Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process

How to Choose a Dissertation Topic | 8 Steps to Follow
Published on November 11, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on November 20, 2023.
Choosing your dissertation topic is the first step in making sure your research goes as smoothly as possible. When choosing a topic, it’s important to consider:
- Your institution and department’s requirements
- Your areas of knowledge and interest
- The scientific, social, or practical relevance
- The availability of data and resources
- The timeframe of your dissertation
- The relevance of your topic
You can follow these steps to begin narrowing down your ideas.
Table of contents
Step 1: check the requirements, step 2: choose a broad field of research, step 3: look for books and articles, step 4: find a niche, step 5: consider the type of research, step 6: determine the relevance, step 7: make sure it’s plausible, step 8: get your topic approved, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about dissertation topics.
The very first step is to check your program’s requirements. This determines the scope of what it is possible for you to research.
- Is there a minimum and maximum word count?
- When is the deadline?
- Should the research have an academic or a professional orientation?
- Are there any methodological conditions? Do you have to conduct fieldwork, or use specific types of sources?
Some programs have stricter requirements than others. You might be given nothing more than a word count and a deadline, or you might have a restricted list of topics and approaches to choose from. If in doubt about what is expected of you, always ask your supervisor or department coordinator.
Start by thinking about your areas of interest within the subject you’re studying. Examples of broad ideas include:
- Twentieth-century literature
- Economic history
- Health policy
To get a more specific sense of the current state of research on your potential topic, skim through a few recent issues of the top journals in your field. Be sure to check out their most-cited articles in particular. For inspiration, you can also search Google Scholar , subject-specific databases , and your university library’s resources.
As you read, note down any specific ideas that interest you and make a shortlist of possible topics. If you’ve written other papers, such as a 3rd-year paper or a conference paper, consider how those topics can be broadened into a dissertation.
After doing some initial reading, it’s time to start narrowing down options for your potential topic. This can be a gradual process, and should get more and more specific as you go. For example, from the ideas above, you might narrow it down like this:
- Twentieth-century literature Twentieth-century Irish literature Post-war Irish poetry
- Economic history European economic history German labor union history
- Health policy Reproductive health policy Reproductive rights in South America
All of these topics are still broad enough that you’ll find a huge amount of books and articles about them. Try to find a specific niche where you can make your mark, such as: something not many people have researched yet, a question that’s still being debated, or a very current practical issue.
At this stage, make sure you have a few backup ideas — there’s still time to change your focus. If your topic doesn’t make it through the next few steps, you can try a different one. Later, you will narrow your focus down even more in your problem statement and research questions .
There are many different types of research , so at this stage, it’s a good idea to start thinking about what kind of approach you’ll take to your topic. Will you mainly focus on:
- Collecting original data (e.g., experimental or field research)?
- Analyzing existing data (e.g., national statistics, public records, or archives)?
- Interpreting cultural objects (e.g., novels, films, or paintings)?
- Comparing scholarly approaches (e.g., theories, methods, or interpretations)?
Many dissertations will combine more than one of these. Sometimes the type of research is obvious: if your topic is post-war Irish poetry, you will probably mainly be interpreting poems. But in other cases, there are several possible approaches. If your topic is reproductive rights in South America, you could analyze public policy documents and media coverage, or you could gather original data through interviews and surveys .
You don’t have to finalize your research design and methods yet, but the type of research will influence which aspects of the topic it’s possible to address, so it’s wise to consider this as you narrow down your ideas.
It’s important that your topic is interesting to you, but you’ll also have to make sure it’s academically, socially or practically relevant to your field.
- Academic relevance means that the research can fill a gap in knowledge or contribute to a scholarly debate in your field.
- Social relevance means that the research can advance our understanding of society and inform social change.
- Practical relevance means that the research can be applied to solve concrete problems or improve real-life processes.
The easiest way to make sure your research is relevant is to choose a topic that is clearly connected to current issues or debates, either in society at large or in your academic discipline. The relevance must be clearly stated when you define your research problem .
Before you make a final decision on your topic, consider again the length of your dissertation, the timeframe in which you have to complete it, and the practicalities of conducting the research.
Will you have enough time to read all the most important academic literature on this topic? If there’s too much information to tackle, consider narrowing your focus even more.
Will you be able to find enough sources or gather enough data to fulfil the requirements of the dissertation? If you think you might struggle to find information, consider broadening or shifting your focus.
Do you have to go to a specific location to gather data on the topic? Make sure that you have enough funding and practical access.
Last but not least, will the topic hold your interest for the length of the research process? To stay motivated, it’s important to choose something you’re enthusiastic about!
Most programmes will require you to submit a brief description of your topic, called a research prospectus or proposal .
Remember, if you discover that your topic is not as strong as you thought it was, it’s usually acceptable to change your mind and switch focus early in the dissertation process. Just make sure you have enough time to start on a new topic, and always check with your supervisor or department.
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Formulating a main research question can be a difficult task. Overall, your question should contribute to solving the problem that you have defined in your problem statement .
However, it should also fulfill criteria in three main areas:
- Researchability
- Feasibility and specificity
- Relevance and originality
All research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly

You can assess information and arguments critically by asking certain questions about the source. You can use the CRAAP test , focusing on the currency , relevance , authority , accuracy , and purpose of a source of information.
Ask questions such as:
- Who is the author? Are they an expert?
- Why did the author publish it? What is their motivation?
- How do they make their argument? Is it backed up by evidence?
A dissertation prospectus or proposal describes what or who you plan to research for your dissertation. It delves into why, when, where, and how you will do your research, as well as helps you choose a type of research to pursue. You should also determine whether you plan to pursue qualitative or quantitative methods and what your research design will look like.
It should outline all of the decisions you have taken about your project, from your dissertation topic to your hypotheses and research objectives , ready to be approved by your supervisor or committee.
Note that some departments require a defense component, where you present your prospectus to your committee orally.
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a dissertation committee) that your research topic is relevant and worthy of being conducted.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, November 20). How to Choose a Dissertation Topic | 8 Steps to Follow. Scribbr. Retrieved April 1, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/dissertation-topic/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to define a research problem | ideas & examples, what is a research design | types, guide & examples, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
How to Choose the Best Topic for Research: Top 100 Dissertation Topics

Are you searching for inspiration while writing your research paper? In this case, try looking up interesting research topics online. This article contains an abundance of dissertation topics, for every imaginable subject, like fashion or business leadership dissertation topics. You are going to find interesting examples! Don't forget that you can also get research paper help from our professional writing team.
Top 100 Dissertation Ideas 2023
Scholars often believe that today there is a lack of new dissertation topics. Indeed, people conduct research non-stop, and it seems like there is nothing new to discuss. So how to become a professional writer and avoid breaking intellectual property rights then?
Luckily for all enthusiastic scientists out there, there are topics for dissertation that cater to any taste. Our essay writers service presents various research topics suitable for multiple degrees. Do you study the job market, quantum physics, or human behavioral patterns? These and even more dissertation ideas are waiting for you.
How to Opt for a Dissertation Topic?
Sometimes, the immense choice of examples of dissertation topics makes you question your decision about your academic paper. Writers get recommendations from multiple sources. Before you write a dissertation, turn to more experienced people, like counselors or professors. They are likely to suggest great topics for dissertation. We also recommend that you read about how to write a dissertation .
For research and reference purposes, go online to discover new engaging themes. Your colleagues in the field of science communicate via special forums or websites, so join them! Some generous people even publish dissertation ideas and samples for free. Hence, you can develop your unique topic by looking at other people’s works.
Which Topic Suits Best for Dissertation?
Whether you search healthy lifestyle, economic crisis, or leadership dissertation topics, the strategy is the same for all of them. These topics for dissertation should meet the following requirements:
- Bring novelty to the science field
- Cover newsworthy issues
- Have enough background data for an academic paper
Undeniably, it is better if the theme heavily appeals to you personally. Then, a sparkle of interest lights up whenever you write your work! On the contrary, less engaging dissertation topics make the whole writing process inefficient. Therefore, opt for themes that draw your attention the most.
Struggle to meet your essay deadline?
Enter the requirements for your work and get your task done asap.
Where to Find a Unique Dissertation Topic?
Throughout life, people constantly have to present something new to the world. Middle school and high-school students show their skills via essays, college students write a thesis, and Ph.D. candidates compose dissertations. Fortunately, emergency methods, like dissertation writing service , are available for quick and quality results. Still, you might suggest your topics for dissertation.
What is the key to creating a one-of-a-kind topic? First, you have to know well enough what other scholars have already studied. Then, perform further research even if your counterparts have covered all nuances. For instance, higher education dissertation topics can cover themes of college-age population or school bullying. Meanwhile, leadership dissertation topics may connect to ethical issues dealing within companies.
Dissertation Title: How to Make It Sound Perfect
In real life, titles are essential in drawing public attention to anything. Would you rather watch a movie with a boring name or pick a film with a short, witty title? The same goes for books, essays, and other scholarly work. The word becomes an anchor, something that pushes a random person to read your written piece. Here is how you properly compose it.
Let’s say that you ponder over higher education dissertation topics. For instance, do you want to study anxiety disorders among students or how online schools are affecting libraries? Raising awareness is crucial in both cases, but you must specify the issue first. For instance, attempt to study an unexpected correlation that current research fails to cover. Use the “how,” “what,” and “why” words to form several topic ideas.
Once you have specified your exact subject of study, your goal is to fit the title in under fifty words. This task seems unproblematic, but it requires talent. Just two sentences must sum up the contents of the humongous dissertation. So, make the title clear and concise!
What are Some Relevant Ideas to Research in 2023?
How long is a dissertation? It ranges from ten thousand to a hundred thousand words, but length is only the first requirement. Without a doubt, all topics for dissertation have one crucial characteristic: relevancy. To develop top-tier academic work, you need to know the global trends and latest tendencies in your specific science field. It would be detrimental to your success to pick dissertation ideas that scholars have recycled multiple times. So instead, look at what people find exciting in 2022:

- Artificial intelligence
Although the theme of AI has been around for a while, it remains fresh and full of potential. One possible research subject is the Metaverse, a virtual reality universe. This concept is quite new, so there are many branches to study. Besides, cybersecurity, especially in the banking sector, would stand out among the interesting examples of dissertation topics.
- Neuroscience and neurobiology
As much as scientists study human brains, there are still too many white spots in their knowledge of the human body. Choosing a topic related to cognitive development, brain implants, etc., could lead to a breakthrough in this sphere.
- Agriculture
With the negative trends in the global food industry, the theme of agriculture is at its peak importance. Food is something that everybody relates to, regardless of ethnicity, age, job, or social status. Therefore, a dissertation could critically analyze the current state of things and solutions for the food industry in crisis.
List of Dissertation Topics 2023
Today, you can do anything with the Internet, like pay someone to write an essay or find information on the necessary subject. Likewise, you may find business dissertation topics examples or dissertation topics in education, world politics, or other themes. This article suggests multiple ideas for your academic work to make things easier.
Top Dissertation Topics in Accounting
Here is a list of engaging dissertation topics in accounting:
- “Financial accounting's contribution to business strategy development.”
- “The things to take into account when investing in financial markets.”
- “How project accounting uses risk factors analysis.”
- “Systematic examination of art galleries cost accounting.”
- “Can computerized bookkeeping gradually replace accountants?”
- “The effect of cryptocurrency on current accounting procedures.”
- “Predicting new professions in the accounting industry.”
- “How are auditing standards becoming more international?”
- “An examination of the differences and parallels between accounting ethics and organizational culture.”
- “Investigation of potential new revenue streams for a bank.”
Best Public Health Dissertation Topics
In case you are looking for interesting public health dissertation topics, here are a few research questions:
- “How is it possible to increase Middle Eastern countries' access to clean, safe drinking water?”
- “What is the contribution of technological progress to bettering public health in affluent nations?”
- “Examining sexual abuse in an Indian public health environment.”
- “Evaluation of several US programs to increase kids' physical activity.”
- “The impact of poverty on public health in African nations.”
- “A study of the effectiveness of the Italian current healthcare system.”
- “Disastrous effects of antibiotic resistance in the upcoming year.”
- “Patient’s immune system and drug addiction.”
- “How does modern technology harm public health?”
- “Impact of the recession on social conditions and public health.”
Sociology Ideas for Dissertation
You should go online if interested in the social work dissertation topics. Articles like this share newsworthy sociology dissertation topics:
- “An analysis of American religious institutions and their impact on social structure.”
- “Examining attitudes toward and reactions to female child sex offenders.”
- “Studying the cultural differences in Scandinavian countries.”
- “Determining the social origins of domestic violence in Russian families.”
- “Global labor market stratification following the Great Recession.”
- “Research on how society influences gender relations.”
- “Analysis of the rise and fall in Japan's fertility rates and their underlying causes.”
- “The practice of social work with bereaved families.”
- “Analyze the racial stratification in European nations.”
- “How can government decrease the stress that social workers endure?”
Dissertation Topics in Education
Whether you want to discover new primary, college, or higher education dissertation topics, you are at the right place:
- “Looking at the effect of financial restraints on female education in east Asia.”
- “Investigating the effects of food sharing in primary education.”
- “Analysis of the covid pandemic's impact on the education sector.”
- “Do stress levels among students and performance on standardized tests correlate?”
- “What difficulties do parents of Muslim immigrants believe their children will encounter in European schools?”
- “What do teachers think about how technology affects students' learning?”
- “What difficulties do teachers encounter throughout their first three years of teaching?”
- “What do parents think the purpose of sex education is?”
- “What learning differences exist between neurodivergent and neurotypical students?”
- “How does the number of students in each class influence grades?”
Business Dissertation Topics
Someone who takes an interest in entrepreneurship would be glad to find the following business or mba dissertation topics:
- “The modern challenges for startups and small businesses in the USA.”
- “The impact of competence and leadership style on emerging business leaders in Europe.”
- “Analyzing how social media and digital platforms will impact business branding in the future.”
- “Do male subordinates' egos feel threatened by the presence of women in leadership positions?”
- “Is Facebook right to create targeted adverts using the user data it collects?”
- “Is a business's dispersed leadership more effective than its lone power center?”
- “TikTok influencer marketing's contribution to higher sales.”
- “An analysis of how globalization has affected Chinese companies' operations.”
- “The socio-cultural context of management and how it affects the dynamics of leadership in Denmark.”
- “What elements influence the probability of a business filing for bankruptcy?”
Political Science Dissertation Topics
Provided that your field of study is politics, consider the next dissertation topics:
- “Contrasting the responses of the Chinese and UK governments to the COVID-19 pandemic.”
- “Emotion's effect on deliberative democracy.”
- “Analysis of the single-party political system, including drawbacks and advantages.”
- “Political choices and environmental management tradeoffs.”
- “Eastern European social movements in the years following World War II.”
- “Ukraine's fragmentation and the competing political forces.”
- “Media bias in the reporting of political news.”
- “The impact of extremism on political life in the West.”
- “Political leaders and their individual goals.”
- “How does US foreign policy affect other nations throughout the world?”
Psychology Dissertation Topics
What if a person struggles to find extensive psychology dissertation topics? The solution is here:
- “Examining the connection between technology and postnatal depression.”
- “Why are some people more prone to feeling depressed in difficult situations?”
- “The long-term effects of childhood trauma on adults.”
- “Patient's mental health during the coronavirus pandemic.”
- “Children who are suffering from oncology: modern recovery programs.”
- “Comparison of cyberbullying and physical bullying psychological impact.”
- “What elements alter our personalities throughout our lives?”
- “What are the key indicators of burnout among executive staff?”
- “Effect of physical appearance on how others perceive us.”
- “Teaching dyslexic kids: potential difficulties.”
PhD Dissertation Topics
A Ph.D. candidate might consider historical, mathematical, or art dissertation topics. So let’s pick a great research topic:
- “US legal system and international criminal law: a comparative study.”
- “Examination of how globalization leads to changes in international law.”
- “The initial causes of cultural appropriation in first-world countries.”
- “What is the social networks’ impact on online marketing and creating demand?”
- “Cyber-diplomacy is the development of a global civilization in the digital era.”
- “What differences exist between US and EU immigration laws?”
- “Changing careers: information seeking by newcomers.”
- “The African-focused foreign policy of China.”
- “How have feminists' objectives evolved over the last ten years?”
- “Bringing the internet of things research and implementation together.”
Economics Dissertation Topics
Let’s see which dissertation topics in finance and economics can draw attention today:
- “Evaluating the cryptocurrency market using behavioral finance perspectives.”
- “Comparative analysis of financial improvements in China and the US.”
- “Issues with older adults and online banking.”
- “Shareholders' effects on the decision-making procedures at banks.”
- “Unscrupulous bank executives' effects on the organization's sustainability.”
- “Possible answers to moral problems of corporate social responsibility.”
- “What impact do taxes have on financial choices?”
- “The impact of India's population growth on economic expansion.”
- “Why are banks so adamantly against digital currency?”
- “What will internet banking resemble in ten years?”
Fashion Topics for Dissertation
An artsy person would appreciate research themes about style, like the following examples:
- “Is there a need for change after examining the impact of fast fashion on the environment?”
- “Comparing fast and ultra-fast supply chain management in the fashion industry.”
- “Critical analysis of the impact of western fashion on Asia's developing nations.”
- “How capitalism contributed to the western fashion and cultural values.”
- “Fashion trends that the K-Pop stars create.”
- “Examining the Vivienne Westwood brand's appeal to Japanese youth.”
- “The fixation with attempting an adult look in children's clothing.”
- “The effects of expensive counterfeit goods on the high-end fashion market.”
- “The origins of the dark and light academic dress trends.”
- “How social networks contribute to the development and spread of fashion trends.”
In brief, there are plenty of research subjects, from psychology dissertation topics to higher education dissertation topics. If you do proper factual and historical research and cite sources, get ready to receive recognition for your efforts. The key thing is to choose something that lights up your interest.
Also, don't forget to read what is important to look out for when you buy dissertation .
Set Your Dissertation Apart with Unique Topics
Elevate your academic journey with a standout dissertation topic. Our experts are here to help you select a topic that not only intrigues but also contributes significantly to your field of study.
Related Articles
%20(1).webp)

- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
How to Choose Dissertation Topics (The Complete Guide for 2022)
by Antony W
February 19, 2022

