstrated pivotal skills or achieved noteworthy results. Detailed answers are not only more memorable but also evidence your capacity to yield real-world results.
- Versatility : Its adaptability is one of the STAR method’s strongest suits. It’s effective in various interview styles, be it behavioral, competency-based, or panel interviews. Whether discussing teamwork, conflict resolution, or project management, the STAR method ensures your answers are always rooted in real-life experiences.
- Enhances Self-Awareness : Regularly using the STAR method encourages introspection. Reflecting on past events—both triumphs and missteps—helps foster a culture of continuous learning and personal growth.
By utilizing the STAR method—you’re not just recounting events; you’re showcasing problem-solving abilities under pressure (Situation), organizational skills (Task), initiative & resourcefulness (Action), and the ability to achieve desired outcomes (Result).
Tips To Craft Your STAR Responses
Crafting your own STAR responses can feel like a daunting task, but with the right strategies and practice, it’s a skill you can master.
Here are some tips and tricks to help you along the way:
- Start with Specifics : The more specific you can be about the situation or task, the better. Vague or generalized descriptions can make it harder for interviewers to understand what you did and why it mattered.
- Action is Key : This is where you get to shine! Detail every step of your action plan – from conception to execution. Show how your actions directly contributed to resolving the situation or completing the task at hand.
- Quantify Your Results : Whenever possible, try to quantify your results. Did you increase sales by 20%? Improve efficiency by 35%? Cut down project delivery time by half? Numbers provide concrete evidence of your achievements.
- Keep It Relevant : Make sure that your STAR response aligns with the job role you’re applying for. If you’re interviewing for a leadership position, highlight situations where you led a team or made crucial decisions.
- Practice Out Loud : This might seem awkward at first, but saying your responses out loud will help them sound more natural during an actual interview.
- Be Honest : Never exaggerate or fabricate elements of your story – honesty is always best in interview scenarios.
- Use Varied Examples : Don’t rely on one experience for all questions; diversify your examples from different areas of work life – projects, teamwork, leadership instances etc.
- Review Job Description : Align examples with key skills/attributes mentioned in job description for maximum impact.
- Think About Lessons Learned : Every experience comes with lessons learned – reflecting on these shows growth mindset and continuous learning attitude which employers value highly.
- Stay Calm & Composed : Interview situations can be stressful, but maintaining a calm and composed demeanor will help you articulate your responses better.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls When Using the STAR Method

For a compelling STAR response, avoid these common mistakes:
- Being too vague : When describing the Situation or Task, many individuals fail to provide enough detail. This leaves interviewers wondering about the context or importance of your actions and results. Avoid this by being specific about what was happening and why it mattered.
- Skipping steps : Each element of STAR is vital for painting a complete picture. Don’t rush through or skip any part of the process—especially Action and Result—as this can leave gaps in your story.
- Focusing on group achievements : While teamwork is important, remember that the goal here is to highlight your skills and contributions. Make sure you’re focusing on what you did, not just your team.
- Neglecting the Result : Some people concentrate so much on the Situation, Task, and Action that they forget to adequately address the Result. Remember, outcomes matter! Be clear about what changed as a result of your actions.
- Over-rehearsing : While practice is important, sounding too rehearsed can come off as insincere or robotic. Keep it natural; let your passion for what you’ve achieved shine through.
- Not aligning with job requirements : Always keep in mind what competencies or qualities the interviewer is looking for and tailor your response accordingly.
- Ignoring non-verbal cues : Body language matters! Maintain eye contact, use open body language, and show enthusiasm through your tone of voice and facial expressions.
- Not learning from past experiences : Use feedback from previous interviews to refine your responses continually.
To avoid these pitfalls:
- Practice crafting detailed yet concise responses.
- Ensure you cover all elements of STAR without neglecting any.
- Highlight personal contributions and achievements.
- Align your responses with the job requirements.
- Pay attention to non-verbal cues.
- Use feedback to improve.
Real-World Examples: STAR Method In Action
Theory is one thing, but practical application is another.
Let’s delve into some real-world examples that illustrate how the STAR method can be employed effectively.
Example 1: A Project Manager Role
Consider a scenario where you’re interviewing for a project manager role and you’re asked, “Can you describe a time when you had to manage a particularly challenging project?”
- Situation : You could start by setting the scene – “At my previous job, I was given the responsibility of managing a project that involved implementing a new software system across all departments.”
- Task : Then, detail your specific responsibilities – “As the Project Manager, it was my duty to ensure smooth coordination between all departments and complete implementation within six months.”
- Action : Next, describe your actions – “I started by conducting meetings with each department head to understand their unique needs. I then created an implementation schedule and assigned tasks to team members based on their expertise. Regular progress meetings were scheduled to address any issues promptly.”
- Result : Finally, highlight the outcomes – “The new software system was successfully implemented across all departments within five months – one month ahead of schedule.”
Example 2: A Customer Service Role
Now imagine you’re interviewing for a customer service position and are asked, “Tell me about a time when you turned around an unhappy customer.”
- Situation : Start by painting the picture – “In my previous role as Customer Service Representative at XYZ Company, I received a call from an irate customer who had received an incorrect product.”
- Task : Detail your responsibilities – “My task was not only to resolve this issue but also to regain the customer’s trust in our company.”
- Action : Describe what steps you took – “I apologized sincerely for our mistake and assured her that we would rectify it immediately. I arranged for express shipping of the correct product along with return postage for the incorrect item. Additionally, I provided a discount code for her next purchase as a gesture of goodwill.”
- Result : Highlight the outcomes – “The customer was appreciative of how we handled the situation and continued to be a loyal customer.”
Adapting STAR For Different Interview Types
The beauty of the STAR technique lies in its universal applicability.
Whether you’re facing a panel, competency-based, behavioral, or even a stress interview, STAR can be your guiding light.
- Panel Interviews : With multiple eyes and ears on you, clarity is crucial. Using the STAR method, structure your answers so that every interviewer grasps your role and its impact. Address each element of your experience, ensuring you resonate with everyone on the panel.
- Competency-Based Interviews : Here, interviewers are seeking proof of specific skills. Lean into the ‘Task’ and ‘Action’ components of STAR. For instance, when discussing leadership, detail a time you led a team, the responsibilities you shouldered, actions you took, and the team’s achievements.
- Behavioral Interviews : These look to past scenarios as indicators of future behavior. Lay out the situation, your role, your actions, and the outcomes using STAR. This structured approach offers a tangible glimpse into your problem-solving and decision-making processes.
- Stress Interviews : While these are designed to see how you fare under pressure, the ‘Action’ component of STAR lets you highlight your adeptness at navigating challenges.
Variations To STAR: STAR-L (With Learning) And Beyond
As you become more comfortable with the STAR method, you may find yourself seeking ways to add depth and nuance to your responses.
One such variation is the STAR-L method, where ‘L’ stands for ‘Learning.’ This model carries you one step further by asking you to reflect on what you learned from the situation.
In this framework, after describing the Situation, Task, Action, and Result (STAR), you elaborate on what Lessons were gleaned from that experience.
This additional step showcases your ability to engage in self-reflection and continuous learning – two assets highly valued in today’s rapidly evolving work environment.
For instance, if your original STAR response was about a project where you led a team through a challenging deadline crunch and achieved success, in the STAR-L method, you might add that the experience taught you about the importance of clear communication or how better planning could have prevented such a tight deadline.
Beyond STAR-L are other variations like STAR-AR (Action-Result) or even SAR (Situation-Action-Result).
These versions are often used when interviewers want more emphasis on actions taken and their direct outcomes rather than focusing too much on context or task details.
The choice between these methods largely depends on the nature of your role and industry.
For example, roles requiring strategic decision-making might benefit more from using STAR-L to highlight learnings from past experiences. In contrast, positions focused on immediate results might prefer SAR or STAR-AR.
Comparing STAR: Differences From PAR (Problem, Action, Result) & CAR (Challenge, Action, Result) Techniques
The STAR method stands distinct from its counterparts – PAR (Problem, Action, Result) and CAR (Challenge, Action, Result).
While they all share a common thread of structuring responses in a clear and concise manner, there are subtle differences that set them apart.
- The STAR method provides a complete narrative by including situational context.
- The PAR method focuses primarily on problem-solving abilities.
- The CAR technique emphasizes resilience in overcoming challenges.
The STAR method is comprehensive in nature as it not only focuses on the problem at hand but also delves into the context or situation that led to it. This enables you to provide a detailed background before explaining your specific role or task. You then proceed to explain your actions and finally emphasize the results achieved.
On the other hand, the PAR technique zeroes in on identifying a Problem first. The focus here is more on problem-solving skills rather than situational context. After identifying a problem, you describe your action taken to resolve it and end with discussing the result. While this approach is direct-to-the-point, it may lack depth without setting up an initial context.
Similarly, the CAR technique begins by outlining a Challenge faced. The emphasis is on overcoming adversity or challenge rather than focusing solely on problem-solving. After describing how you tackled the challenge (Action), you discuss the result achieved.
Incorporating Emotion: The Role Of Feelings In STAR Responses
Incorporating emotion into your STAR responses can be a game-changer.
Emotion, when appropriately expressed, adds a layer of authenticity and relatability that can make your narrative more compelling.
It’s not just about what you did but how you felt while doing it.
Remember that interviews are not just an evaluation of your technical skills or experiences; they’re also about understanding who you are as a person.
Your emotions can indicate passion, dedication, resilience, and empathy – qualities that often define great employees.
When setting the scene in the ‘Situation’ step of STAR, don’t shy away from expressing how the situation made you feel. Were you daunted by the challenge? Excited at the prospect? This helps paint a vivid picture and draws your interviewer into the story.
During the ‘Task’ phase, sharing your emotional state can help showcase your motivation levels and commitment to tackling challenges head-on. Did the task fill you with dread or did it spark determination?
As you move on to ‘Action’, feelings play an integral role in demonstrating your work ethic and character. Were you frustrated when things didn’t go as planned? How did overcoming obstacles make you feel? These details provide depth to your response and highlight personal growth.
Finally, in discussing ‘Results’, emotions can emphasize the significance of your achievements. Was there a sense of relief or accomplishment? Did it boost your confidence or reaffirm your abilities?
However, there’s a delicate balance to strike here. Over-emphasizing emotions might make you come across as overly dramatic or unprofessional.
Keep it genuine and relevant; every emotional reference should serve to enhance understanding of your actions and results.
Pay attention to positive emotions – they leave interviewers with an optimistic impression of both past experiences and potential future performance. Negative emotions aren’t off-limits but frame them as part of learning curves or stepping stones towards success.
Role Of Non-Verbal Cues: Enhancing STAR Responses With Body Language
Non-verbal cues are the unspoken elements of communication that can significantly influence how your STAR responses are perceived.
Here’s how you can harness them effectively:
- Eye Contact : This is a primary indicator of confidence and honesty. As you detail the Situation or Task, direct eye contact shows you’re genuinely recounting your experiences and engaging with the interviewer.
- Posture : Your posture speaks volumes. Sit upright to show attentiveness. As you delve into the Action phase of your STAR response, a slight forward lean can subtly indicate your enthusiasm and engagement.
- Hand Gestures : These can breathe life into your narratives. Used rightly, gestures can make your Actions and Results more tangible. However, moderation is key—ensure your movements are purposeful and not distracting.
- Facial Expressions : They mirror your inner emotions. A genuine, relaxed smile or a thoughtful expression during the Result phase can underscore the positive outcomes of your story.
- Tone of Voice : Though not strictly ‘body language’, it is a pivotal non-verbal cue. Introduce variations in pitch to keep the interviewer engaged.
Remember, consistency between what you say (your STAR responses) and how you say it (your non-verbal cues) is key for effective communication during interviews.
Feedback Mechanisms: How To Refine Your STAR Responses
Feedback is crucial when mastering the STAR method for interviews.
By incorporating diverse feedback mechanisms, you can refine your answers for maximum impact.
Here’s how:
- Self-Evaluation : After practicing, pause and assess. Did you address the Situation, Task, Action, and Result effectively? Were there moments you lost focus? Recognizing your own strengths and pitfalls is the first step to improvement.
- Peer Review : Invite a friend or mentor to listen to your answers. Their external viewpoint can pinpoint areas that need refinement. Ask for feedback on both content and delivery, such as maintaining eye contact and speaking confidently.
- Record and Review : Film yourself during mock interviews. Observing yourself offers insights into non-verbal cues like body language and facial expressions, helping you make necessary adjustments.
- Seek Professional Guidance : A career coach or interview expert can offer seasoned insights, enhancing the depth and delivery of your responses.
- Embrace AI Feedback Tools : Several online platforms now provide AI-driven feedback on aspects like speech clarity, emotional tone, and response coherence. They can be a unique and modern tool in your preparation arsenal.
Refinement doesn’t happen overnight; it’s a gradual process that involves constant practice and willingness to learn from feedback received.
Practice Makes Perfect: Tips For Rehearsing STAR Answers
Naturally, the best way to master the STAR method is through practice.
Here are some strategic tips to guide you in rehearsing your STAR answers.
- Identify Potential Questions: Begin by identifying common interview questions related to your field or role. These questions will serve as a basis for your STAR responses. Look for those that ask about specific situations, tasks, actions, and results.
- Draft Your Responses: Once you’ve identified potential questions, draft your answers using the STAR format. Be specific and detailed in each section—Situation, Task, Action, Result—to paint a clear picture of your experience.
- Use Real-Life Experiences: Make sure to use real-life examples from your past experiences—whether they’re from previous jobs, volunteer work, or even academic projects. This not only makes it easier for you to remember details but also adds authenticity to your response.
- Rehearse Out Loud: Practicing out loud allows you to hear how your responses sound and gives you an opportunity to refine them further. Try practicing in front of a mirror or record yourself for playback; this can help identify any areas of awkwardness or confusion in your delivery.
- Get Feedback: Ask someone—a mentor, colleague or friend—to listen to your responses and provide feedback. They can point out any inconsistencies or gaps in your story that you may have missed.
- Time Yourself: While it’s important to be thorough with your responses, keep in mind that recruiters don’t want overly long answers either. Aim for two minutes per response—a stopwatch can help keep track!
- Adapt and Refine: Based on the feedback received and self-assessment done during rehearsal sessions, adapt and refine your responses until they’re polished and succinct.
- Keep It Fresh: Don’t memorize word-for-word as this can make you sound robotic during interviews; instead understand the key points you want to convey.
Evaluating Success: How Interviewers Assess STAR Responses
Interviewers are adept at assessing STAR responses, and they look for several key elements to gauge the success of your answer.
Understanding these criteria can help you tailor your responses more effectively.
- Relevance: First and foremost, interviewers assess whether the Situation, Task, Action, and Result you present align with the question asked or the competency being evaluated. Your response must be directly relevant to demonstrate that you understand what’s being asked of you.
- Specificity: Vague answers can leave interviewers guessing about your abilities. They prefer specific scenarios that showcase concrete actions taken and tangible results achieved. The more detailed your answer without rambling, the better.
- Action Orientation: Interviewers want to see that you’re a doer. They will evaluate how much of your story focuses on the actions you took versus background details or other people’s contributions.
- Result Impact: Your result should not just be a successful outcome; it should have had a significant impact on your team, project, or organization. Interviewers look for this to gauge how effective and influential you are in your role.
- Consistency: Consistency between what you say and what is known about you from other sources (like references or LinkedIn) adds credibility to your STAR response.
- Behavioral Indicators: Interviewers often use behavioral indicators to understand how likely it is that past behavior will predict future performance in similar situations.
- Non-verbal Cues: Your body language, tone of voice, facial expressions – all these non-verbal cues play a role in how well your STAR response is received.
- Learning Reflections: Some interviewers also appreciate when candidates reflect on their experiences and articulate what they learned from them or how they would improve their approach in future similar scenarios.
In conclusion, mastering the STAR method is not just about acing job interviews.
It’s a powerful tool that enhances your communication skills , helping you to present yourself in the best possible light.
Remember, like any skill, perfecting the STAR method requires practice and patience. Don’t be discouraged by initial challenges; instead, consider them as opportunities for learning and growth.
Use feedback constructively to refine your responses until they truly shine.
And don’t forget the power of non-verbal cues – a confident posture and genuine smile can add a whole new dimension to your story!
The STAR method is more than a technique; it’s a strategy for success. So go ahead – embrace it, and let your star shine bright!
877 Interview Blog Names To Spotlight Your Unique Voice
The Editorial Team at InterviewGuy.com is composed of certified interview coaches, seasoned HR professionals, and industry insiders. With decades of collective expertise and access to an unparalleled database of interview questions, we are dedicated to empowering job seekers. Our content meets real-time industry demands, ensuring readers receive timely, accurate, and actionable advice. We value our readers' insights and encourage feedback, corrections, and questions to maintain the highest level of accuracy and relevance.
Similar Posts