The first step to writing a dissertation fast is to choose a topic to investigate. However, coming up with a relevant topic for the project can be hard and agonizing if you don’t know how to go about it. That’s why in this guide, you’ll learn exactly how to choose dissertation topics for your project so you can get started with research as soon as possible.
We’ve been in the academic writing space long enough to know how difficult coming up with a dissertation topic is.
In fact, one of the common questions many readers ask us has to do with choosing the right topics, which means topic selection can be such a tedious process for many students.
Given our experience in dissertation writing, we have some useful tips that can save you a lot of time and stress by making it incredibly easy for you to choose the right topic for your dissertation assignment.
How to Choose Dissertation Topics
Here are some useful tips that can help you choose the best dissertation topics for your next thesis project:
Don’t Fret if Your Topic Isn’t Unique
Many students fail at choosing topics for their dissertation because they think too much outside the box and end up with nothing to show for it.
The thing is:
Spending too much of your time trying to think about some unique topic ideas that no student has ever explored is just but a waste of your precious time.
So instead of trying to come up with a topic that might blow your instructor’s mind away, pick a topic to which you can make a unique contribution and stick with it.
One thing you need to keep in mind when selecting a topic for your dissertation assignment is that it doesn’t matter if someone else already discovered the topic.
Choose whatever topic you want provided you can make useful contributions to it and expand the already existing body of knowledge.
At the end of the day, students get the opportunity to make unique contributions to their dissertations once they’ve completed their literature review for the dissertation .
First, that means you don’t have to invest a topic yourself, because there would be no existing studies to examine. Second, you’ll have more time to figure out new ways of approaching the topic you choose.
Search the Web for Topic Ideas
Good dissertation topics don’t often pop when you need them the most. So looking at the web for ideas can be a great way to find inspiration to help you come up with a topic you that you can work on.
The best thing about this approach is that there are several place to get topic ideas fast.
- Use Google to find previously published topics. You can find just about any topic ideas by a simple search. Whether you need early childhood education topics or something completely different, you’ll find Google to be incredibly helpful.
- Look at Journals that publish content in your area of study. You more than likely will find more topic ideas than you need, but make sure you focus on the topics that are in your area of interest.
Really you can use these sources as the starting point to come up with the most suitable topic for your dissertation.
Make Sure You’re Interested in the Topic
The worst mistake you can make when choosing a dissertation topic is to focus on a subject you know nothing about or an area you’re just not interested in.
Keep in mind that there’s no turning back when you choose a topic to explore in your research.
In other words, once your instructor approves you for a given topic, their expectations is that you stick to the topic right from the beginning to the end.
So make your life easier by identifying and picking a topic you’re interested in, or a subject that focuses on an area you’ve always wanted to explore.
But how do you know if you’re even interested in a topic in the first place?
The first option is to consider what you always think about from time to time.
It could be something that intrigues you, makes you angry, or gets you inspired quite too often.
Also, consider what you love talking about from time to time when you hang out with friends on campus or family at home, as that, too, can help you come up with an interesting topic for your dissertation.
The second option is to look at assignments you’ve already done and single out the topics you found the most interesting to research and write.
Choose one of the topics, zoom on it further, and see if it can be a good topic for your dissertation.
Choose a Topic that’s Relevant to Your Career Goals
A dissertation is an assignment you have to take seriously. And when it comes to choosing a topic to explore, it had better be relevant to your career goals give or take.
The idea here is that you should consider choosing a topic that will get you exactly where you want to go depending on the expert knowledge that you already have.
Simple is Always Better
Many students make choosing dissertation topics difficult because they focus on unnecessarily complex and insanely complicated topics.
As if that’s not enough, they come up with long research questions that are just hard to understand.
In the end, they struggle to write their dissertations so they have to repeat the process all over again.
We discourage this approach and strongly recommend that you choose a topic that’s simple and straightforward.
By simplifying your dissertation topic, you’ll easily control the growth of you research project and never have to worry about dead end.
Again, keeping things simple allows you to have a clear focus group. And when you have a very clear focus, even your research methodology won’t break you as you go deeper with the project.
Choosing dissertation topics can be challenging, but it doesn’t have to be difficult at all.
Have a second, or even a third, look at these tips, and you’ll be amazed just how quick you can find a bunch of topics to brain storm and eventually figure out what option is best for your research.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.
- How it works
How to Choose a Dissertation Topic
Published by Jamie Walker at August 16th, 2021 , Revised On October 3, 2023
The dissertation is one of the most testing academic assignments for undergraduate, graduate, or doctoral students. When writing a dissertation , you are expected to answer a particular research question and derive findings that can have implications for future research.
Nevertheless, writing can be a daunting task because dissertations are complex academic documents with intricate rules. Particularly, students need to select a good dissertation topic.
However, the prospect of selecting the appropriate topic can be overwhelming because many lack experience writing dissertations . In other cases, students might have limited time for writing as they have to manage their personal and professional needs.
Here we bring to you important guidelines that can facilitate if you are unsure how to choose a dissertation topic that is interesting, relevant, and manageable.
Step 1. Assess the Course Requirements
If you have just started to look for a topic, you might be wondering how I chose a dissertation topic that could leave a lasting impression on my supervisor and help me score a high academic grade.
It is important to note that each course has specific requirements or terms and conditions that guide students to determine the dissertation topic that best suits their needs. The nature and suitability of your chosen dissertation topic are dependent on the academic course being studied.
For example, you might have wanted to know how to choose a thesis topic for a master’s or how to choose a thesis topic for an undergraduate course but overlooked your course requirements.
It is vitally important to look into your course requirements before narrowing down the topics instead of being caught up in confusion.
Your department’s dissertation writing requirements , in some cases, can be very extended and perplexing; specifying the minimum and maximum word count, outline the list of possible topics , and identify the methodological requirements.
On the other hand, the prerequisites might be very limiting and unclear, with only the deadline and word count requirements being specified. No matter the requirements, it is essential to check with the course coordinator if students are unsure about choosing a topic for the dissertation.
ORDER FREE DISSERTATION TOPIC
Step 2. Select an Extensive Field
A prudent practise is to evaluate topics that are interesting for students in their courses. For instance, students can select a familiar topic that guides them during research. It is relatively easy to start research with known topics since you will not have to write from the beginning.
One way to find a topic is to search how to choose a dissertation topic on Google . There is no need to have advanced knowledge about the topic since basic information can guide students to investigate the topic further and narrow it down to something relevant, valuable, and manageable.
At ResearchProspect, we have created hundreds of topics for undergraduate, Masters and Ph.D. students. Please click here to find your topic in our free dissertation topics database, no matter the academic subject. We are the only company in the UK that provides free topics along with an aim and justification to help you get started.
Hire an Expert Writer
Proposal and dissertation orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in academic style
- Plagiarism free
- 100% Confidential
- Never Resold
- Include unlimited free revisions
- Completed to match exact client requirements
Step 3. Search Relevant Academic Literature
This is another important aspect of how to choose a dissertation topic. Students should find reliable and credible books, online dissertation topics databases, and articles to explore possible topics.
Highly rated journals frequently publish articles that introduce readers to new research on any topic. One way of choosing a dissertation topic is to use Google Scholar , which is a good resource for finding relevant journals for any subject.
It includes abstracts of relevant research that can inspire students to select their dissertation topic. Many universities have online libraries that students can access to find information about their specific subjects.
For example, students might want to know how to choose a dissertation topic in English literature . The above methods can assist them in the research process. While reading different books and articles, students should make notes about ideas that can be used to create a list of possible topics.
Also Read: What is Research Problem in Dissertation?
Step 4: Narrow Topic to Niche
Now that you have already completed the preliminary research, the next step would be to evaluate every topic and scrap the ones that are either too broad or too narrow.
The key to choosing a great dissertation topic is to identify a niche that still needs more research or a topic that is still debatable among researchers. You can investigate contemporary issues that have an impact on humans and society.
An example of a niche topic is “Social media strategies for business organizations”.
Another example would be “Identification of barriers that act as obstacles towards the popularity of sustainable architecture”.
Whatever the specific niche, it is crucial that adequate information on the topic is available because of the need to provide a robust theoretical basis for the dissertation. Develop a research problem statement and research questions to further narrow the topic.
Here are some ideas for you to consider;
Identify the time needed to study the academic sources on the topic.
If the list of sources is extensive then it might be necessary to narrow the topic even further.
If you are unable to perform primary research, make sure there is adequate information to complete the objectives of your descriptive dissertation.
Step 5. Evaluate the Best Research Approach when Choosing Topic
Select the research method that is most suitable for your dissertation and meets your degree programme. This is an important stage of choosing a dissertation topic, but there is no need to panic.
The two methods of research employed in academic research are known as primary research and secondary research . It is recommended that students evaluate artefacts or examine various theoretical approaches.
For example, if you have chosen a dissertation topic in education , then you might decide to base your dissertation on primary research because primary research would enable you to address a research problem that is of critical importance to the education industry by filling an obvious gap in knowledge.
On the other hand, if you are testing a hypothesis and you find out that there is sufficient literature already available on the subject, then you could base your dissertation purely on secondary data.
However, dissertations can include one or multiple approaches to research. You should consult with your mentors about the best research method, especially when unsure about how to choose a dissertation topic for a PhD level assignment .
Primary research can be costly and time-consuming, while secondary research is cost-effective and saves time. Selecting the right approach is dependent on the resources and time available to students.
Here are the most notable advantages and disadvantages of primary and secondary research.
Step 6. Demonstrate the Relevance of Topic
Perhaps the most important step is to ensure the topic is relevant to your field of study. Your topic should be academically relevant and aim to fill a gap in existing knowledge or provide new insights into the field.
It should also be socially relevant as the results should promote social change and contribute towards an understanding of society.
Finally, it must be practically relevant by contributing towards problem-solving or improving quality of life. A relevant topic should be interlinked with contemporary subjects, debates, and topics. The research problem can be used to demonstrate the relevance of the topic.
For example, if you are stuck on how to choose a dissertation topic for a master’s course, a master’s dissertation on strategic human resource management could identify the implications of the research for modern firms and their HR practices.
Similarly, if you are doing all this research to choose a doctoral dissertation topic, a doctoral dissertation on a political science topic could assess the implications for policymakers.
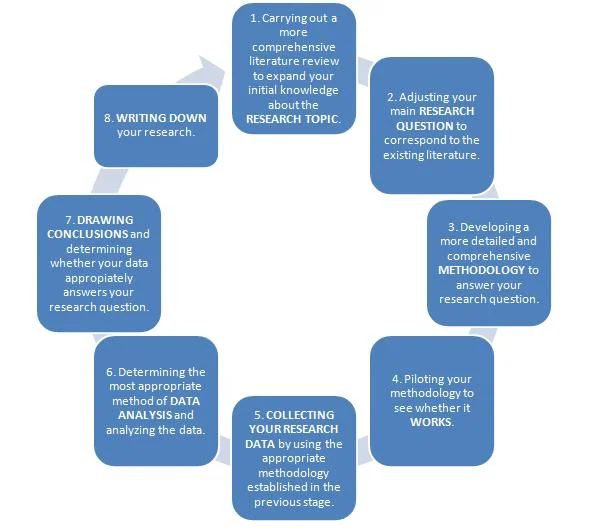
Step 7. Submit the Topic to Committee
Once you have selected a topic, and are ready to proceed, submit the topic with a brief description to the program supervisor or coordinator. Once approved, a dissertation research proposal will be needed as the next step.
If your supervisor doesn’t approve of your chosen topic, there is still no need to panic. You can follow the same steps on how to choose a dissertation topic and send them more suggestions.
Each of the steps described in this article is part of a gradual and systematic process that will assist students in how to choose a dissertation topic. It is important to use planning and preparation because the result of your dissertation project, to some extent, will depend on your chosen topic.
At ResearchProspect, we have created hundreds of free topic suggestions for students. Whether you are an undergraduate, Master’s, or Ph.D. student, you can find an interesting, relevant, suitable, and manageable topic for your research in our free dissertation topics library .
Our dissertation writers can also provide you with free custom topic ideas and a plan/outline on your chosen topic to help you get your topic and plan of research approved by your supervisor.
Order a Proposal
Worried about your dissertation proposal? Not sure where to start?
- Choose any deadline
- Unlimited free amendments
- Free anti-plagiarism report
- Completed to match exact requirements
Frequently Asked Questions
Does your dissertation topic matter.
Yes, your dissertation topic matters significantly. It shapes your research, impacts your engagement, and influences your academic and career path. A well-chosen topic aligns with your interests, contributes to your field, and enhances your overall learning experience.
How to choose a dissertation topic?
- Assess the course requirements
- Select an extensive field
- Search relevant academic literature
- Narrow topic to the niche
- Demonstrate the relevance of your topic
- Submit topic to the committee’
Can I change my dissertation topic?
Yes, you can change your dissertation topic, but the process varies by institution and department. Consult with your advisor and review departmental guidelines. Changing topics may require additional time, research, and resources, so weigh the benefits and drawbacks before making a final decision. Always prioritise your academic and research interests.
How to choose a dissertation topic for an undergraduate?
Identify your interests within your field. Explore coursework, readings, and discussions that intrigued you. Conduct preliminary research to gauge existing literature. Discuss potential topics with professors or advisors. Ensure feasibility in terms of data, resources, and time. Opt for a unique angle but remain within the scope of undergraduate expectations.
How many words is a dissertation title?
A dissertation title’s length varies, but it is typically concise. Most titles range between 10 and 15 words. The aim is to be descriptive and clear while capturing the essence of the research. It should give readers an immediate understanding of the topic without being overly lengthy or ambiguous. Always follow institutional guidelines.
Does a dissertation need a title?
Yes, a dissertation needs a title. The title succinctly conveys the essence of the research and provides a first impression to readers. It helps in identifying the work’s main theme and acts as a reference point for scholars, researchers, and anyone engaging with the dissertation. A clear, relevant title is crucial.
You May Also Like
Not sure how to approach a company for your primary research study? Don’t worry. Here we have some tips for you to successfully gather primary study.
Penning your dissertation proposal can be a rather daunting task. Here are comprehensive guidelines on how to write a dissertation proposal.
Repository of ten perfect dissertation research question examples will provide you a better perspective about how to create dissertation research questions.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
What is a Dissertation (And How To Choose a Topic)?
Nailing down a dissertation topic can be difficult. We share thoughts and tips on choosing a topic for your dissertation that will have lasting impact.
Key Takeaways
- Most graduate students must complete a dissertation.
- A dissertation should be based on an original research topic of your choosing.
- Your goal is to choose a dissertation topic that addresses an important, unanswered question in your field.