24 Answers To “Why Do You Want To Be A Waitress” (2024)

27 Chick-fil-A Interview Questions (With Perfect Answers)

28 Answers To “Why Do You Want To Work As A Barista”

25 Answers To “Why Do You Want To Be A Bartender”

25 In-N-Out Burger Interview Questions (And Insider Answers)

31 Answers To “Why Do You Want To Work As A Cook” (2024)
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 9 min read
STAR Method
A model approach to nail your next interview.
By the Mind Tools Content Team

"Can you tell me about a time when you…" is a phrase that can strike fear into interviewees. Your mind goes blank, you get flustered and blurt out the first ill-thought-out example that comes to mind.
Fortunately, the STAR Method can prepare you to answer this type of tricky interview question effectively. And, as we'll see, you can also use the framework beyond interviews to help you identify, reflect on, and demonstrate positive behaviors in other areas of your work life.
What Is the STAR Method for Interviews?
STAR stands for Situation, Task, Action and Result . It's a framework developed to prepare for and answer competency-based questions in interviews.
Employers ask behavioral-based questions to understand how you've dealt with issues and challenges in the past – and to predict how you'll likely react to situations in their workplace. They're also used to assess whether you have the skills and knowledge needed for the role.
When you use the STAR Method, you draw from real-life work experiences, and communicate them clearly to your interviewer. Let's look at each step in turn.
The Four-Step STAR Interview Method
Competency-based interviews ask open-ended questions designed to reveal how you approach and overcome workplace challenges. Think of the STAR technique as the structure to tell a story that demonstrates your skills .
- Situation: start by setting the scene for your example. Here, you outline a specific challenge you faced and give the interviewer some context. For example, you could name a project you worked on, where it took place, and the size of your team.
- Task: this is where you explain your role in the situation. Again, give a few brief details. For example, were you the leader? What was your goal? What were you tasked to do?
- Action: now you explain what you did. Be specific and explain how you overcame the challenge. Outline the steps you took to resolve the situation. Even if it was a team effort, explain what you did and lead with "I" instead of "we" to detail your approach.
- Result: finally, summarize the effects of your actions. Mention specific results in your answer, and, if possible, talk about facts, figures and stats that quantify your success. You can also discuss what you learned and share insights that you can apply to future challenges.
How to Answer STAR Interview Questions
Let's look at a STAR Method example, and answer a classic interview question: "Describe a problem that you faced at work – and how you dealt with it."
Situation: "In my last job as a studio manager, two of my designers left just after we landed new business with a big client. Our first deadline was in four weeks!"
Task: "I didn't have time to recruit new designers, given the tight timescale. So, as well as manage the studio, I had to step in and do some of the design work and hold weekly progress updates with the client."
Action: "First, I revised my task list and delegated as many jobs as possible to my studio assistant. For example, they set up job descriptions for the new roles and liaised with recruitment agencies. I also reached out to freelancers I knew, to plug the gaps until we found new hires. With that, and a few late nights, we hit the deadline for our first campaign. It brought in a much-needed $15,000 for that quarter."
Result: "The client loved our work. Now, they account for 40 percent of our business. The situation also taught me to keep a bank of freelancers. I looked into our work culture, too. Exit interviews with the employees who left revealed that they wanted more learning opportunities. So I now take a greater role in making learning and development part of our company culture."
At each stage of the STAR model, career coach Michael Higgins [1] recommends that you:
- Be specific to engage and convince your interviewers.
- Be concise to hold their attention for every question.
- Finish on a positive note to leave a strong impression.
Prepping for Behavioral Interview Questions
Recruiters want to see beyond your resumé to understand how you have behaved in work situations. They're looking for a combination of knowledge, skills, and attributes. These usually fall under common competencies such as teamwork, leadership and decision-making.
You can use the STAR approach to turn your experiences into answers for almost any question that comes your way.
Following the tips below will give you a bank of answers you can turn to.
You'll find examples of typical questions in our article How to Answer Interview Questions .
- Update your CV/resumé using the STAR Method as a guide. This will enable you to create more compelling applications for future jobs, and then better articulate past achievements in an interview. Tell a story that illustrates how you put your training and experience to practical and effective use in the workplace.
- Review the job description and match up your skill sets using the STAR framework, so that you can later illustrate them in the interview. You should also research the company and industry to which you're applying, to help predict the types of challenges they face. Where have you experienced and resolved similar issues?
- Look for the similarities between behavioral interview questions. The wording of questions may be different, but they will be looking for evidence of the same behaviors. For example, with some tweaking, you can apply the same STAR answer to: "Tell me about a time when you had to rely on a team to get things done," and "Think of a time when you worked effectively in a team situation."
- Practice your answers in front of a mirror or get a friend to interview you. That way, talking about your achievements will come more naturally. And you'll learn how to flex and adapt your bank of answers to fit almost any competency-based question.
- Be honest. Don't be tempted to use the STAR Technique dishonestly or to exaggerate your skill level . You'll come unstuck if you're hired and later called on to put those skills into practice.
The STAR Technique for Hiring Managers
Use the following tips to make best use of the STAR method if you are interviewing candidates:
- Match your questions to the role requirements. Spend time considering the competency level and behavioral skill set you want to see. The more specific you are, the more effective your STAR interview questions are likely to be.
- Take a balanced approach. Don't base too much of the interview around the STAR technique. Or you may end up clear about how the candidate might react in certain situations, but have little idea of who they are as an individual.
- Allow for nerves. If a candidate is struggling to answer a STAR interview question, don't be afraid to reframe it slightly. This can encourage them to get over their anxiety, and to better communicate their knowledge and experience.
Looking Beyond STAR Interviews
The ability to reflect on – and articulate – your successes is also useful outside of the interview room. For example:
- Self-reflection. Use the STAR method to help recognize your strengths and weaknesses anytime, to build your confidence and aid in plotting your career. Similarly, a Personal SWOT Analysis identifies opportunities and obstacles in your life, based on your talents. This can point your career in a direction that plays to your strengths and away from your weaknesses.
- Reframing negative thoughts into positive ones. The STAR approach can also be used to create affirmations . And studies by the National Center for Biotechnology Information in the U.S. [2] support the idea that repeating positive statements about your successes will improve your outlook and build your resilience.
- Giving feedback. If you're a manager, coach or mentor, you can use the STAR technique to support people so they can recognize their strengths , boost their confidence and develop themselves.
Infographic
Check out our STAR Treatment infographic .

The STAR Method ( Situation, Task, Action and Result ) is a framework to help you to prepare, reflect on, and answer behavioral interview questions effectively. It's not a tool to memorize "perfect answers." Rather, it's a skeleton key to unlock your strengths and experiences.
If you're a recruiter, understanding the method enables you to uncover the skills, behaviors and knowledge required for a particular role.
Use the STAR Technique at any time to help yourself (and others) to recognize strengths, build confidence and think more positively.
[1] The Guardian. (2014). ‘Using the Star technique to shine at job interviews: a how-to guide’ [Online]. Available here . [Accessed December 18, 2020]
[2] NCBI. (2016). ‘Self-affirmation activates brain systems associated with self-related processing and reward and is reinforced by future orientation’ [Online]. Available here .
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
The star treatment infographic.
Infographic Transcript
Interview Skills
What to Do Before, During and After Your Interview
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Get 20% off your first year of Mind Tools
Our on-demand e-learning resources let you learn at your own pace, fitting seamlessly into your busy workday. Join today and save with our limited time offer!
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Newest Releases

Team Briefings

Pain Points Podcast - Procrastination
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Pain points podcast - starting a new job.
How to Hit the Ground Running!
Pain Points Podcast - Vacations
Taking a Break – and Returning Well to Work
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Centennials.
With Alex Hill
Expert Interviews
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
How to Use the STAR Interview Method to Land a Job

During a job interview , you will probably be asked to tell a story, or prompted to “describe a time when” you encountered a particular situation. The best way to answer these types of questions is to use the STAR method.
What Is the STAR Interview Method?
The STAR method is a guide for how to answer behavioral questions in an interview, and it helps to effectively show your interviewer how you behave in certain situations. The four steps — which form the acronym STAR — are as follows:
- Situation: Set up the scene of the situation and give necessary context.
- Task: Describe your task and responsibilities in the situation.
- Action: Explain the actions and steps you took to complete the task.
- Result: Discuss the results and positive outcomes of your actions.
The STAR method comes in handy, especially for interviewees who aren’t great at thinking on their feet.
“It provides a candidate with a method of communicating a response in an organized method with a focus on behaviors and results,” said Theresa Adams, senior HR knowledge advisor at the Society for Human Resource Management .
How Does the STAR Method Work?
The best STAR interview answers follow each letter of the acronym as a step.
As an example of what STAR looks like in practice, let’s turn to James Durago, director of people operations at FeatureBase (formerly Molecula). Durago used the STAR method when he was interviewing for his job at Molecula. The question posed to him: “When did you have to quickly grow a team and how did you do it?”
1. Set Up the Situation
First, set up the situation at hand. Give the interviewer a clear (but brief) picture of where your example takes place and what was occurring.
Durago’s situation: He had been charged with staffing Google Cloud’s program management five times in a single year to keep pace with business goals and plans.
2. Describe the Task
Describe your main task, objective or goal in the situation, and what your responsibilities entailed.
For this and all elements of STAR answers, interviewers will listen for the amount of detail, for personal accountability and for consistent information, said Adams of SHRM. Blaming or shaming clients, colleagues or other parties in the case of an anecdote relaying a mistake can send up a red flag, as can stories thin on detail or those packed with inconsistencies.
Durago’s task: He was tasked to find and interview thousands of candidates, with the goal of hiring hundreds.
3. Explain How You Took Action
Explain what you did to accomplish your task, and what was significant about the action you chose to carry out. Don’t give a generic overview — it’s worth highlighting any details specific to your action and scenario.
Durago’s action: He talked to others on his team to get a perspective on why the team needed to grow five-fold. He also figured out constraints to hiring, formulated a plan, executed the plan, and iterated as needed.
4. Share the Results
This is the time to not only reveal the result, but share what you learned during the experience and how you might handle it differently.
Remember that stories you tell during an interview need to accomplish two things: Demonstrate your past capabilities and show the value you’ll add in the future. The STAR format is a strategic way to focus your accomplishments into a strong narrative.
Durago’s result: His team grew and met expectations, making for a result that met the challenge Durago was handed.
More on Interview Questions How to Answer ‘Tell Me About Yourself’ In a Job Interview
How to Prepare for an Interview With the STAR Method
Anyone can say that they’re hardworking, responsible or adaptable — but you need to back up your claims with evidence. Instead of listing your qualities and skills , tell a specific story about a time you exemplified them. Doing so will make your interview more memorable and give the employer a glimpse into how you behave in the workplace.
Here’s a few tips for practicing the STAR method and how to best apply it in an interview.
“Do your best to avoid long-winded answers,” said Octavia Goredema , a career coach and author of Prep, Push, Pivot: Essential Career Strategies for Underrepresented Women . Practicing pre-interview so you’re able to share answers confidently and with impact. “Interviewers will listen for relevant examples and details that convey how you solved a problem or overcame a challenge,” Goredema said.
WAIT FOR YOUR CUE
Getting your timing right is as important as choosing the right story. Relying too heavily on the STAR method can make your answers seem unnatural and may signal that you aren’t engaged in the current conversation, which is a turnoff for employers. Don’t leap in to share an anecdote every chance you get. Instead, listen for cues from your interviewer to pick the right moment to share.
“When an interviewer is asking you to give an example of a situation where you had to overcome major obstacles to meet your objectives, the STAR method can be a useful tool in thinking about how to frame your answers and effectively answer their questions,” said Savanna Thompson, vice president of people at 98point6 .
BE AUTHENTIC
An effective workplace story doesn’t have to be one where everything went perfectly. Don’t be afraid to tell stories where mistakes were made or things didn’t go entirely according to plan. Ultimately, the STAR method should show how you generated a positive impact at work and give you a chance to explain what you learned.
SEE INTERVIEWS HOLISTICALLY
“Tell me about a time when…” most likely won’t encompass the entire interview, Goredema said. She recommends making a list of all tough questions (“ where do you see yourself in five years ” and “ why should we hire you ” are among them) and practicing responses.
What Are Behavioral Interview Questions?
Behavioral interview questions gauge how candidates may react in certain work situations. They intend to uncover employee characteristics beyond just hard skills, and can reveal how employees navigate aspects like teamwork, communication, problem solving and stress.
Examples of behavioral questions can include “tell me about a time you led a work project” or “tell me about a time you experienced conflict with a coworker.”
Behavioral questions are one of three widely used interview techniques , Adams said. The others are competency-based, which aims to discover how a person performed in certain situations, and then situational, which asks a candidate how they’d approach a hypothetical situation.
The STAR method is designed to help job seekers formulate clear and compelling answers to behavioral interview questions.
Example STAR Method Questions
Tell me about a time you overcame a difficult challenge .
Situation: “I was just about to go into a board committee meeting when I received some emergency family news.”
Task: “I knew my attention wouldn’t be completely on the meeting, but this meeting had been on the books for months. I had to decide how to handle the situation.”
Action: “I decided that transparency was the best course of action. I went to the meeting and told the board what had happened. I offered to stay at the meeting. The board chair told me I should leave, and she offered to record the meeting so I could listen to it later.”
Result: “I was able to attend to the emergency and the board meeting continued. I listened to the recording during the week and was able to share a few thoughts with the board chair. I felt that trusting them with my news, and that in this case, vulnerability was a desirable leadership quality. The board’s understanding verified my choice.”
Tell Me About a Time You Were Suddenly Given a Leadership Opportunity
Situation: “I had been at my company for about six months when my manager had to take substantial FMLA leave to care for his parents. I was asked if I’d step in as acting manager during the time he was away.”
Task: “My task was to keep my team on track and handle my own workload.”
Action: “Before he left, my manager, his manager and I met to go over the day-to-day aspects of managing our team as well as prioritize projects. Because I was cognizant that I’d have to get my own work done and manage the team, I got permission to place two long-term projects on hold until my manager returned. I then met with my team to devise a weekly plan for meeting deadlines and we set up a weekly 15-minute team meeting, in lieu of formal one-on-ones, to keep us on track. To keep my own work on track, I created a day-by-day plan and stuck to it.”
Result: “Everything ran smoothly during my manager’s time away. I felt proud that I had asked for, and gotten, certain dispensations during his absence; I feel it showed that I understood priorities, for instance handling my own work and keeping the team’s day-to-day work on track, and didn’t try to be a superhero. My manager returned and was happy how things had gone during his absence, and six months later, I received a promotion.”

Describe a Time When a Project of Yours Didn’t Turn Out as Expected
Situation: “My team was asked to onboard a client that had been with the company in the past. The client had left the company because it felt it wasn’t getting proper customer service, but decided to give us a second chance.”
Task: “My task was to onboard and welcome this boomerang client in a way that they would feel that they made the right decision in returning.”
Action: “Before meeting the client, my team, sales and customer service met to figure out exactly what happened during the first go-round, and then outlined clear steps for rectifying those situations. For instance, the client had previously gotten check-in communication from customer service every two weeks; we decided to ask the client if one week would work better. We also decided that the account manager would, situation permitting, fly out to see the client every three months, and also offered the client a three-month free trial of a product we’d just introduced.”
Result: “The client seemed happy and satisfied with our efforts, but still left our company after a few months. In retrospect, maybe we tried too hard to keep them as a client, or perhaps it was just meant to be. In any event, I, my team, and the other teams learned a lot about each other and about client retention tools, so end over end it was a good experience.”
Why Is the STAR Interview Method Effective?
STAR answers form a connection between job candidates and interviewers, said Timothy Golden, a professor in the Lally School of Management at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute . They help demonstrate your merits as a candidate, and also give interviewers a glimpse into how they’d operate as a potential employee.
“The beauty of the STAR method is that you never know what you’ll get,” said Martin Welker, CEO of Zenkit . “The open-ended questions can reveal a wealth of information about the candidate’s potential as an employee as well as how they would fit into the team and company culture .”
That’s especially true for remote interviews . “One of the biggest differences in remote interviews is that the job candidate and the interviewer have the potential to feel psychologically distant from one another,” Golden said. “They feel less psychological closeness because they are spatially distant from each other. Both the job candidate and interviewer should work to psychologically connect with each other, through sharing stories and facial expressions.”
Successful interviews, for both interviewer and candidate, will bridge that separation, and create an environment where the job interview can help both parties to truly understand one another. Where one person walks away with a job offer, and the other rejoices in a fine addition to their staff, it’s a win-win.
How the STAR Method Can Help Alleviate Implicit Bias
Behavioral-based questions produce key insights into a candidate’s competencies, said Elaine Obukhova, Academy of Management Scholar and assistant professor at McGill University in Toronto. Understanding how people have responded to certain past situations can help predict how they’ll respond in the future.
So how can STAR curb implicit bias ? Obukhova offers one example: Chinese-American job candidates, she said, can be stereotypically viewed as competent, but also as “cold” or “lacking leadership potential.” STAR questions can get past that bias because they focus on what people did rather than how they seem.
“People from different backgrounds express themselves differently,” she said. “Interviews that focus on the discovery of ‘fit’ or ‘passion’ often disadvantage people from different cultural and socio-economic backgrounds,” she said. “Asking about strengths and weaknesses will tell interviewers how well-spoken the candidate is, not necessarily reveal competence.”
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the star method.
The STAR method is an interview technique that helps candidates format answers for behavioral questions. STAR stands for situation, task, action and result.
What are examples of STAR questions?
"Tell me about a time you led a project" or "Describe a time when you were under pressure at work: how did you handle it?" are examples of STAR questions.
How long should a STAR method response be?
Between one to four minutes long; approximately a few minutes.
What are the 4 steps in STAR?

Great Companies Need Great People. That's Where We Come In.
How To Master the STAR Method For Interview Questions
Mike Simpson 0 Comments

By Mike Simpson
Updated 6/5/2022.