The Dissertation—A Basic Overview
Graduate students are typically expected to create an original research question and conduct research based on this question while adhering to a formal experimental or scientific process. Subsequently, students must identify and pursue research aims and produce an original research paper providing critical analysis and outlining meaningful findings resulting from the research.
But for many students, selecting a dissertation topic can be the hardest part. That’s why we’ve outlined the helpful tips below.
It’s also worth noting that while high school students and undergraduate students in U.S. schools won’t typically be required to write a dissertation, the tips below can be useful for learning how to choose and write thesis topics at every level of education. Moreover, for students in pursuit of a master’s degree, the same tips can be readily applied to choosing from master’s thesis topics.
What to Know Before Choosing a Topic
For graduate students, a major part of the dissertation process will include working closely with an advisor or mentor. Your mentor will typically provide feedback and guidance at various steps of the process from fielding preliminary dissertation ideas and identifying your dissertation title to analyzing your research data and completing your research paper.
Your mentor may also be a part of the dissertation review board. Most graduate students will be required to defend their dissertation before this committee of scholars and experts. For most graduate students, and some undergraduate students in specialized programs, dissertation completion will be a major part of academic performance evaluation.

Choosing Dissertation Topics
Of course, before you get to all of the challenging steps above, you must choose a dissertation topic. The good news is that you have almost infinite options to choose from within your field. But that’s also the bad news. When it comes to choosing dissertation topics, the toughest part may be narrowing it down to a single topic.
With that in mind, we offer 10 Tips for choosing your dissertation topic .
1. Identify Your Dissertation Type
Dissertation topics will depend on the type of research you intend to do. This, in turn, depends on your field of study. Dissertation topics will often fall into two primary categories—empirical research and qualitative research.
Empirical research is often driven by your own independent field research and data gathering. This is more common in medical and natural science fields such as psychology dissertation topics, nursing dissertation topics, and subjects engaging modern technology such as computer science.
Qualitative research may be more common in fields where critical analysis is essential, such as art dissertation topics, international criminal law, business dissertation topics, and more. In these cases, existing knowledge would serve as a starting point for deeper assessment.

2. Explore Existing Data
Regardless of your subject area, your starting point will likely be existing research. This will help you differentiate between areas of existing knowledge and opportunities for deeper exploration.
Moreover, this step will give you a sense of the higher education dissertation topics that have been used in the past to explore your field. This can be a useful way to help you understand what might qualify as a viable dissertation topic.
3. Record Your Sources
As you delve into existing ideas and findings, you can also begin to gather your own body of sources on the subject. If this research is fruitful, many of these preliminary scholarly sources will form the backbone of your reference list. As you get deeper into your specific dissertation topic, this list will only grow.
4. Identify Unanswered Questions
As you explore the existing research, identify unanswered questions. Scholarly research articles will often recognize limitations to the existing study and even identify additional areas for future research. Highlight questions that might be worthy of deeper consideration as you conduct your preliminary research and reading.
5. Expand Your Research Based On Unanswered Questions
Follow the research trail for some of the most intriguing unanswered questions. Find out how deep the research goes on such topics.
Is there additional research that actually does address these questions? Have others in your field proposed similar questions in recent journal articles, scientific conferences or other public contexts? In other words, is this really an original idea? This step should help you eliminate any supposedly “unanswered questions” that are, in fact, answered elsewhere.

6. Consider Feasibility
How will you conduct the study? Using comparative analysis? Field research? Laboratory experiments with innovative technologies? In light of these needs, how realistic will it be to explore a given dissertation topic?
Be sure your institution has the resources to facilitate your research project. If additional funding or outside support is required, consider how realistic it will be to procure this support.
7. Weigh the Ethical Implications
Be sure that any research questions under consideration can be explored with full adherence to experimental ethics. This is an especially important point of consideration for those exploring sensitive topics like domestic violence, modern recovery programs, human rights abuses, and more.
Evaluate the possibility of ethical issues dealing with your topic or proposed experimental framework. Ultimately, your dissertation proposal will have to address these issues. This is a good first step in that direction.
8. Narrow Questions Based on Potential Impact
Now that you’ve narrowed down to dissertation topics that are original, feasible, and ethical, it’s time to think about why a given question might be worthy of exploration.
Some examples of questions you may want to explore include:
- How might your education dissertation topic improve our understanding of human cognitive development?
- Have you considered economics dissertation topics that might address unequal wealth distribution in America?
- Would your international law dissertation contribute to the way the global community handles human rights violations in developing countries?
Think about the ways that your research paper might help bring about real world policy change, improvements to the legal system, enhanced opportunity in the higher education sector, solutions to an economic crisis, more effective business management practices, or anything else that might positively impact knowledge, understanding and real-world outcomes in your field.

9. Identify Opportunities for Future Research
One indicator that you’ve stumbled onto a rich topic for research is the ability to mine the subject for continued exploration. Think about the ways that relevant data, empirical analysis, or consequent findings could spark additional critical thinking.
Can your chosen dissertation topic serve as the basis for future academic work? Will future college students or graduate students find the seedlings for their own research aims in your research?
While you may not necessarily choose to explore these additional questions yourself, one of the primary goals of your dissertation is to make a direct and lasting contribution to your field. Creating opportunities for others to critically analyze your findings and conduct further research is an indication that you have achieved this goal.
10. Factor in Personal Development
Dissertations certainly qualify as major academic achievements. But there’s a lot more to them. Most graduate students are already embedded in professional careers.
One of the best ways to whittle down your prospective dissertation topics is to look for ideas that apply both in your educational and professional pursuits. Indeed, aligning these interests will allow you to dive deeper into a topic that will advance your knowledge and expertise in the field where you currently work.
As a computer science student working in the gaming industry, you may conduct your research on a subject like the impact of educational games on cognitive development. A student pursuing a doctorate in business management while building a startup company might produce a dissertation on the impact of organizational culture when working in a virtual environment.
In other words, consider ways that your chosen dissertation topic can serve to advance your career even as you remain entrenched in your pursuit of a terminal degree.
And for more valuable tips on succeeding in your advanced degree program, see our Guide to Life in Graduate School .
Or get tips on studying, student life, and much more with a look at our Student Resources .
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
What Is a Dissertation? | 5 Essential Questions to Get Started
Published on 26 March 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on 5 May 2022.
A dissertation is a large research project undertaken at the end of a degree. It involves in-depth consideration of a problem or question chosen by the student. It is usually the largest (and final) piece of written work produced during a degree.
The length and structure of a dissertation vary widely depending on the level and field of study. However, there are some key questions that can help you understand the requirements and get started on your dissertation project.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
When and why do you have to write a dissertation, who will supervise your dissertation, what type of research will you do, how should your dissertation be structured, what formatting and referencing rules do you have to follow, frequently asked questions about dissertations.
A dissertation, sometimes called a thesis, comes at the end of an undergraduate or postgraduate degree. It is a larger project than the other essays you’ve written, requiring a higher word count and a greater depth of research.
You’ll generally work on your dissertation during the final year of your degree, over a longer period than you would take for a standard essay . For example, the dissertation might be your main focus for the last six months of your degree.
Why is the dissertation important?
The dissertation is a test of your capacity for independent research. You are given a lot of autonomy in writing your dissertation: you come up with your own ideas, conduct your own research, and write and structure the text by yourself.
This means that it is an important preparation for your future, whether you continue in academia or not: it teaches you to manage your own time, generate original ideas, and work independently.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
During the planning and writing of your dissertation, you’ll work with a supervisor from your department. The supervisor’s job is to give you feedback and advice throughout the process.
The dissertation supervisor is often assigned by the department, but you might be allowed to indicate preferences or approach potential supervisors. If so, try to pick someone who is familiar with your chosen topic, whom you get along with on a personal level, and whose feedback you’ve found useful in the past.
How will your supervisor help you?
Your supervisor is there to guide you through the dissertation project, but you’re still working independently. They can give feedback on your ideas, but not come up with ideas for you.
You may need to take the initiative to request an initial meeting with your supervisor. Then you can plan out your future meetings and set reasonable deadlines for things like completion of data collection, a structure outline, a first chapter, a first draft, and so on.
Make sure to prepare in advance for your meetings. Formulate your ideas as fully as you can, and determine where exactly you’re having difficulties so you can ask your supervisor for specific advice.
Your approach to your dissertation will vary depending on your field of study. The first thing to consider is whether you will do empirical research , which involves collecting original data, or non-empirical research , which involves analysing sources.
Empirical dissertations (sciences)
An empirical dissertation focuses on collecting and analysing original data. You’ll usually write this type of dissertation if you are studying a subject in the sciences or social sciences.
- What are airline workers’ attitudes towards the challenges posed for their industry by climate change?
- How effective is cognitive behavioural therapy in treating depression in young adults?
- What are the short-term health effects of switching from smoking cigarettes to e-cigarettes?
There are many different empirical research methods you can use to answer these questions – for example, experiments , observations, surveys , and interviews.
When doing empirical research, you need to consider things like the variables you will investigate, the reliability and validity of your measurements, and your sampling method . The aim is to produce robust, reproducible scientific knowledge.
Non-empirical dissertations (arts and humanities)
A non-empirical dissertation works with existing research or other texts, presenting original analysis, critique and argumentation, but no original data. This approach is typical of arts and humanities subjects.
- What attitudes did commentators in the British press take towards the French Revolution in 1789–1792?
- How do the themes of gender and inheritance intersect in Shakespeare’s Macbeth ?
- How did Plato’s Republic and Thomas More’s Utopia influence nineteenth century utopian socialist thought?
The first steps in this type of dissertation are to decide on your topic and begin collecting your primary and secondary sources .
Primary sources are the direct objects of your research. They give you first-hand evidence about your subject. Examples of primary sources include novels, artworks and historical documents.
Secondary sources provide information that informs your analysis. They describe, interpret, or evaluate information from primary sources. For example, you might consider previous analyses of the novel or author you are working on, or theoretical texts that you plan to apply to your primary sources.
Dissertations are divided into chapters and sections. Empirical dissertations usually follow a standard structure, while non-empirical dissertations are more flexible.
Structure of an empirical dissertation
Empirical dissertations generally include these chapters:
- Introduction : An explanation of your topic and the research question(s) you want to answer.
- Literature review : A survey and evaluation of previous research on your topic.
- Methodology : An explanation of how you collected and analysed your data.
- Results : A brief description of what you found.
- Discussion : Interpretation of what these results reveal.
- Conclusion : Answers to your research question(s) and summary of what your findings contribute to knowledge in your field.
Sometimes the order or naming of chapters might be slightly different, but all of the above information must be included in order to produce thorough, valid scientific research.
Other dissertation structures
If your dissertation doesn’t involve data collection, your structure is more flexible. You can think of it like an extended essay – the text should be logically organised in a way that serves your argument:
- Introduction: An explanation of your topic and the question(s) you want to answer.
- Main body: The development of your analysis, usually divided into 2–4 chapters.
- Conclusion: Answers to your research question(s) and summary of what your analysis contributes to knowledge in your field.
The chapters of the main body can be organised around different themes, time periods, or texts. Below you can see some example structures for dissertations in different subjects.
- Political philosophy
This example, on the topic of the British press’s coverage of the French Revolution, shows how you might structure each chapter around a specific theme.