Job interviews are stressful, especially when faced with the dreaded behavioral-style interview. Behavioral questions help a hiring manager determine if a candidate also has the skills, experience, and traits to do the job effectively. As Monster puts it, it gives hiring managers an “honest glimpse behind the resume.”
That’s why you need an effective approach to create great answers. Luckily, we’re here to teach you about the STAR method and how, with a little preparation, you can provide answers that are on-point.
What Is the STAR Method?
Considering that behavioral interviews are the second-most popular format , having a strategy is essential. That’s where the STAR method comes into play.
In the simplest sense, the STAR interview method is a technique for answering behavioral interview questions. The STAR method interview approach relies heavily on story-telling strategies. You “show” the hiring manager how you’d handle a situation using examples with a clear beginning, middle, and end for the scenario you present.
“STAR” is actually an acronym in this case. Each letter outlines a component of a great answer, effectively giving you a framework to follow when creating responses to behavioral interview questions.
STAR Stands for Situation, Task, Action & Result
So, STAR stands for Situation, Task, Action, Result. Let’s take a second to break down exactly what each letter means.
The “situation” is the initiating event that launched the scenario you’re about to discuss . For example, getting an assignment from a manager is a situation. The same goes for encountering an obstacle. Essentially, you’re setting the stage with the situation part of the strategy.
Think of a situation similar to what the interviewer is asking you about that had a successful outcome. It doesn’t necessarily have to be work-related as long as it’s relevant. Remember to include the who, what, where, when, and how.
The “task” is the aspect of the situation you had to manage . You outline the work that was laid before you, giving the hiring manager insights about your role in the equation.
Describe the task you were responsible for in that situation. Keep it specific but concise. Make sure to highlight any challenges you faced.
The “action” is the part where you describe exactly what you did . How did you complete the task you were assigned? What skills did you use? How did you collaborate with? What traits helped you during the journey?
Remember to focus on skills and characteristics the hiring manager will find desirable, primarily by choosing ones that align with the job and company culture. That way, you come across as a stronger match.
The “result” is functionally a closing to the story . You’re discussing what happened after you were given the task and took action.
Share what the outcome of the situation was and how you specifically contributed to that outcome. What did you accomplish? What did you learn? What were the results of your actions?
When to Use the STAR Method
While there is literally an unlimited amount of possible behavioral questions a hiring manager could ask you, there are several specific categories they all fall into:
- Problem Solving/Planning
- Initiative/Leadership
- Interpersonal Skills/Conflict
- Pressure/Stress
Prior to going in for your interview, make sure you take a hard look at the job you’re applying for and use clues from that to prepare your STAR answers. By picking out what skills the company is specifically looking for or are required for the job, it will help you target your success stories.
Once you have those skills identified, go through your own personal history and background and find success stories that align with those skills.
In fact we we wanted to let you know that we created an amazing free checklist for behavioral questions that covers all the critical info you need when dealing with these tricky types of job interview questions!
Click below to get your free PDF now:
CLICK HERE TO GET THE BEHAVIORAL INTERVIEW CHECKLIST
Common Mistakes While Answering STAR Questions
1. not answering the question at all.
If an interviewer asks you a question and you can’t think of a single specific success story from your past that you can apply to the situation, then tell them that! It’s far better to be honest than make something up.
Of course, this doesn’t mean you get to tell the interviewer to move on to the next question. Instead, you’re going to flip the question back onto yourself and follow up with “…but if I had encountered a situation like that, this is how I would deal with it.”
2. Not being prepared
This one is a no-brainer. Coming up with a story on the spot often means an interviewer is stuck listening to you ramble on and on.
Doing your homework ahead of time means not only will you have your success story prepared, but it will be concise and targeted. We recommend coming up with 3 to 5 success stories that collectively demonstrate a wide variety of common behaviors a hiring manager would be looking for.
3. Being too prepared
Yes, this is possible. You want your story to seem effortless but not so rehearsed as to be robotic. Review your answers before you go in for your interview, but don’t overdo it. Keep it light and conversational rather than rehearsing a story you have practiced word-for-word.
4. Telling a story that is anything but a success
You want the job, right? So why would you tell a story where you fail miserably and learn absolutely nothing from the experience? While it might be a funny story overall, it’s not one that’s going to get you a job.
Telling a story that has absolutely no positive outcome, either from the final results or the lessons you learned, hurts your chances of getting hired; it’s that simple.
5. Telling a story that has nothing to do with the question asked
This goes along with being prepared. Telling a story that is unrelated to the question demonstrates to a hiring manager that you lack focus and attention to detail, two key qualities that every good candidate should possess.
6. Telling a story that makes you seem like an unrealistic superhero
Don’t tell a story where you are “the only employee doing anything right ever.” Nobody is absolutely perfect, and telling a story where you singlehandedly saved the entire company isn’t going to just come off as impossible; it’s going to come off as fiction.
Top 5 Tips for Getting the Most Out of STAR
So, now that you know what you are not supposed to do, let’s focus on what you do need to do to get the most out of the STAR method interview questions.
1. Be prepared
I know we said this above, but it really is a necessity for answering STAR interview questions. Going in with a solid set of targeted success stories will not only make answering them easier for you but will help you highlight to the hiring manager the specific qualities and skills that make you perfect for the position and set you apart from the other candidates.
2. Be specific
The STAR Method is not about being vague and wishy-washy. This goes hand in hand with being prepared. Prior to your interview, you should have identified the skills and qualities the company is looking for. Make sure your stories are specific and targeted. Remember, you need to highlight the behavior that the hiring manager is interested in, and your success story should clearly align with that.
Being vague or general will not only make it difficult for the hiring manager to properly evaluate you, but it will dilute the impact of your success story.
3. Be quantitative
This is very important. Hiring Managers absolutely LOVE numbers, so have solid, tangible results to back up your stories. Did you increase sales for your department by 58% ? Did your actions make your team 89% more efficient? Back up your successes with hard facts and numbers wherever possible.
4. Be concise
Keep your stories short, sweet, and targeted. No extra info or boring details that are irrelevant to the specific question. By embracing brevity, your answers can be more impactful, particularly if you touch on each of the points that make the STAR method of interviewing what it is.
5. Be honest
The last thing you want to do is dazzle your interviewer with a story that isn’t 100% true. Not only do you undermine your credibility down the road if they find out you weren’t honest, but it calls into question their ability to trust you overall…and nobody wants to hire someone they don’t trust.
Example Question and Answer Breakdown
Now that we’ve gone over all this, let’s put it into practice with an example behavioral question and a STAR method interview answer, focusing on problem-solving and initiative with the response.
“Can you tell me about a time you went above and beyond your expected duties?”
Situation : “I was a part of a team working on a presentation meant to help us secure a major new client for our company. The weather was bad, and as a result, my supervisor got caught in a snowstorm and was unable to make it back in time. It looked like we were going to have to cancel the meeting and potentially lose the client.”
Task : “I had been looking for ways to take on more responsibility, so I volunteered to finish up the presentation.”
Action : “I worked with my supervisor via the phone, and between the two of us, we were able to go ahead with the scheduled meeting.”
Result : “As a result of my initiative, we not only landed the client but I was also recommended for a promotion.”
Here’s another question.
“Tell me about a time when you took the lead on a difficult project?”
Here’s our answer broken into the STAR Method. The quality we are highlighting is Leadership:

STAR Method Interview Questions and Answers
While the options above show you how to break down the answers when you use the interview STAR method, having a few more STAR method examples can help you see how the answers flow once they’re together. Here are a few more STAR interview questions and answers to get you headed in the right direction.
1. Can you tell me about a time you were in a stressful situation and how you handled it?
EXAMPLE ANSWER:
“In my last role, a coworker that was handling a large project for a critical client experienced a medical emergency, taking them out of the office unexpectedly for a significant period. The deadline for their project was looming, and there was no way they’d be back in time to handle it.
“My manager reached out and asked me to take over the project. At this point, there was the equivalent of five days’ worth of work and just three days to get it done. The pressure was significant.
“I began by familiarizing myself with the project requirements, as I didn’t have an in-depth understanding initially. Next, I broke down the remaining tasks into micro-goals, creating a functional roadmap for success. Then, I blocked out each responsibility on my calendar. As I did, I determined that overtime would be necessary, so I quickly secured the needed approval using my plan to outline why it was essential.
“After that, I took a deep breath and got to work. Additionally, I engaged with colleagues to expedite various pieces, such as supporting critical data, allowing me to remain focused. While it was a difficult undertaking, the project was ultimately a success. I completed the work with two hours to spare, and the client was thrilled with the end result.”
2. As a team leader, how do you handle conflict? Tell me about a time when you experienced conflict and what you did to resolve it.
“When I’m overseeing a team, I find that communication and compromise are keys to mitigating conflict. In my current job, I was working with a multi-disciplinary project team to create a new application for a client. There was a debate about the best way to design a particular interface, with two team members having different perspectives based on their unique professional expertise.
“While the conflict could have delayed the project, I acted quickly to ensure that didn’t happen. I met with each team member one-on-one to learn more about their perspective. Along the way, I discovered that one team member didn’t inherently dislike the other’s idea; it was that the approach wasn’t possible based on the technologies used.
“Once I learned that detail, I brought the two colleagues together to oversee a discussion. I outlined the technical constraint, ensuring the other team member knew that was the only reason their colleague didn’t want to move forward with their idea. Then, I worked with them to find a similar solution that was feasible, creating a functional compromise.”
3. Tell me about a time you made a mistake at work
“In my last position, I was responsible for hiring seasonal workers for the first time. We needed to bring in more than a dozen short-term hires and had very little time to do so. While I was meeting with a candidate, it seemed like they had all of the necessary technical ability. However, I ignored a red flag – namely, a negative attitude about training – assuming that their existing skills would make it a non-issue.
“When they came on board, it was clear that their mindset would hinder them from reaching full productivity quickly. Additionally, their attitude negatively impacted other new hires that were taking part in initial training.
“Ultimately, that new hire had to be let go and replaced, which wasn’t ideal. However, it taught me the importance of not overlooking mindset and attitude when choosing candidates. As a result, my subsequent hiring decisions were much better fits, resulting in higher productivity and better retention.”
4. Have you ever had to work with someone you didn’t like? How did you handle that?
“In my last job, I was assigned to a project with a colleague with a work style that didn’t mesh well with mine. I’m generally a planner, and I like to outline my responsibilities in advance, divvying out tasks fairly to make them manageable and easier to track. My colleague favored a more organic approach, essentially deciding what to tackle next as they completed the previous task.
“In the end, this led to a disagreement about how to proceed. However, instead of digging in, I figured there had to be a reasonable compromise. I sat down with them and explained why I favored a planned approach and asked them to let me know why they preferred theirs. Ultimately, I learned that over-planning made them feel constrained, which hampered their creativity.
“With that knowledge, I proposed a solution. We would create a general framework for the entire project, using it as a joint roadmap. Then, as we moved forward, we would take ownership of tasks as needed. That gave them space while giving me structure, allowing us to complete the work on time.”
5. How do you handle setting goals? Can you give an example?
“Generally, I find that goals are beneficial when I need to stay on target. In my last job, I used goal-setting to enhance my personal performance. Initially, I was meeting expectations as a sales professional, but I wanted to exceed them.
“I began by outlining my sales numbers, letting me know where I currently sat. Next, I choose a target, aiming for a 10 percent increase in three months. Then, I broke down what I’d need to do each day to make that happen, such as conducting a specific number of calls or securing a particular number of qualified leads.
“After that, I used the information to create mini-goals for my time. This gave me a functional to-do list that guided me toward success. Ultimately, I was able to reach by target two weeks early, and by continuing with that strategy, achieved a 25 percent increase by the end of six months.”
Putting It All Together
So, the next time you’re meeting with a hiring manager and they ask you a behavioral question, don’t panic. With the STAR method for interviews, you’re prepared. Use the information above to your advantage, ensuring you can create your own amazing responses and stand out from the competition.
FREE : Behavioral Interview Questions PDF Checklist
Ok the next thing you should do is download our handy "Behavioral Interview Questions Checklist PDF ".
In it you'll get 25 common behavioral questions along with tips on how to answer them with the STAR METHOD and the traps you need to avoid ....
All in a beautifully designed pdf Jeff spent hours working on. ---- He made me put that in 😉

Co-Founder and CEO of TheInterviewGuys.com. Mike is a job interview and career expert and the head writer at TheInterviewGuys.com.
His advice and insights have been shared and featured by publications such as Forbes , Entrepreneur , CNBC and more as well as educational institutions such as the University of Michigan , Penn State , Northeastern and others.
Learn more about The Interview Guys on our About Us page .
About The Author
Mike simpson.

Co-Founder and CEO of TheInterviewGuys.com. Mike is a job interview and career expert and the head writer at TheInterviewGuys.com. His advice and insights have been shared and featured by publications such as Forbes , Entrepreneur , CNBC and more as well as educational institutions such as the University of Michigan , Penn State , Northeastern and others. Learn more about The Interview Guys on our About Us page .
Copyright © 2024 · TheInterviewguys.com · All Rights Reserved
- Our Products
- Case Studies
- Interview Questions
- Jobs Articles
- Members Login
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Career Planning
- Finding a Job
- Interview Strategies
How to Use the STAR Interview Response Method
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/ADHeadshot-Cropped-b80e40469d5b4852a68f94ad69d6e8bd.jpg)
STAR: Situation, Task, Action, Result
What is the star interview response method, star key concepts, how to prepare for an interview using star, examples of interview questions and answers using star, frequently asked questions (faqs).
Are job interviews challenging for you? Do you struggle to give concise answers to interview questions? Are you unsure how to share your accomplishments during an interview without sounding boastful? What's the best way to let the interviewer know that you're the right candidate for the job?
The STAR interview response method can help make the process easier. Using this method of answering interview questions allows you to share concrete examples of how you successfully handled situations at work to show that you possess the experience and skills required for the job you’re interviewing for.
Read below for a detailed description of the STAR interview response technique and examples of how to best use it.
Key Takeaways
- STAR stands for situation, task, action, result.
- Each concept in the STAR acronym is a step that candidates can use to respond to interview questions.
- By following all four steps, applicants can provide comprehensive answers to interview questions.
STAR stands for S ituation, T ask, A ction, R esult. Using this strategy is particularly helpful in response to competency-focused questions , which typically start with phrases such as, "Describe a time when..." or, "Share an example of a situation where...."
Jon Marchione / The Balance
The STAR interview response method is a way of answering behavioral interview questions. Behavioral interview questions are questions about how you have behaved in the past. Specifically, they are about how you have handled certain work situations.
Employers using this technique analyze jobs and define the skills and qualities that high-level performers have exhibited in that job. Since past performance can be a good predictor of the future, interviewers ask these questions to determine whether candidates have the skills and experiences required to excel in the job.
For example, employers might be looking for proof of problem-solving skills, analytical ability, creativity, perseverance through failure, writing skills, presentation skills, teamwork orientation, persuasive skills, quantitative skills, or accuracy.
Examples of behavioral interview questions include the following:
- Tell me about an occasion when you had to complete a task under a tight deadline.
- Have you ever gone above and beyond the call of duty?
- What do you do when a team member refuses to complete his or her quota of the work?
Some interviewers structure their questions using the STAR technique. However, job seekers can also use the STAR interview method to prepare for behavioral interview questions.
STAR is an acronym for four key concepts. Each concept is a step the job candidate can take when answering a behavioral interview question. By following all four steps, the job candidate will provide a comprehensive answer. The four steps referenced in the acronym are the following:
Situation: Describe the context within which you performed a job or faced a challenge at work. For example, perhaps you were working on a group project, or you had a conflict with a co-worker. This situation can be drawn from a work experience, a volunteer position, or any other relevant event. Be as specific as possible.
Task: Next, describe your responsibility in that situation. Perhaps you had to help your group complete a project within a tight deadline, resolve a conflict with a co-worker, or hit a sales target.
Action: You then describe how you completed the task or endeavored to meet the challenge. Focus on what you did rather than what your team, boss, or co-worker did.
Instead of saying, "We did XYZ," say, "I did XYZ.")
Result: Finally, explain the outcomes or results generated by the action taken. It may be helpful to emphasize what you accomplished or what you learned.
Since you won’t know in advance what interviewing techniques your interviewer will be using, you’ll benefit from preparing several scenarios from the jobs you’ve held.
Make a list of the job qualifications. First, make a list of the skills and/or experiences that are required for the job you're applying for. It may help to look at the job listing and similar job listings for indications of the required or preferred skills/qualities. You can then match your qualifications to those listed in the posting .
Create a list of examples. Then, consider specific examples of occasions when you displayed those skills. For each example, name the situation, task, action, and result .
Match your skills to the job. Whatever examples you select, make sure they are as closely related to the job you’re interviewing for as possible.
Prepare a response. For each example, prepare a brief response:
- Describe the situation (2-3 sentences).
- Explain your task (1-2 sentences).
- Describe the action you took (2-3 sentences).
- Share your result (2-3 sentences).
You can also take a look at common behavioral interview questions and try answering each of them using the STAR technique.
Tell me about a time you had to complete a task within a tight deadline. Describe the situation and explain how you handled it.
Example answer.
While I typically like to plan out my work in stages and complete it piece by piece, I can also achieve high-quality work results under tight deadlines. Once, at a former company, an employee left days before the deadline of one of his projects. I was asked to assume responsibility for it, with only a few days to learn about and complete the project. I created a task force and delegated work, and we all completed the assignment with a day to spare. In fact, I believe I thrive when working under tight deadlines.
What do you do when a team member doesn't complete their share of the work?
When there are team conflicts or issues, I always try my best to step up as team leader if needed. I think my communication skills make me an effective leader and moderator. For example, one time, when I was working on a team project, two of the team members got embroiled in an argument, both refusing to complete their assignments. They were both dissatisfied with their workloads, so I arranged a team meeting in which we reallocated all the assignments among the team members. This made everyone happier and more productive, and our project was a success.
Tell me about a time you showed initiative on the job.
Last winter, I was acting as an account coordinator, supporting the account executive for a major client at an ad agency. The account executive had an accident and was sidelined three weeks before a major campaign pitch.
I volunteered to fill in and orchestrate the presentation by coordinating the input of the creative and media teams. I called an emergency meeting and facilitated a discussion about ad scenarios, media plans, and the roles of various team members in relation to the presentation.
I was able to achieve a consensus on two priority ad concepts that we had to pitch and on related media strategies. I drew up a minute-by-minute plan of how we would present the pitch. Based on our discussions, the plan was warmly received by the team. The client loved our plan and adopted the campaign. I was promoted to account executive six months later.
How can you share examples of your achievements during a job interview?
One of the best ways to share your accomplishments with an interviewer is by telling a story . When answering questions, share a description of what you did and how you achieved a positive outcome. This way, you’re showing the interviewer what you’re able to do rather than just telling them you can do the job.
What can you do when you can’t think of an answer to an interview question?
When you’re asked a challenging question, use the STAR interview technique to respond. Think of something you did at work related to the question, then explain how you handled the situation and what the outcome was.
MIT.edu. “ Using The STAR Method for Your Next Behavioral Interview .”
CareerOneStop. “ Types of Interviews .”
Case.edu. " STAR Strategy Examples ."
The University of New Mexico. “ STAR Method Interview Prep .”
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Using the Star technique to shine at job interviews: a how-to guide
Here’s our guide to using the Star technique when answering questions in competency-based job interviews
- Looking for a job? Explore the range of vacancies on Guardian Jobs and find the perfect role for you
There are many types of interviews, from the free flowing to the formal, but one that you are likely to come up against at some point is the competency-based interview.
They’re designed to make the job application process as objective as possible, removing any conscious or subconscious bias by the interviewer by asking each candidate the same questions. Some people feel this type of interview is more stilted – there can be less opportunity to build rapport. However, they are very common, especially in large organisations and the public sector, so it’s worth refining your technique.
The questions will be driven by a competency framework that’s required for the job. For example, a marketing executive may require problem-solving skills, or a job in customer services may require conflict management skills.
The interview questions tend to start with a variation of, “Tell me about a time when…” This may sound simple but, in the heat of the interview, it’s easy to give an unstructured answer, miss out key details, or let the story peter to a halt.
One way of avoiding this is by using the Star acronym to structure your response. Here are two examples of how to implement the technique:
A candidate for a marketing executive role might be asked: “Tell me about a time that you solved a problem to a tight timescale.” Here’s how you could structure your response:
S ituation – set the context for your story. For example, “We were due to be delivering a presentation to a group of 30 interested industry players on our new product and Stuart, the guy due to deliver it, got stuck on a train from Birmingham.”
T ask – what was required of you. For example, “It was my responsibility to find an alternative so it didn’t reflect badly on the company and we didn’t waste the opportunity.”
A ctivity – what you actually did. For example, “I spoke to the event organisers to find out if they could change the running order. They agreed so we bought ourselves some time. I contacted Susan, another member of the team, who at a push could step in. She agreed to drop what she was doing and head to the event.”
R esult – how well the situation played out. For example, “Stuart didn’t make the meeting on time but we explained the problem to the delegates and Susan’s presentation went well – a bit rough around the edges but it was warmly received. Stuart managed to get there for the last 15 minutes to answer questions. As a result we gained some good contacts, at least two of which we converted into paying clients.”
There are a few things to note with this response: it’s important to speak in specific rather than general terms and quantify your success. In this example, we mentioned 30 delegates, the names of the people involved and quantified two contacts converted to clients. From a listener’s perspective, this makes the story more interesting and they are more able to gauge your success. Nameless figures and undefined successes can make the answer less feel less convincing. Secondly, as there are likely to be many questions and interviewers have short attention spans, it’s important to keep your answers concise: convey the maximum achievement in the minimum time. Finally, it’s important to finish on a positive note so the overall impression is strong.
In a second example, a candidate for a customer services role is asked: “Describe a situation when you had to deliver excellent customer service following a complaint”
S ituation: “A customer rang up complaining that they’d waited more than two weeks for a reply from our sales team regarding a product query.”
T ask: “I needed to address the client’s immediate query and find out what went wrong in the normal process.”
A ctivity: “I apologised, got the details and passed them to our head salesperson, who contacted the client within the hour. I investigated why the query hadn’t been answered. I discovered that it was a combination of a wrong mobile number and a generic email address that wasn’t being checked. I let the client know and we offered a goodwill discount on her next order.”
R esult: “The client not only continued to order from us but posted a positive customer service tweet.”
Used at its best, the Star structure is invisible to the listener and it simply comes across as a well-articulated example. Create a bank of answers in this format in advance, so don’t struggle to do it on the day and can make it appear as seamless as possible.
Michael Higgins is a career coach at This is My Path and is author of Pit Stop: A Career Workbook for Busy People .
Looking for a job? Browse Guardian Jobs for your next career step.
- Guardian Careers
- The Careers Blog
- Applications
- Work & careers
Comments (…)
Most viewed.
- DACA/Undocumented
- First Generation, Low Income
- International Students
- Students of Color
- Students with disabilities
- Undergraduate Students
- Master’s Students
- PhD Students
- Faculty/Staff
- Family/Supporters
- Career Fairs
- Post Jobs, Internships, Fellowships
- Build your Brand at MIT
- Recruiting Guidelines and Resources
- Connect with Us
- Career Advising
- Distinguished Fellowships
- Employer Relations
- Graduate Student Professional Development
- Prehealth Advising
- Student Leadership Opportunities
- Academia & Education
- Architecture, Planning, & Design
- Arts, Communications, & Media
- Business, Finance, & Fintech
- Computing & Computer Technology
- Data Science
- Energy, Environment, & Sustainability
- Life Sciences, Biotech, & Pharma
- Manufacturing & Transportation
- Health & Medical Professions
- Social Impact, Policy, & Law
- Getting Started & Handshake 101
- Exploring careers
- Networking & Informational Interviews
- Connecting with employers
- Resumes, cover letters, portfolios, & CVs
- Finding a Job or Internship
- Post-Graduate and Summer Outcomes
- Professional Development Competencies
- Preparing for Graduate & Professional Schools
- Preparing for Medical / Health Profession Schools
- Interviewing
- New jobs & career transitions
- Career Prep and Development Programs
- Employer Events
- Outside Events for Career and Professional Development
- Events Calendar
- Career Services Workshop Requests
- Early Career Advisory Board
- Peer Career Advisors
- Student Staff
- Mission, Vision, Values and Diversity Commitments
- News and Reports