This example, on the topic of Plato’s and More’s influences on utopian socialist thought, shows a different approach to dividing the chapters by theme.

This example, a master’s dissertation on the topic of how writers respond to persecution, shows how you can also use section headings within each chapter. Each of the three chapters deals with a specific text, while the sections are organised thematically.

Like other academic texts, it’s important that your dissertation follows the formatting guidelines set out by your university. You can lose marks unnecessarily over mistakes, so it’s worth taking the time to get all these elements right.
Formatting guidelines concern things like:
- line spacing
- page numbers
- punctuation
- title pages
- presentation of tables and figures
If you’re unsure about the formatting requirements, check with your supervisor or department. You can lose marks unnecessarily over mistakes, so it’s worth taking the time to get all these elements right.
How will you reference your sources?
Referencing means properly listing the sources you cite and refer to in your dissertation, so that the reader can find them. This avoids plagiarism by acknowledging where you’ve used the work of others.
Keep track of everything you read as you prepare your dissertation. The key information to note down for a reference is:
- The publication date
- Page numbers for the parts you refer to (especially when using direct quotes)
Different referencing styles each have their own specific rules for how to reference. The most commonly used styles in UK universities are listed below.
You can use the free APA Reference Generator to automatically create and store your references.
APA Reference Generator
The words ‘ dissertation ’ and ‘thesis’ both refer to a large written research project undertaken to complete a degree, but they are used differently depending on the country:
- In the UK, you write a dissertation at the end of a bachelor’s or master’s degree, and you write a thesis to complete a PhD.
- In the US, it’s the other way around: you may write a thesis at the end of a bachelor’s or master’s degree, and you write a dissertation to complete a PhD.
The main difference is in terms of scale – a dissertation is usually much longer than the other essays you complete during your degree.
Another key difference is that you are given much more independence when working on a dissertation. You choose your own dissertation topic , and you have to conduct the research and write the dissertation yourself (with some assistance from your supervisor).
Dissertation word counts vary widely across different fields, institutions, and levels of education:
- An undergraduate dissertation is typically 8,000–15,000 words
- A master’s dissertation is typically 12,000–50,000 words
- A PhD thesis is typically book-length: 70,000–100,000 words
However, none of these are strict guidelines – your word count may be lower or higher than the numbers stated here. Always check the guidelines provided by your university to determine how long your own dissertation should be.
At the bachelor’s and master’s levels, the dissertation is usually the main focus of your final year. You might work on it (alongside other classes) for the entirety of the final year, or for the last six months. This includes formulating an idea, doing the research, and writing up.
A PhD thesis takes a longer time, as the thesis is the main focus of the degree. A PhD thesis might be being formulated and worked on for the whole four years of the degree program. The writing process alone can take around 18 months.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2022, May 05). What Is a Dissertation? | 5 Essential Questions to Get Started. Scribbr. Retrieved 1 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/what-is-a-dissertation/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to choose a dissertation topic | 8 steps to follow, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples.

The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Dissertation Topics
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Definition: Dissertation Topics
- 3 Finding a Dissertation Topic
- 4 Good Dissertation Topics
- 5 Academic Writing
- 6 Dissertation Topics Examples
- 7 In a Nutshell
Definition: Dissertation Topics
The dissertation topic is essentially the subject of the dissertation. However, if you think seriously about which topic you want to write, you will find that the dissertation often contains several overlapping topics; for instance, historical work can discuss certain events together with broader cultural origins. So we can say that the topic of the dissertation is best viewed not as a separate topic, but rather as a practical summary that can cover and combine several different themes.
Choosing a dissertation topic can be difficult, but there are ways to simplify the task. This article is intended to help you decide which topic is right for you. The final decision is of course entirely up to you; in this article, however, you will find some tips and tricks to help you select potential dissertation topics.
How do I choose a dissertation topic?
The best dissertation topics are the ones that inspire you and that you can easily explore. Your dissertation topic should have lots of current information and research, but should also not be too bulky. You need to be filling in research gaps and contributing something to the academic community with your dissertation . Be sure to brainstorm before you jump straight into your research.
What are the best topics for a dissertation?
There are various dissertation topics and each student will find a certain topic more interesting or suitable than the others. Once you’ve conducted your preliminary research, focus on a single topic and create your research questions . If you still have problems with making your selection, you should take a look at the dissertation topics of former students for some inspiration. Continue reading this article for some research topic examples.
Why is it important to narrow down a dissertation topic?
This way, you can decide whether you would like to select a more general or a more specific topic in your chosen area. If you don’t narrow down your dissertation topic, you may find it very difficult to create your dissertation proposal . When your topic is too bulky, it is unclear in which direction your research will take you.
What makes a quality dissertation topic?
A good dissertation topic should be clearly stated in the dissertation introduction so that there is no confusion. It needs to be clearly defined and have only one meaning. Your reader must know exactly what to expect when reading through your dissertation.
Can a dissertation topic be a question?
In theory, it can be. However, this is often not advised. Since the purpose of the dissertation is to provide answers, it is better to avoid formulating dissertation topics like questions, as this may only obscure your reasoning. What you may be thinking of is the research question . The research question is established once you’ve chosen your dissertation topic and it dictates exactly what will be covered in your dissertation.
What is the difference between a purpose statement and a dissertation topic?
A purpose statement describes the general scope of the dissertation and it is located towards the end of the introduction in the dissertation structure . It outlines the purpose of the research that you’re conducting and the direction that it will take. Unlike a thesis statement, it does not include any conclusions that have been made by the author. The dissertation topic on the other hand is simply the overarching theme of your dissertation.
Finding a Dissertation Topic
There are several steps you can try in case you are to choose one of the possible dissertation topics. These include:
Possibly you could put together a mini-project to assist you to choose. You can try out a small part of academic writing to better understand which dissertation topics are relevant to your interests and resources.
• Determination of the Required Resources
Your dissertation will not end well if you miss important research material. Ensure that you have adequate material on your topic (also in the library and on the Internet) before you make a final decision on the topic of your dissertation. This will help you to write your final paper more efficiently.
• Brainstorming
An important part of the creation of dissertation topics is making short notes. Get a piece of paper and write down ideas; the more concepts you put on a sheet of paper, the more dissertation topics you can choose.
• Relevance Trees
This method creates topics based on a comprehensive concept. Each of these topics forms an independent branch that can lead to sub-sectors. You can analyze these subsectors and combine them to create new dissertation topics. Your project manager or teaching assistant can help you choose the final topic from the selected topics in case you are unable to narrow your selection to one topic.
Good Dissertation Topics
When choosing a dissertation topic, it is important to consider whether it ends or not. If the dissertation topics are too specific or too narrow, you may not have enough content to write to complete the entire dissertation. This will most likely result in you either extending out a small portion of useless content or diverting from the topic to something inappropriate.
Simultaneously, dissertation topics that are too wide should be avoided so that they can be adequately considered in the dissertation. Ideal topics for the dissertation are those that find the correct balance: on one hand, narrow enough to fit easily; then again, with enough effects and factors to withstand the breakdown and the detailed discussion of the components.
TIP: Always use transition words to properly connect the sentences and paragraphs in your thesis or essay.
Academic Writing
The final topic of the dissertation is important for any piece of academic writing . When it comes to academic writing, structure and form result from the main topic. Therefore, if you miss a topic or have not decided what your theme should be, your piece has no form and is not recognized in the academic communities.
Although there are many samples of successful dissertations that lack accurate, easily generalized topics, they differ from scientific ones. Therefore, you should not imitate their approaches to the dissertation topics.
Dissertation Topics Examples
Here are examples of potential dissertation topics in various disciplines.
Psychological Dissertation Topics
– The relationship between expectation, neurotic fear, frustration, and pain. – Depression and its impact on student performance – Psychological treatment of the child’s parents in the autistic spectrum – The influence of the divorce of parents on the early development of the child – Integration of wild therapy in traumatized children
Architecture Dissertation Topics
– How to construct structures that can stay for a long time – The implementation of cultures when designing structures – Create architectural beauty without absurd money – Hospitals: creating healthy spaces for the sick – Integrate renowned architects into your architectural concepts without imitating their work
Education Dissertation Topics
– Use of motivation theory in the classroom – The educational observation process: How does this happen in the 21st century? – Improve career guidance for students – Negativity towards learning: how this affects undergraduates and their education process? – The innovative learning model: everything you need to know
Human Resources Dissertation Topics
– Possibilities for implementing different theories of personnel management in a work environment. – The role of administrative management: does it work with HR departments? – Hard vs. soft skills: recruitment of personnel – Worker evaluation: Subjectivity vs. objectivity – Awards and their impact on employee inspiration
Business Dissertation Topics
– Administrations and their usage of tax incentives to inspire filmmakers to produce films in certain regions – Common challenges for companies in enforcing international patent laws – Integrity in financial institutions – The role of intermediaries in financial disputes – Why ethnic awareness helps you do business

Dissertation printing & binding
You are already done writing your dissertation and need a high quality printing & binding service? Then you are right to choose BachelorPrint! Check out our 24-hour online printing service. For more information click the button below :
In a Nutshell
When choosing dissertation topics, the following basic rules must be observed: • Choose a theme that interests you • Ensure you have enough resources • Make sure your topic is wide enough to support a dissertation, but not too broad to be bulky • Ensure that you understand the topic sufficiently to structure your dissertation coherently • Use the methods for finding dissertation topics which include brainstorming, Research, Determination of the required resources, and relevance trees
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint
EdDPrograms.org
What is an Ed.D. Dissertation? Complete Guide & Support Resources
Wondering how to tackle the biggest doctoral challenge of all? Use our guide to the Ed.D. dissertation to get started! Learn about the purpose of a Doctor of Education dissertation and typical topics for education students. Read through step-by-step descriptions of the dissertation process and the 5-chapter format. Get answers to Ed.D. dissertation FAQs . Or skip to the chase and find real-world examples of Doctor of Education dissertations and websites & resources for Ed.D. dissertation research.
What is an Ed.D. Dissertation?
Definition of an ed.d. dissertation.
An Ed.D. dissertation is a 5-chapter scholarly document that brings together years of original research to address a problem of practice in education. To complete a dissertation, you will need to go through a number of scholarly steps , including a final defense to justify your findings.
Purpose of an Ed.D. Dissertation
In a Doctor of Education dissertation, you will be challenged to apply high-level research & creative problem-solving to real-world educational challenges. You may be asked to:
- Take a critical look at current educational & administrative practices
- Address urgent issues in the modern education system
- Propose original & practical solutions for improvements
- Expand the knowledge base for educational practitioners
Topics of Ed.D. Dissertations
An Ed.D. dissertation is “customizable.” You’re allowed to chose a topic that relates to your choice of specialty (e.g. elementary education), field of interest (e.g. curriculum development), and environment (e.g. urban schools).
Think about current problems of practice that need to be addressed in your field. You’ll notice that Ed.D. dissertation topics often address one of the following:
- Academic performance
- Teaching methods
- Access to resources
- Social challenges
- Legislative impacts
- System effectiveness
Wondering how others have done it? Browse through Examples of Ed.D. Dissertations and read the titles & abstracts. You’ll see how current educators are addressing their own problems of practice.
Ed.D. Dissertation Process
1. propose a dissertation topic.
Near the beginning of a Doctor of Education program, you’ll be expected to identify a dissertation topic that will require substantial research. This topic should revolve around a unique issue in education.
Universities will often ask you to provide an idea for your topic when you’re applying to the doctoral program. You don’t necessarily need to stick to this idea, but you should be prepared to explain why it interests you. If you need inspiration, see our section on Examples of Ed.D. Dissertations .
You’ll be expected to solidify your dissertation topic in the first few semesters. Talking to faculty and fellow Ed.D. students can help in this process. Better yet, your educational peers will often be able to provide unique perspectives on the topic (e.g. cultural differences in teaching methods).