Using the STAR method for your next behavioral interview (worksheet included)
- Share This: Share Using the STAR method for your next behavioral interview (worksheet included) on Facebook Share Using the STAR method for your next behavioral interview (worksheet included) on LinkedIn Share Using the STAR method for your next behavioral interview (worksheet included) on X
The purpose of behavioral interviewing is to objectively measure a potential employee’s past behaviors as a predictor of future results. In behavioral interviews, candidates are asked to give specific examples of when they demonstrated particular behaviors or skills. Here are some example behavioral interview questions:
- Tell me about a time when you worked as part of a team to successfully execute a project.
- Do you have any experience with solving complex problems?
- What is a project that you are most proud of?
- Tell me about a time you failed.
You may notice that a couple of these questions are close-ended, meaning that in a normal every-day conversation you may respond with a simple “yes” or “no.” In a behavioral interview, it is important to practice a “yes, and…” mentality. In other words, provide context for your interviewer with an example that can help you demonstrate the depth of your skills and knowledge.
Interview Tips
When preparing your responses for a behavioral interview, you will also want to keep in mind the following:
- Focus your responses on actual behaviors and emotions. It can be tempting to say what you think will help you get the job, but bending the truth in a job interview can be risky. What you say, if not truthful, can come across as disingenuous to an interviewer, and may not match up with your application materials ( resume, CV, cover letter ) or what a referral has shared about you.
- Describe your role in past situations. When it comes to sharing your experiences with a potential employer, it is important to show ownership of accomplishments by using “I” statements. This can be especially tricky when giving examples of teamwork or collaboration, but using “we” statements can make it difficult for an employer to have a clear understanding of what your skills are. Instead, focus your response on how you contributed to the outcomes of the team efforts.
- Provide specific examples of your actions. Avoid giving answers that are too generalized. When responding to behavioral interview questions, it is important to share specific and clear examples that can give your interviewer insight to your potential as a candidate.
- Reveal your skills related to the job. Your interviewer will prepare questions that will relate directly to the responsibilities of the role. For example, if the target role requires supervision of others or working in a team-based environment, you may be asked to share examples of times when you demonstrated effective leadership or collaboration. If you are asked to share your strengths, refer to the job description to hone in on what skills are important to the role. The ability to communicate effectively, work well with others, and think creatively are a few common descriptors used in internship postings.
The STAR method
S.T.A.R. is a useful acronym and an effective formula for structuring your behavioral interview response. Let’s start by breaking down the formula:
- Situation (20%), explain the situation so that your interviewer understands the context of your example, they do not need to know every detail!
- Task (10%), talk about the task that you took responsibility for completing or the goal of your efforts.
- Action (60%), describe the actions that you personally took to complete the task or reach the end goal. Highlight skills or character traits addressed in the question.
- Result (10%), explain the positive outcomes or results generated by your actions or efforts. Here, it is important to highlight quantifiable results. You may also want to emphasize what you learned from the experience or your key takeaways.
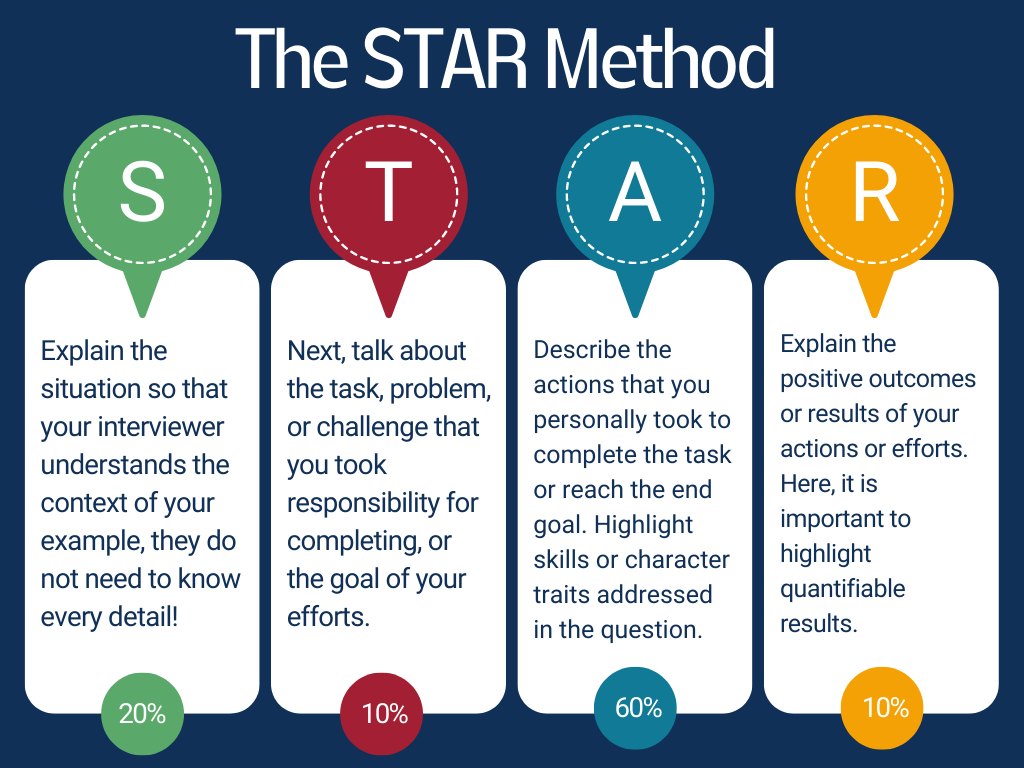
The percentages listed in the graphic above represent the time to dedicate to each section of your story. These numbers are meant to guide you, but don’t worry about getting it exactly right! The most important thing to keep in mind is that most of your response should focus on your A ctions.
Sample response
Here is an example STAR-formatted response for the prompt, “tell me about a time when you demonstrated leadership.” Instead of responding simply with “I tutored kids in math,” provide context for your interviewer and demonstrate your skills through an engaging example.
- Situation: When I was a junior in high school, there were several students in my math class who were struggling with some of the more difficult concepts.
- Task: With an upcoming national exam, I was asked by my math teacher to start an after school session to assist the other students.
- Action: I stayed after school twice a week to review class materials and homework. I created a comprehensive study guide. I demonstrated the best methods for solving difficult problems, explained strategies that worked for me, and developed new problems to help them practice.
- Result: Our class average for the national exam was the highest it had been in over ten years, and overall the students I helped were able to develop a better understanding and appreciation for math.