2. Meet Your Dissertation Chair & Committee
You won’t be going through the Ed.D. dissertation process alone! Universities will help you to select a number of experienced mentors. These include:
- Dissertation Chair/Faculty Advisor: The Chair of the Dissertation Committee acts as your primary advisor. You’ll often see them referred to as the Supervising Professor, Faculty Advisor, or the like. You’ll rely on this “Obi Wan” for their knowledge of the field, research advice & guidance, editorial input on drafts, and more. They can also assist with shaping & refining your dissertation topic.
- Dissertation Committee: The Dissertation Committee is made up of ~3 faculty members, instructors and/or adjuncts with advanced expertise in your field of study. The Committee will offer advice, provide feedback on your research progress, and review your work & progress reports. When you defend your proposal and give your final defense , you’ll be addressing the Dissertation Committee.
3. Study for Ed.D. Courses
Doctor of Education coursework is designed to help you: a) learn how to conduct original research; and b) give you a broader perspective on your field of interest. If you take a look at the curriculum in any Ed.D. program, you’ll see that students have to complete credits in:
- Practical Research Methods (e.g. Quantitative Design & Analysis for Educational Leaders)
- Real-World Educational Issues (e.g. Educational Policy, Law & Practice)
When you’re evaluating possible Ed.D. programs, pay attention to the coursework in real-world educational issues. You’ll want to pick an education doctorate with courses that complement your dissertation topic.
4. Complete a Literature Review
A literature review is an evaluation of existing materials & research work that relate to your dissertation topic. It’s a written synthesis that:
- Grounds your project within the field
- Explains how your work relates to previous research & theoretical frameworks
- Helps to identify gaps in the existing research
Have a look at Literature Review Guides if you’d like to know more about the process. Our section on Resources for Ed.D. Dissertation Research also has useful links to journals & databases.
5. Craft a Dissertation Proposal
During the first two years of your Doctor of Education, you’ll use the knowledge you’ve learned from your coursework & discussions to write the opening chapters of your dissertation, including an:
- Introduction that defines your chosen topic
- Literature Review of existing research in the field
- Proposed Research Methodology for finding the answer to your problem
When you’re putting together these elements, think about the practicals. Is the topic too big to address in one dissertation? How much time will your research take and how will you conduct it? Will your dissertation be relevant to your current job? If in doubt, ask your faculty advisor.
6. Defend Your Dissertation Proposal
About midway through the Ed.D. program, you will need to present your proposal to your Dissertation Committee. They will review your work and offer feedback. For example, the Committee will want to see that:
- Your research topic is significant.
- Your research methodology & timeline make sense.
- Relevant works are included in the literature review.
After the Committee approves your proposal, you can get stuck into conducting original research and writing up your findings. These two important tasks will take up the final years of your doctorate.
7. Conduct Original Research into Your Topic
As a Doctor of Education student, you will be expected to conduct your own research. Ed.D. students often use a qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods (quantitative/qualitative) approach in this process.
- Quantitative Research: Collection & analysis of numerical data to identify characteristics, discover correlations, and/or test hypotheses.
- Qualitative Research: Collection & analysis of non-numerical data to understand & explain phenomena (e.g. questionnaires, in-depth interviews, focus groups, video artifacts, etc.).
Your Ed.D. coursework will ground you in research methods & tools, so you’ll be prepared to design your own project and seek IRB approval for any work involving human subjects.
Note: Occasionally, universities can get creative. For example, the Ed.D. program at San Jose State University asks students to produce a documentary film instead of conducting traditional research.
8. Write the Rest of Your Dissertation
Once you have written up the first few chapters of your dissertation (Intro, Literature Review & Proposed Methodology) and completed your research work, you’ll be able to complete the final chapters of your dissertation.
- Chapter 4 will detail your research findings.
- Chapter 5 is a conclusion that summarizes solutions to your problem of practice/topic.
This is where you and your faculty advisor will often have a lot of interaction! For example, you may need to rework the first few chapters of your dissertation after you’ve drafted the final chapters. Faculty advisors are extremely busy people, so be sure to budget in ample time for revisions and final edits.
9. Defend Your Dissertation
The final defense/candidacy exam is a formal presentation of your work to the Dissertation Committee. In many cases, the defense is an oral presentation with visual aides. You’ll be able to explain your research findings, go through your conclusions, and highlight new ideas & solutions.
At any time, the Committee can challenge you with questions, so you should be prepared to defend your conclusions. But this process is not as frightening as it sounds!
- If you’ve been in close contact with the Committee throughout the dissertation, they will be aware of your work.
- Your faculty advisor will help you decide when you’re ready for the final defense.
- You can also attend the defenses of other Ed.D. students to learn what questions may be asked.
Be aware that the Committee has the option to ask for changes before they approve your dissertation. After you have incorporated any notes from the Committee and addressed their concerns, you will finalize the draft, submit your dissertation for a formal review, and graduate.
Ed.D. Dissertation Format: 5 Chapters
Chapter 1: introduction.
Your Doctor of Education dissertation will begin with an introduction. In it, you’ll be expected to:
- Provide an overview of your educational landscape
- Explain important definitions & key concepts
- Define a real-world topic/problem of practice
- Outline the need for new studies on this topic
Chapter 2: Literature Review
The literature review is a summary of existing research in the field. However, it is not an annotated bibliography. Instead, it’s a critical analysis of current research (e.g. trends, themes, debates & current practices). While you’re evaluating the literature, you’re also looking for the gaps where you can conduct original research.
Sources for a literature review can include books, articles, reports, websites, dissertations, and more. Our section on Resources for Ed.D. Dissertation Research has plenty of places to start.
Chapter 3: Research Methodology
In the research methodology, you’ll be expected to explain:
- The purpose of your research
- What tools & methods you plan to use to research your topic/problem of practice
- The design of the study
- Your timeline for gathering quantitative & qualitative data
- How you plan to analyze that data
- Any limitations you foresee
Chapter 4: Results & Analysis
Chapter 4 is the place where you can share the results of your original research and present key findings from the data. In your analysis, you may also be highlighting new patterns, relationships, and themes that other scholars have failed to discover. Have a look at real-life Examples of Ed.D. Dissertations to see how this section is structured.
Chapter 5: Discussions & Conclusions
The final chapter of your Ed.D. dissertation brings all of your work together in a detailed summary. You’ll be expected to:
- Reiterate the objectives of your dissertation
- Explain the significance of your research findings
- Outline the implications of your ideas on existing practices
- Propose solutions for a problem of practice
- Make suggestions & recommendations for future improvements
Ed.D. Dissertation FAQs
What’s the difference between a dissertation and a thesis.
- Dissertation: A dissertation is a 5-chapter written work that must be completed in order to earn a doctoral degree (e.g. Ph.D., Ed.D., etc.). It’s often focused on original research.
- Thesis: A thesis is a written work that must be completed in order to earn a master’s degree. It’s typically shorter than a dissertation and based on existing research.
How Long is a Ed.D. Dissertation?
It depends. Most Ed.D. dissertations end up being between 80-200 pages. The length will depend on a number of factors, including the depth of your literature review, the way you collect & present your research data, and any appendices you might need to include.
How Long Does it Take to Finish an Ed.D. Dissertation?
It depends. If you’re in an accelerated program , you may be able to finish your dissertation in 2-3 years. If you’re in a part-time program and need to conduct a lot of complex research work, your timeline will be much longer.
What’s a Strong Ed.D. Dissertation Topic?
Experts always say that Doctor of Education students should be passionate about their dissertation topic and eager to explore uncharted territory. When you’re crafting your Ed.D. dissertation topic , find one that will be:
- Significant
See the section on Examples of Ed.D. Dissertations for inspiration.
Do I Have to Complete a Traditional Dissertation for an Ed.D.?
No. If you’re struggling with the idea of a traditional dissertation, check out this guide to Online Ed.D. Programs with No Dissertation . Some Schools of Education give Ed.D. students the opportunity to complete a Capstone Project or Dissertation in Practice (DiP) instead of a 5-chapter written work.
These alternatives aren’t easy! You’ll still be challenged at the same level as you would be for a dissertation. However, Capstone Projects & DiPs often involve more group work and an emphasis on applied theory & research.
What’s the Difference Between a Ph.D. Dissertation and Ed.D. Dissertation?
Have a look at our Ed.D. vs. Ph.D. Guide to get a sense of the differences between the two degrees. In a nutshell:
- Ed.D. dissertations tend to focus on addressing current & real-world topics/problems of practice in the workplace.
- Ph.D. dissertations usually put more emphasis on creating new theories & concepts and even completely rethinking educational practices.
How Can I Learn More About Ed.D. Dissertations?
Start with the section on Examples of Ed.D. Dissertations . You can browse through titles, abstracts, and even complete dissertations from a large number of universities.
If you have a few Doctor of Education programs on your shortlist, we also recommend that you skim through the program’s Dissertation Handbook . It can usually be found on the School of Education’s website. You’ll be able to see how the School likes to structure the dissertation process from start to finish.
Ed.D. Dissertation Support
University & campus resources, dissertation chair & committee.
The first port of call for any questions about the Ed.D. dissertation is your Dissertation Chair. If you get stuck with a terrible faculty advisor, talk to members of the Dissertation Committee. They are there to support your journey.
University Library
An Ed.D. dissertation is a massive research project. So before you choose a Doctor of Education program, ask the School of Education about its libraries & library resources (e.g. free online access to subscription-based journals).
Writing Center
Many universities have a Writing Center. If you’re struggling with any elements of your dissertation (e.g. editing), you can ask the staff about:
- Individual tutoring
- Editorial assistance
- Outside resources
Mental Health Support
It’s well-known that doctoral students often face a lot of stress & isolation during their studies. Ask your faculty advisor about mental health services at the university. Staff in the School of Education and the Graduate School will also have information about on-campus counselors, free or discounted therapy sessions, and more.
Independent Dissertation Services
Dissertation editing services: potentially helpful.
There are scores of independent providers who offer dissertation editing services. But they can be expensive. And many of these editors have zero expertise in educational fields.
If you need help with editing & proofreading, proceed with caution:
- Start by asking your Dissertation Chair about what’s permitted for third party involvement (e.g. you may need to note any editor’s contribution in your dissertation acknowledgments) and whether they have any suggestions.
- The Graduate School is another useful resource. For example, Cornell’s Graduate School maintains a list of Editing, Typing, and Proofreading Services for graduate students.
Dissertation Coaches: Not Worth It
Dissertation coaches are defined as people who offer academic & mental support, guidance, and editorial input.
- That means the person who should be your coach is your Dissertation Chair/Faculty Advisor. Remember that faculty members on the Dissertation Committee can also provide assistance.
- If you’re looking for extra support, you might consider consulting a mentor in your line of work and collaborating with fellow Ed.D. students.
But hiring an independent Ed.D. dissertation coach is going to be an absolute waste of money.
Dissertation Writing Services: Just Don’t!
Universities take the dissertation process very seriously . An Ed.D. dissertation is supposed to be the culmination of years of original thought and research. You’re going to be responsible for the final product. You’re going to be defending your written work in front of a phalanx of experienced faculty members. You’re going to be putting this credential on your résumé for everyone to see.
If you cheat the process by having someone else write up your work, you will get caught.
Ed.D. Dissertation Resources
Examples of ed.d. dissertations, dissertation databases.
- Open Access Theses and Dissertations
- ProQuest Dissertations & Theses
- EBSCO Open Dissertations
Ed.D. Dissertations
- USF Scholarship Repository: Ed.D. Dissertations
- George Fox University: Doctor of Education
- UW Tacoma: Ed.D. Dissertations in Practice
- Liberty University: School of Education Doctoral Dissertations
- University of Mary Hardin-Baylor: Dissertation Collection
Ed.D. Dissertation Abstracts
- Michigan State University: Ed.D. Dissertation Abstracts
Ed.D. Dissertation Guides & Tools
General ed.d. guides.
- SNHU: Educational Leadership Ed.D./Ph.D. Guide
Dissertation Style Manuals
- Chicago Manual of Style
Style manuals are designed to ensure that every Ed.D. student follows the same set of writing guidelines for their dissertation (e.g. grammatical rules, footnote & quotation formats, abbreviation conventions, etc.). Check with the School of Education to learn which style manual they use.
Examples of Ed.D. Dissertation Templates
- Purdue University: Dissertation Template
- Walden University: Ed.D. Dissertation Template
Each School of Education has a standard dissertation template. We’ve highlighted a couple of examples so you can see how they’re formatted, but you will need to acquire the template from your own university.
Literature Review Guides
- UNC Chapel Hill: Writing Guide for Literature Reviews
- University of Alabama: How to Conduct a Literature Review
Resources for Ed.D. Dissertation Research
Journal articles.
- EBSCO Education Research Databases
- Education Resources Information Center (ERIC)
- Emerald Education eJournal Collection
- Gale OneFile: Educator’s Reference Complete
- Google Scholar
- NCES Bibliography Search Tool
- ProQuest Education Database
- SAGE Journals: Education
Useful Websites
- Harvard Gutman Library: Websites for Educators
- EduRef: Lesson Plans
Educational Data & Statistics
- Digest of Education Statistics
- Education Policy Data Center (EPDC)
- ICPSR Data Archive
- National Assessment of Educational Progress
- National Center for Education Statistics (NCES)
- UNESCO Institute for Statistics

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

Dissertation Topics
- Updated on
- Apr 24, 2023

The final step in a PhD or Master’s course is the submission of a dissertation . A dissertation is a research paper that summarises the research conducted and includes findings either on a question or a topic chosen by the student. It is important as it demonstrates a student’s knowledge of the subject and ability to use research methods to define a topic. Students are required to select a dissertation topic of their choice. Choosing a topic can be confusing so this blog helps you understand how to narrow down a dissertation topic and provides a list of dissertation topics in various disciplines.
This Blog Includes:
Empirical dissertation, non-empirical dissertation, different types of research methods for dissertation, how to choose a dissertation topic, list of dissertation topics subject-wise, economics dissertation topics, mba dissertation topics, medical dissertation topics, arts and humanities dissertation topics, law dissertation topics, science dissertation topics, social science dissertation topics, psychology dissertation topics, dissertation topics in education, what makes a good dissertation topic, types of dissertation.
There are mainly two types of dissertations- empirical and non-empirical. The choice of the dissertation depends mainly on your field of study.
An empirical dissertation involves collecting data and researching through methods where conclusions of the study are strictly drawn from concretely empirical evidence, and therefore “verifiable” evidence. It focuses on collecting and analyzing original data. Students can conduct research using qualitative and quantitative research methods like case studies, surveys, observation, laboratory experiments, and interviews. Empirical research tests hypotheses in order to arrive at valid research outcomes and assumptions are tested.
A non-empirical dissertation involves the use of theoretical data and working with existing research or other texts, presenting original analysis, and argumentation, but there is no original data. It focuses more on theories, methods, and their implications for educational research. Non-empirical research theorizes the logical assumptions of research variables and assumptions are entirely theorized.
Also Read: Dissertation Topic in Finance
Two types of primary research for the dissertation include qualitative and quantitative research methods:
- Quantitative Research Methods gather information through numerical data. It is used to quantify opinions, behaviors, or other defined variables. It can be used to study a large group of people. The information is gathered by performing statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques. Examples of quantitative research methods include surveys, experimental research, correlational research, longitudinal study, cross-sectional, causal-Comparative research, descriptive research, etc
- Qualitative research methods gather non-numerical data. It is used to find meanings, opinions, or underlying reasons from its subjects. It is associated with studying human behavior from an informative perspective. It aims at obtaining in-depth details of the problem. Examples of qualitative research methods include case studies, Observational methods, one-on-one interviews, focus groups, text analysis, etc
- Mixed method research is where quantitative and qualitative methods of research are combined
Also Read: Dissertation vs Thesis
When it comes to choosing a topic for your dissertation, many students find themselves confused. Here are some tips that will help you narrow down a topic for your dissertation:
- First, check the requirements of your course
- Since your dissertation and research will take time, probably months, you should select a topic that interests you.
- Start by brainstorming and researching your field of study
- Get inspired by previous students’ work and research
- Make a list of broad topics you find interesting. Shortlist the one on which you can do research.
- Narrow down your topic by picking a niche
- Try to pick something original and a small and specific topic. Remember not to be too vague or too narrow
- Consider the type of research to want to perform and whether the topic has academic and social relevance
- Ask your lecturers or supervisor for advice and get your topic approved
Here are all the subject-wise dissertation topics to explore:
- Comparing the Economies of Developed vs Developing Countries
- How Social Networks Contribute to the Growth of the Global Economy
- Covid-19 Implications on the Economy
- Consumer Behavior and Eco-Friendly Production
- Gender Wage Gap: Legislative and Ethical Issues Dealing with Salaries in Developing Countries
- How China’s Production Influences the Global Economy
- Micro-financing Institutions and the Level of Poverty in Developing Countries
- How Oil Consumption Influences Global Economy
- The impact of local and regional cultures on shaping entrepreneurial economic development.
- How do habits and routines affect productivity? The case of (an industry).
- Research to identify the impacts of Coronavirus on banking and the future of banking after the pandemic
- How Globalization leads to Mergers and International Economic Cooperation
- Role of the World Bank in the International Economy
- Technological innovations and their influence on green and environmental products.
- Fiscal policy and the global economy: The scope for, and benefits from, international Coordination Fiscal and labor market policies in response to Covid-19 in different countries
- Is Online Marketing Effective for Technological Startups?
- How Globalization Impacts Small Business
- The Specifics of Instagram Marketing and Advertisement Placement
- Consumer behavior during a recession.
- Brands Influencing Consumers Buying Behaviors – A Case Study On (Brand/Company)
- The Influence Of Advertising On Consumer Behavior
- Evaluation of best HR practices for improving employee commitment
- Strategies to continually maintain customers’ satisfaction and trust levels in an electronic shopping
- Surviving political turmoil
- Digital marketing during the COVID-19 crisis.
- Recent research and responses of various countries for the treatment of COVID-19.
- Is it good to take antibiotics during the infection of microbes in the human body?
- Exploring the ethical dilemmas faced by healthcare professionals during COVID-19: Establishing policies for best practice.
- Management of Drug Dependency Programs
- Detailed assessment of the long-term usage of steroids on the overall health conditions of individuals.
- Communication and Public Health during the Pandemic
- Implementation of Modern Recovery Programs in Hospital Care System
- Challenges in recognizing rare infectious diseases
- Epidemics versus pandemics
- Sequelae and effective diabetes management
- How Capitalism Contributed to the Development of Conceptual Art
- Shift in Gender Roles in Marvel Comic Books in the Last 20 Years
- Social Networks’ Impact on Slang Language
- How has Globalization Influenced Cultural Relativism?
- New Ethics in a Digital Age
- Economical, Social and Political Causes and Results of the Great Depression
- Effects of the Industrial Revolution concerning World War I.
- Body Image and Social Construction of Normality
- Warfare and Violence in Ancient Times
- The history of design in various periods of human existence
- How Gender Roles and Stereotypes Influence the Divorce Process
- The Rise of Cyber Crimes and Punishments
- Race Discrimination in Modern Law System
- A deeper look at the history of the death penalty.
- Did the US involvement in Iraq provide justice or violate the law?
- Analyzing the impact of trade unions and their work
- Assessing the mediating role of corporate social responsibility in companies’ performance.
- Evaluating the implications of Brexit on the protection of intellectual property rights in the UK.
- Section 377 and the Dignity of Indian Homosexuals
- Legal Issue of Child Labor in the Third World Countries
- Modern Technology that Contributes to Biology Science
- Effects of Pesticide Use on the Quality of Water
- The Concept of Uncertainty in Quantum Physics Based on Particle-Wave Duality
- String Theory and Black Holes
- Discovery of New Species: Can We Expect More?
- How to Fight Mercury Contamination in the Environment
- Could Ebola be Used As a Biological Weapon?
- Solid-state physics and its modern implication in different fields.
- The Future of Synthetic Chemistry
- Nearby Galaxies and Young Stellar Clusters
- Political Reasons Behind Gender Inequality
- Tectonic Theory and Forecasting of Earthquakes
- The role of mass media in the electoral process of a state or a country and how its influence dictates the results of an election.
- The process of the formation of coral reefs and their use.
- Effect of Deglaciation on the polar volcanoes
- Contraction of One’s Identity in Urban Landscape
- Youth Activism and Social Work
- Emission profile of a fast-food restaurant
- Post 9/11 Pakistan-Afghanistan relations and their impact on world politics
- The gap between ideology and competency of foreign political powers
- Correlation Between Raise of Social Networks and Anxiety Disorders Among Teenagers
- Correlation Between Patient’s Immune System and Mental Health
- Treating Strategies for Patients with PTSD
- Preparing Patients With Anxiety to Return to the Workplace
- Media violence and children
- Relapse in the addictive behaviors
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) From A Neurosciences And Behavioural Approach
- How does separation between parents cause distress among children
- The mental health of homeless people
- Why is there an increase in eating disorders among the youth?
- Social Anxiety and social depression effects on an introverted child
- Workplace Bullying and its Psychological Impact on Employees’ Performance
- Impact of Covid-19 on mental health
- childhood trauma and outline its effects
- A study of long-term psychological effects of divorce on the adult children of divorcees
- Impact of the Internet on the social life of Students.
- Educational assessment of students using virtual reality technologies
- Interaction between students of different ethnicities based on a differentiated approach
- Harassment Prevention of younger students in School
- Illegal behavior of students in high-school
- Importance of self-studying for students
- Development of Time management for students
- Personal development of teachers in educational institutions
- The role of Sustainability in educational institutions
- The rising cost of academic education
Something that will allow you to produce “a polished piece of work within a limited amount of time and with a limited amount of cost.” A good dissertation topic seeks to challenge and subdue the existing assumptions and theories. It introduces a new and unique perspective on the status quo. Here are some defining factors of a good dissertation topic:
- Choose a topic you love to research and unravel
- A topic that challenges the pre-existing theories in your discipline
- Seeks practical, philosophical, and social solutions and answers
Hopefully, this blog assisted you in finding out popular dissertation topics. If you require any assistance regarding your application process while enrolling for your further studies, our experts at Leverage Edu are just one click away. Call us anytime at 1800 572 000 for a free counseling session!
Team Leverage Edu
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Dissertation – Format, Example and Template
Dissertation – Format, Example and Template
Table of Contents