Preparing your responses
When preparing examples to share in an interview, it can feel overwhelming and unrealistic to predict and prepare responses for all questions that may (or may not) come up. While the example shared above was in response to a question about leadership, it could also be adapted to questions regarding communication skills, work ethic, and time management/organization. Consider how the examples you prepare may connect to one or more question, and prepare to adapt your responses on the fly.
Start by identifying both technical and transferable skills needed within a particular role. Review the job description and role responsibilities, paying close attention to the usage and frequency of certain action verbs. Depending on the size and age of a company, you can also use Glassdoor Interview Reviews to learn about others’ experiences and find potential interview questions. Prepare 3-5 stories by creating a bulleted outline or jotting down notes using CAPD’s STAR method worksheet . It can be tempting to script or memorize certain stories, but doing so may limit your ability to adapt as needed in an interview, and can seem unnatural or disingenuous to an interviewer.
Want to learn more as you prepare? Here are more interview tips .
Time to practice
Ready to start practicing? Schedule a behavioral mock interview with a CAPD staff member to practice your responses, receive feedback, and gain confidence before the real thing. With MIT’s Alumni Advisors Hub , you may be able to find alum from your target company who are willing to provide insight and conduct behavioral mock interviews, as well as coding or technical question prep. You can also use LinkedIn’s Interview Prep tool to receive instantaneous, AI-powered feedback on pacing, how many times you’re using filler words, and sensitive phrases to avoid.
After the interview
Take some time to reflect. What went well? What could go better next time? Jot down some notes to celebrate your wins and to help yourself prepare for future interviews.
Lastly you’ll want to email to your interviewer(s) within 24 hours to thank them for their time and reiterate your interest and excitement for the role. If you spoke with multiple interviewers, consider emailing each one individually. It doesn’t hurt to include some reasons why you think you’d be a great fit, and mention anything worth noting or revisiting from the interview. Our professional correspondence samples can help you to get started.
Explore Jobs
- Jobs Near Me
- Remote Jobs
- Full Time Jobs
- Part Time Jobs
- Entry Level Jobs
- Work From Home Jobs
Find Specific Jobs
- $15 Per Hour Jobs
- $20 Per Hour Jobs
- Hiring Immediately Jobs
- High School Jobs
- H1b Visa Jobs
Explore Careers
- Business And Financial
- Architecture And Engineering
- Computer And Mathematical
Explore Professions
- What They Do
- Certifications
- Demographics
Best Companies
- Health Care
- Fortune 500
Explore Companies
- CEO And Executies
- Resume Builder
- Career Advice
- Explore Majors
- Questions And Answers
- Interview Questions
How To Use The STAR Method In A Job Interview (With Examples)
- Interview Preparation Checklist
- Star Method For Answering Questions
- Star Interview Questions
- Words To Use In An Interview
- Mock Interview Preparation
- How To Make A Good Impression
- Bring Writing Samples
- How To Relax Before An Interview
- Interview Coaching
- Common Video Interview Mistakes
- Common Phone Interview Mistakes
- How To Ace Your Interview For A Remote Job
- Good Weaknesses For A Job Interview
- Good Strengths For A Job Interview
- Talk About Being Laid Off
- How To Prepare For A Phone Interview
- How To Decline An Interview
- How Early Should You Arrive For An Interview
Find a Job You Really Want In
Using the STAR method when answering interview questions can help you impress your interviewer and help you land the job. The STAR method helps you answer behavioral and situational interview questions so it’s important to know how to use it.
If you have an interview coming up and want to use this method in your answers, we’ll go over how to use the STAR method in a job interview, provide some example answers using this method, and we’ll go over some mistakes to avoid when answering.
Key Takeaways:
STAR stands for Situation, Task, Action, Result.
The STAR method is an efficient and effective way to highlight your skills through experience when answering interview questions.
The STAR method is particularly useful for behavioral questions as well as certain situational questions.
Be as specific as possible in your answers to make the most of the STAR method.
How to use the STAR method when answering interview questions
Example questions and answers using the star method, 14 common behavioral interview questions that require the star method, how to prepare for an interview using the star method, common star method mistakes to avoid, situational interview questions and the star method, star method faq.
- Sign Up For More Advice and Jobs
STAR stands for Situation, Task, Action, Result. The STAR method can help you stay on track and answer behavioral interview questions quickly and thoroughly. Here is a breakdown of each step:
Situation. Set the scene for your story — discuss who was involved and what was going on. Your answer won’t work unless you can come up with an appropriate anecdote to discuss. Make sure you really listen to the interviewer’s question so you don’t start telling an irrelevant story.
Here is an example of how your answer should look:
“In my last role, my team and I were facing a significant challenge with declining customer satisfaction scores. We were tasked with finding a solution to improve these scores and retail more customers.”
Task. Next, state what your responsibility was in this situation. It might have been a task you were given or an initiative you took on your own. Often, you can combine the situation and task to fit in one sentence.
“My task was to identify and implement strategies that would lead to a measurable increase in customer satisfaction within a three-month period.”
Action. This is the meat of your answer. Discuss what actions you took along with your thought process and reason for choosing that approach. Make that your direct impact is obvious in the context of the story.
“I decided to propose a new customer feedback system that would allow us to gather real-time feedback and identify areas of improvement. To do this I gathered information and collected data to support my proposal. I also scheduled one-on-one meetings with team members and I addressed any of their concerns and listened to their feedback. I also made sure to keep open communication and provide regular updates throughout the process.”
Result. Wrap up your story with a positive result that clearly shows how your actions created a better situation. Even if the question is about a negative topic, like making a mistake, be sure to finish with positivity — lessons learned and improvements made since then.
“As a result of these efforts, we were able to implement the new customer feedback which led to a 25% increase in customer satisfaction scores within the first three months.”
Answering behavioral or situation questions with the STAR method will help you keep your responses focused and give the interviewer the information they’re looking for in a concise way. Think of STAR as a framework that you can use to stay on track and ease the nervousness of not knowing what to say in an interview.
Here are some common behavioral interview questions with example answers using the STAR method to help you get an understanding of how to answering using it:
Tell me about a time you made a mistake . How did you fix the situation?
Situation: At the beginning of my career I was responsible for collecting the week’s sales figures from sales team leaders and compiling them for my supervisor . One week, I forgot to get figures from a few of the teams, resulting in skewed data to present to my supervisor. Task: I had to fix the situation quickly before my supervisor’s big monthly meeting so she could accurately present the company’s sales figures. Action: I quickly called, emailed, and checked in on all the sales team leaders to make sure I had all of the correct information. I had to track down one team leader who was out of the office for the day, but luckily his assistant knew the figures for the week. Result: I was able to remedy my mistake within an hour and provide my supervisor with all the correct data in time for her meeting.
Can you tell me about a time when you boosted monthly sales figures for your team?
Situation: I led a sales team at my previous company and I was responsible for making sure we reached the sales goals my supervisor set. Task: We were meeting our goals, but I wanted to surpass the expectations so I implemented a “check back” policy. Action: I asked everyone on my team to begin checking back with leads that went cold. We began reaching back out to people who asked for more information about our services but never followed up. Result: We were able to convert 50% of those dead leads just by checking back in and seeing if the customer wanted to resume our conversation, bringing us $15,000 above our usual sales goal for the month.
When have you demonstrated leadership skills?
Situation: As a consultant , I worked on various different teams to complete projects. One time, our designated team leader was suddenly reassigned to a new project so I stepped up and offered to lead our team. Task: We had a few days to research, compile, and present our recommendations to a client so I had to manage the team to make sure we were all completing our work and staying within the guidelines the client provided. Action: This meant that I had to balance both my own work for the proposal as well as fielding questions from teammates and overseeing the occasional disagreement. Acting as a mediator , I better understood the recommendations my teammates were proposing and helped them come to an agreement. Result: We successfully pitched our proposal to the client, resulting in an ongoing partnership with them. I was also recognized as a strong leader and became a designated group leader for future projects.
Have you had a time when you disagreed with your boss? How did you handle it?
Situation: We were given a small budget to run paid advertising campaigns for a new product that the company was launching. My boss thought that the money would be better spent on a Google Search Ad, but I wanted to spend it on a social media campaign. Task: I had to convince her that an ad on social media would have a higher ROI than a Google Search Ad, so I had to calculate costs and results for both campaigns to show her why a social media ad made more sense for our budget and goals. Action: I researched and compiled information about what we could expect to gain from these two different ads with our budget. I presented the findings to my boss to convince her to start a paid social media campaign. Result: My work convinced her that we would ultimately see more conversion from a highly targeted social media ad than a Google Search Ad, so I became the person in charge of the project. I oversaw the creation of the content, the targeting, and more, and by the end, we saw a much higher conversion rate than we usually did.
Share an example of when you had to deliver bad news to a coworker.
Situation: As a sales manager , I had to make sure that everyone on my team was meeting their weekly and monthly sales goals. There was one month when a man on my team was barely meeting the goal or did not reach it for four weeks. Our company policy was that after a month of inconsistent performance, we had to have a serious talk with the employee. Task: I had to ask this employee about his work performance and inform him that if his sales remained low for another two weeks, he would be let go. Action: Instead of approaching the situation as a chance to blame him for low sales or scare him about his future, I wanted to understand his point of view. We had a productive conversation about his work and what he was doing to improve his performance so it became a working discussion instead of a chance for me to talk down to him for not meeting our goals. Result: After our conversation, I saw the suggestions he made come to life and I watched his sales numbers rise. Luckily, he improved before the two weeks were up and he became one of my best sales associates after that.
Can you share a time when you successfully persuaded a team or individual to adopt your ideas or recommendations?
Situation: In my previous role at XYZ Inc. we were dealing with a challenge with declining sales. My team was struggling to find a solution and it was impacting our performance. Task: I decided to analyze the situation, come up with a new strategy to boost sales, and convince the team to adopt this new strategy. Action: To create this new strategy, I started by conducting a comprehensive analysis of our sales data to identify any sales trends or customer preferences. Based on this research, I developed a detailed proposal that outlines a new market approach, a revised product positioning, and targeted promotional campaigns. I made sure to meet with key team members one-on-one to communicate this and address any of their concerns. Once everyone agreed to this new strategy, I created a detailed implementation plan with clear milestones, responsibilities, and timelines. Result: As a result of our collaborative efforts and adoption of the new strategy, we saw a significant turnaround in our sales figures. Within six months, our sales in the target product category increased, exceeding our initial goals.
Behavioral questions are easy to identify since they are meant to gather specific information about a task you performed or a goal you achieved in a previous job. If the question starts with something along the lines of “ tell me about a time you… ” or “describe an experience where…” then the interviewer is looking to get concrete examples of how you complete tasks and achieve goals.
Here are some common behavioral interview questions that require the STAR method:
Tell me about a time you had to complete a project with a short deadline.
Can you tell me about a time you disagreed with a coworker? How did you resolve it?
Is there a time when you had to set a goal and meet it?
Tell me about a situation where you failed to meet a specific goal. How did you deal with it?
Have you had to make an unpopular decision?
Can you explain a time when you were under a lot of pressure at work? How did you handle it?
Have you ever worked with multiple departments to complete a project? How did it go?
What do you do when you need to motivate your coworkers?
Have you been in a situation where one of your coworkers refused to complete their work?
Tell me about a time you showed initiative in a professional setting.
Tell me about a time when you had to deal with a difficult coworker or team member. How did you handle the situation?
Tell me about a situation where you had to handle a dissatisfied customer or client. How did you address their concerns and ensure their satisfaction?
Describe a moment when you demonstrated strong problem-solving skills. What was the problem, and how did you approach it?
Can you share an experience where you had to provide constructive feedback to a colleague or subordinate? How did you deliver the feedback, and what was the outcome?
To prepare for an interview using the STAR method, the best way to do it is to review common behavioral and situational questions and practice your answers. The more you practice with the format of the STAR method, the better you’ll be at using it during an interview.
Start by writing out your answer to a behavioral question so you can read it back and make sure it sounds like a good answer. You should also answer the questions aloud to practice how you’ll organize your thoughts on the spot. You can do this alone or ask a friend to listen to your responses and help you fine-tune them.
The great thing about behavioral interview questions is that they can be broken down into categories. Consider the following common topics:
Adaptability
Problem-solving
Attention to detail
Customer-focused
Communication
Decision-making
Goal-setting
Taking initiative
Interpersonal skills
Time management
Negotiation
Conflict management
Most of these examples will overlap in some way or another, which will help you when it comes to coming up with an answer.
For example, if you have a story about a time you helped an angry customer reach a positive conclusion, that covers stress, problem-solving, customer interaction, communication, interpersonal skills , and conflict management.
As long as you have a number of stories that cumulatively cover all of the above topics, you should be plenty prepared for your interview. Just be sure to review the job description before heading into your interview, to make sure that all of your stories paint yourself as the ideal candidate the hiring manager is looking for.
You should avoid making your answer sound rehearsed or robotic and being too vague with your answers when using the STAR method. Here are some more mistakes to avoid when using the STAR method:
Sounding rehearsed. It’s good to prepare and practice your answers, but you don’t want to sound like a robot. In order to avoid this, we recommend writing bullet points instead of full answers. That way, you’re sure to hit all the key parts of your story, but your phrasing will sound more natural.
Telling stories that make you look bad. All the stories you tell using the STAR method should end on a positive note. And if the interviewer asks you about a time you made a mistake, don’t bring up the time you cost your former employer hundreds of thousands of dollars.
Being vague. It’s important that your direct impact is super evident in your story. It’s good to talk about team efforts, but make sure that your specific contribution is what’s highlighted.
If you can, use numbers whenever possible. Hiring managers won’t know about your various company policies, but they know that a 10% increase in revenue is always a good thing.
Not being prepared. Coming up with your story on the spot can have you leaving out details or dragging on your answers. There’s also a chance that you could forget to include relevant skills or miss a step in your answers. Being prepared with knowing each step and knowing what you want will help you answer smoothly.
Lying. It’s better to admit you don’t have a great example story rather than make one up. But don’t just flat out say “I don’t know, that never happened to me.” Instead, turn the behavioral interview question into a situational one. Imagine how you would behave in that circumstance, and apply the STAR method as normal.
Situational interview questions are very similar to behavioral questions, except they ask about a hypothetical scenario instead of a real one. These questions start with phrases like “What would you do if…” and “How would you respond when…”
The great news is that the STAR method works just as well for situational interview questions as behavioral ones. After all, the hiring manager or recruiter will be thrilled to hear about a real example that relates to their hypothetical situation.
Even if you don’t have a concrete example for a situational question, you can still use the STAR method to format your answer into a neat and coherent narrative.
What is the STAR method when interviewing?
When interviewing, the STAR method means your answer will address a Situation, what your Task was, what Action you took, and what was the final Result. The STAR method is a great way to neatly organize your answer in such a way that shows how your skills result in success. This helps the interviewer see that you understand the question and have the ability to effectively communicate a relevant answer.
How do you use the STAR technique?
Use the STAR technique by following each step in order. Start with a situation that is appropriate for the question. Then describe what your task or role was to resolve the situation. After, explain what actions you took to fulfill your task. Finally, in a positive manner, describe what were the results of your actions.
Is the STAR method a good technique?
Yes, the STAR method is a good technique for interviews. The STAR method follows a logical progression of your involvement. It gives context, shows skills in actions, and provides results. These are all bits of information the interviewer can use to learn about you and see how you are a great candidate.
When should you use the STAR method in interviews?
You should use the STAR method when answering behavioral interview questions. The STAR method allows you to answer behavioral interview questions with a story or example from your past. This helps the interviewer see how you are as an employee.
Massachusetts Institute of Technology – Using the STAR method for your next behavioral interview
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics – Employment Interviewing: Seizing the Opportunity and the Job
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating / 5. Vote count:
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.

Amanda is a writer with experience in various industries, including travel, real estate, and career advice. After taking on internships and entry-level jobs, she is familiar with the job search process and landing that crucial first job. Included in her experience is work at an employer/intern matching startup where she marketed an intern database to employers and supported college interns looking for work experience.
Denise Bitler has 30+ years of HR experience working in various industries and with all level of employees from hourly through C-suite, as well as company Board Members.She is the founder of Resume-Interview Success, LLC and is an expert in best practices related to resume, cover letter, and Executive bio writing, LinkedIn Profile optimization, job search strategies, and interview coaching.
Recent Job Searches
- Registered Nurse Jobs Resume Location
- Truck Driver Jobs Resume Location
- Call Center Representative Jobs Resume Location
- Customer Service Representative Jobs Resume
- Delivery Driver Jobs Resume Location
- Warehouse Worker Jobs Resume Location
- Account Executive Jobs Resume Location
- Sales Associate Jobs Resume Location
- Licensed Practical Nurse Jobs Resume Location
- Company Driver Jobs Resume
Related posts

How To Prepare For Your Third Job Interview (Step-By-Step Guide)

How To Answer “What Do You Do For Fun?” (With Examples)

How To Do A Great Skype Interview
How To Ace Your Open Interview (With Example Questions + Answers)
- Career Advice >
- Interview >
- Star Method

Julio Torres on Solving the Problemista of Problemista
F or Julio Torres, the writer-director-star of the A24 comedy Problemista , the word problemista represents an entanglement of one's aspirations and problems. One pushes the other forward, until both grow bigger, sometimes putting dreams and nightmares into a repetitive loop.
In the film, he plays Alejandro, an aspiring toy designer from El Salvador, struggling to get a job at Hasbro in New York City. Torres says the problemista of Problemista was writing, acting, and directing his debut feature film.
"It’s a very ambitious movie for a first-time director. It seems like the path is usually to make a more grounded, simple movie for your first time," says Torres. "And this is not that."
He co-stars with Tilda Swinton, who plays Elizabeth, an esoteric art-world outcast who will stop at nothing to make a name for her deceased husband Bobby (played by RZA) and his egg paintings. She hires Alejandro to bring her dream to life - in exchange for sponsoring his soon-to-expire work visa.
We talked with Torres, a former Saturday Night Live writer and co-creator of HBO's Los Espookys , about making problems to fix problems.
Joshua Encinias: You create surreal environments in your HBO series Los Espookys and Problemista using theatrical, handmade techniques.
Julio Torres: These are very broad strokes, because obviously, I have seen digital special effects that are completely breathtaking that I love when they’re inventive. When it’s like a once-in-a-decade thing like The Matrix that comes out and invents their own visual language.
Also Read: SNL Behind the Scenes: 12 Wild Stories From the Nearly 50 Years of Saturday Night Live
But for the most part, I feel like we’ve been oversaturated with CG to the point where sometimes you see these huge superhero movies, and because they have all the money in the world and they can make anything happen, then the human stakes no longer feel like they matter. They live in a world where a car can disintegrate in front of your very eyes, so… nothing matters. I think that in reaction to that, I felt very keen to explore the tactile and having very theatrical, very human-made sets that feel like you can actually touch them and be in them.
Julio Torres on Being a Problemista to Fix a Problemista
Joshua Encinias: Your most fantastical character creation in the movie is Larry Owens playing a visual and living manifestation of Craigslist. Will you talk about selecting the products that you built into his character?
Julio Torres: It feels like his costume and the set are all melded into one thing. And I think that is because Craigslist as a website is so confusing and it’s so chaotic. It’s like this stream of junk is thrown at you at the same time - at least that’s how it felt to me.
To abstract that, we use the combination of real props and then 2D flat versions of props. So like a real lamp next to like a painting of an air conditioner. And then it’s making you feel like you don’t know where one thing starts and the other one ends. Larry is at the center of it, wearing this holographic garment we designed.
Joshua Encinias: Is there an inspiration or art trend that inspired Bobby's egg paintings in the movie? They look like something I would see at a thrift store - or at the Museum of Modern Art.
Julio Torres: Katie Byron, our production designer, got them made and they look exactly like I imagined. What I like about Bobby's character is that I don’t think he’s attuned to the trend. I think that for some reason this is the one thing that he wants to create. And really, the inspiration was that question: "Is this bad, or is it good?" I can’t tell.
I feel like the answer to so many of those questions is like context. It’s like who is making them and where are they? So I wanted the artistry of the eggs to be of ambiguous quality and to feel like Bobby is an other - he's pushed aside and treated like he's not important. I want you to question why, and have it live in this ambiguous state.
Joshua Encinias: What does Alejandro see in Elizabeth - aside from her being able to fix his immigration status? Her behavior toward him and everyone around her is quite nasty.
Julio Torres: I think that because she is a challenge and he feels like he’s never had a challenge. He’s been so treasured by his mom and I think that in her, he sees an opportunity to prove himself. And also, I think he’s a very empathetic person and a very curious person.
Joshua Encinias: Tilda's character is terrible with technology. Is Tilda good with it in real life?
Julio Torres: I would say she has a pretty… I would call her average in terms of her technology abilities. I would say I am below average. Anything that requires a password, I’m like, "I don’t know my password." I lose my debit cards once every three months. Then every streamer cancels my subscription and then I have to start all over again. So I feel like in that regard, Elizabeth is closer to me in the technology aspect.
Joshua Encinias: I feel like one of the takeaways from the movie is that you have to be a problem to fix a problem. Will you elaborate on what that means?
Julio Torres: I don’t think the takeaway is to become a nightmare for someone else, it’s more an appeal to humanity and appeal to empathy.
I can think of an example from college. I was given the maximum amount of financial aid that an international student could get, for which I’m very grateful. But then come the second semester, I needed more money. And they were like, "We can’t give you more money."
So then I just went ahead and wrote to the president of the school. I was like, "Do you really want one of the few international students you have to go away ’cause he can’t pay for it?" And then they ended up giving me more money. That was a case of finding someone and becoming a problem for them.
Problemista is now in theaters.
The post Julio Torres on Solving the Problemista of Problemista appeared first on MovieMaker Magazine .


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
STAR interview question examples While you won't know the interview questions ahead of time, most behavioral interviews will focus on various work-related challenges that demonstrate critical thinking and problem-solving, and situations that showcase leadership skills, conflict resolution and performance under pressure. Here's some ...
FAQs. The STAR method is the best way to answer behavioral interview questions. STAR stands for Situation, Task, Action, and Result, and will help you create structured, concise, and engaging responses. Whenever you need to tell a story to demonstrate your skills, STAR is your go-to. If "telling a story" sounds intimidating, don't worry.
The STAR method is an acronym that stands for Situation, Task, Action, and Result. It is a technique that helps you organize your thoughts and tell a story that demonstrates your problem-solving ...
Here is a selection of some difficult STAR interview questions taken from the InterviewGold online training system. Take a few moments and see how you would answer, what examples would you use. 1. Describe a time when your leadership skills made a difference. (Exploring Leadership competency) 2.
The PAR method focuses primarily on problem-solving abilities. The CAR technique emphasizes resilience in overcoming challenges. The STAR method is comprehensive in nature as it not only focuses on the problem at hand but also delves into the context or situation that led to it.
STAR stands for Situation, Task, Action, and Results. It provides a helpful framework for structuring your answers to interview questions. Specifically, the STAR method is useful when you need to tell a concise and logical story—usually in response to behavioural questions such as "Tell me about a time when…".
The Four-Step STAR Interview Method. Competency-based interviews ask open-ended questions designed to reveal how you approach and overcome workplace challenges. Think of the STAR technique as the structure to tell a story that demonstrates your skills. Situation: start by setting the scene for your example.
Follow these steps to use the STAR interview technique: 1. Describe the situation. Answer the interview question by describing a relevant situation where you faced a challenge or completed a project at work. The situation you describe could be taken from an experience at work, a volunteer experience, or some other relevant situation.
1. Prepare your STAR examples before the interview. First, think of several STAR questions and answers a hiring manager might ask you during an interview. Consider writing a big list of STAR questions and answers a hiring manager might ask so you'll be better prepared for any questions that come your way. This method is especially helpful if ...
During a job interview, you will probably be asked to tell a story, or prompted to "describe a time when" you encountered a particular situation.The best way to answer these types of questions is to use the STAR method. What Is the STAR Interview Method? The STAR method is a guide for how to answer behavioral questions in an interview, and it helps to effectively show your interviewer how ...
STAR Method Interview Questions and Answers. While the options above show you how to break down the answers when you use the interview STAR method, having a few more STAR method examples can help you see how the answers flow once they're together. Here are a few more STAR interview questions and answers to get you headed in the right ...
What is the STAR interview response method, how to use it to prepare for job interviews, and examples of questions and answers using the STAR technique. ... For example, employers might be looking for proof of problem-solving skills, analytical ability, creativity, perseverance through failure, writing skills, presentation skills, teamwork ...
The STAR method helps you showcase your problem-solving skills by providing a clear and concise story that illustrates your actions and outcomes. Add your perspective Help others by sharing more ...
Common STAR interview method questions focus on soft skills like communication, collaboration, leadership behaviors, or problem-solving. For instance, you may be asked to describe a time you disagreed with a team member or talk about a time you resolved a work-related conflict .
The STAR method stands for Situation, Task, Action, Results. With this behavioral interview approach, employers can find out how candidates would act in certain situations on the job based on their past experiences. Candidates' answers would describe a situation, the required task, the candidate's chosen action, and the result of that action.
Pro Tip: When using the STAR format for interviews, bring up stories where you were the main actor, and use the first person singular in your answers, like this: "I did…" rather than "We did.". Keep the focus on you. When making a resume in our builder, drag & drop bullet points, skills, and auto-fill the boring stuff.
For example, a marketing executive may require problem-solving skills, or a job in customer services may require conflict management skills. The interview questions tend to start with a variation ...
Here is an example STAR-formatted response for the prompt, "tell me about a time when you demonstrated leadership." Instead of responding simply with "I tutored kids in math," provide context for your interviewer and demonstrate your skills through an engaging example. ... I demonstrated the best methods for solving difficult problems ...
The STAR technique is a method of answering questions that is comprised of four steps: Situation: Describe the situation and when it took place. Task: Explain the task and what was the goal. Action: Provide details about the action you took to attain this. Result: Conclude with the result of your action.
The STAR technique is a method used to prepare for behavioural interview questions. Read our blog to learn how to use it to ace your next job interview. ... e.g. problem-solving, leadership skills, project management: Action: Outline the steps you took to accomplish the objectives or resolve the problem. At this stage, be sure to focus on what ...
The STAR method can help you stay on track and answer behavioral interview questions quickly and thoroughly. Here is a breakdown of each step: Situation. Set the scene for your story — discuss who was involved and what was going on. Your answer won't work unless you can come up with an appropriate anecdote to discuss.
The STAR method is an interview technique that gives you a straightforward format you can use to tell a story by laying out the situation, task, action, and result. Situation: Set the scene and give the necessary details of your example. Task: Describe what your responsibility was in that situation. Action: Explain exactly what steps you took ...
STAR Problem-Solving Showcase STAR stands for Situation, Task, Action, and Result. It is a structured method used to effectively communicate experiences, accomplishments, and problem-solving ...
The three-body problem exists beyond the VR game — it's the very real fate of the San-Ti themselves. The San-Ti hail from an unstable three-body star system four light years from Earth, where ...
F or Julio Torres, the writer-director-star of the A24 comedy Problemista, the word problemista represents an entanglement of one's aspirations and problems. One pushes the other forward, until ...