Dissertation
Definition:
Dissertation is a lengthy and detailed academic document that presents the results of original research on a specific topic or question. It is usually required as a final project for a doctoral degree or a master’s degree.
Dissertation Meaning in Research
In Research , a dissertation refers to a substantial research project that students undertake in order to obtain an advanced degree such as a Ph.D. or a Master’s degree.
Dissertation typically involves the exploration of a particular research question or topic in-depth, and it requires students to conduct original research, analyze data, and present their findings in a scholarly manner. It is often the culmination of years of study and represents a significant contribution to the academic field.
Types of Dissertation
Types of Dissertation are as follows:
Empirical Dissertation
An empirical dissertation is a research study that uses primary data collected through surveys, experiments, or observations. It typically follows a quantitative research approach and uses statistical methods to analyze the data.
Non-Empirical Dissertation
A non-empirical dissertation is based on secondary sources, such as books, articles, and online resources. It typically follows a qualitative research approach and uses methods such as content analysis or discourse analysis.
Narrative Dissertation
A narrative dissertation is a personal account of the researcher’s experience or journey. It typically follows a qualitative research approach and uses methods such as interviews, focus groups, or ethnography.
Systematic Literature Review
A systematic literature review is a comprehensive analysis of existing research on a specific topic. It typically follows a qualitative research approach and uses methods such as meta-analysis or thematic analysis.
Case Study Dissertation
A case study dissertation is an in-depth analysis of a specific individual, group, or organization. It typically follows a qualitative research approach and uses methods such as interviews, observations, or document analysis.
Mixed-Methods Dissertation
A mixed-methods dissertation combines both quantitative and qualitative research approaches to gather and analyze data. It typically uses methods such as surveys, interviews, and focus groups, as well as statistical analysis.
How to Write a Dissertation
Here are some general steps to help guide you through the process of writing a dissertation:
- Choose a topic : Select a topic that you are passionate about and that is relevant to your field of study. It should be specific enough to allow for in-depth research but broad enough to be interesting and engaging.
- Conduct research : Conduct thorough research on your chosen topic, utilizing a variety of sources, including books, academic journals, and online databases. Take detailed notes and organize your information in a way that makes sense to you.
- Create an outline : Develop an outline that will serve as a roadmap for your dissertation. The outline should include the introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion.
- Write the introduction: The introduction should provide a brief overview of your topic, the research questions, and the significance of the study. It should also include a clear thesis statement that states your main argument.
- Write the literature review: The literature review should provide a comprehensive analysis of existing research on your topic. It should identify gaps in the research and explain how your study will fill those gaps.
- Write the methodology: The methodology section should explain the research methods you used to collect and analyze data. It should also include a discussion of any limitations or weaknesses in your approach.
- Write the results: The results section should present the findings of your research in a clear and organized manner. Use charts, graphs, and tables to help illustrate your data.
- Write the discussion: The discussion section should interpret your results and explain their significance. It should also address any limitations of the study and suggest areas for future research.
- Write the conclusion: The conclusion should summarize your main findings and restate your thesis statement. It should also provide recommendations for future research.
- Edit and revise: Once you have completed a draft of your dissertation, review it carefully to ensure that it is well-organized, clear, and free of errors. Make any necessary revisions and edits before submitting it to your advisor for review.
Dissertation Format
The format of a dissertation may vary depending on the institution and field of study, but generally, it follows a similar structure:
- Title Page: This includes the title of the dissertation, the author’s name, and the date of submission.
- Abstract : A brief summary of the dissertation’s purpose, methods, and findings.
- Table of Contents: A list of the main sections and subsections of the dissertation, along with their page numbers.
- Introduction : A statement of the problem or research question, a brief overview of the literature, and an explanation of the significance of the study.
- Literature Review : A comprehensive review of the literature relevant to the research question or problem.
- Methodology : A description of the methods used to conduct the research, including data collection and analysis procedures.
- Results : A presentation of the findings of the research, including tables, charts, and graphs.
- Discussion : A discussion of the implications of the findings, their significance in the context of the literature, and limitations of the study.
- Conclusion : A summary of the main points of the study and their implications for future research.
- References : A list of all sources cited in the dissertation.
- Appendices : Additional materials that support the research, such as data tables, charts, or transcripts.
Dissertation Outline
Dissertation Outline is as follows:
Title Page:
- Title of dissertation
- Author name
- Institutional affiliation
- Date of submission
- Brief summary of the dissertation’s research problem, objectives, methods, findings, and implications
- Usually around 250-300 words
Table of Contents:
- List of chapters and sections in the dissertation, with page numbers for each
I. Introduction
- Background and context of the research
- Research problem and objectives
- Significance of the research
II. Literature Review
- Overview of existing literature on the research topic
- Identification of gaps in the literature
- Theoretical framework and concepts
III. Methodology
- Research design and methods used
- Data collection and analysis techniques
- Ethical considerations
IV. Results
- Presentation and analysis of data collected
- Findings and outcomes of the research
- Interpretation of the results
V. Discussion
- Discussion of the results in relation to the research problem and objectives
- Evaluation of the research outcomes and implications
- Suggestions for future research
VI. Conclusion
- Summary of the research findings and outcomes
- Implications for the research topic and field
- Limitations and recommendations for future research
VII. References
- List of sources cited in the dissertation
VIII. Appendices
- Additional materials that support the research, such as tables, figures, or questionnaires.
Example of Dissertation
Here is an example Dissertation for students:
Title : Exploring the Effects of Mindfulness Meditation on Academic Achievement and Well-being among College Students
This dissertation aims to investigate the impact of mindfulness meditation on the academic achievement and well-being of college students. Mindfulness meditation has gained popularity as a technique for reducing stress and enhancing mental health, but its effects on academic performance have not been extensively studied. Using a randomized controlled trial design, the study will compare the academic performance and well-being of college students who practice mindfulness meditation with those who do not. The study will also examine the moderating role of personality traits and demographic factors on the effects of mindfulness meditation.
Chapter Outline:
Chapter 1: Introduction
- Background and rationale for the study
- Research questions and objectives
- Significance of the study
- Overview of the dissertation structure
Chapter 2: Literature Review
- Definition and conceptualization of mindfulness meditation
- Theoretical framework of mindfulness meditation
- Empirical research on mindfulness meditation and academic achievement
- Empirical research on mindfulness meditation and well-being
- The role of personality and demographic factors in the effects of mindfulness meditation
Chapter 3: Methodology
- Research design and hypothesis
- Participants and sampling method
- Intervention and procedure
- Measures and instruments
- Data analysis method
Chapter 4: Results
- Descriptive statistics and data screening
- Analysis of main effects
- Analysis of moderating effects
- Post-hoc analyses and sensitivity tests
Chapter 5: Discussion
- Summary of findings
- Implications for theory and practice
- Limitations and directions for future research
- Conclusion and contribution to the literature
Chapter 6: Conclusion
- Recap of the research questions and objectives
- Summary of the key findings
- Contribution to the literature and practice
- Implications for policy and practice
- Final thoughts and recommendations.
References :
List of all the sources cited in the dissertation
Appendices :
Additional materials such as the survey questionnaire, interview guide, and consent forms.
Note : This is just an example and the structure of a dissertation may vary depending on the specific requirements and guidelines provided by the institution or the supervisor.
How Long is a Dissertation
The length of a dissertation can vary depending on the field of study, the level of degree being pursued, and the specific requirements of the institution. Generally, a dissertation for a doctoral degree can range from 80,000 to 100,000 words, while a dissertation for a master’s degree may be shorter, typically ranging from 20,000 to 50,000 words. However, it is important to note that these are general guidelines and the actual length of a dissertation can vary widely depending on the specific requirements of the program and the research topic being studied. It is always best to consult with your academic advisor or the guidelines provided by your institution for more specific information on dissertation length.
Applications of Dissertation
Here are some applications of a dissertation:
- Advancing the Field: Dissertations often include new research or a new perspective on existing research, which can help to advance the field. The results of a dissertation can be used by other researchers to build upon or challenge existing knowledge, leading to further advancements in the field.
- Career Advancement: Completing a dissertation demonstrates a high level of expertise in a particular field, which can lead to career advancement opportunities. For example, having a PhD can open doors to higher-paying jobs in academia, research institutions, or the private sector.
- Publishing Opportunities: Dissertations can be published as books or journal articles, which can help to increase the visibility and credibility of the author’s research.
- Personal Growth: The process of writing a dissertation involves a significant amount of research, analysis, and critical thinking. This can help students to develop important skills, such as time management, problem-solving, and communication, which can be valuable in both their personal and professional lives.
- Policy Implications: The findings of a dissertation can have policy implications, particularly in fields such as public health, education, and social sciences. Policymakers can use the research to inform decision-making and improve outcomes for the population.
When to Write a Dissertation
Here are some situations where writing a dissertation may be necessary:
- Pursuing a Doctoral Degree: Writing a dissertation is usually a requirement for earning a doctoral degree, so if you are interested in pursuing a doctorate, you will likely need to write a dissertation.
- Conducting Original Research : Dissertations require students to conduct original research on a specific topic. If you are interested in conducting original research on a topic, writing a dissertation may be the best way to do so.
- Advancing Your Career: Some professions, such as academia and research, may require individuals to have a doctoral degree. Writing a dissertation can help you advance your career by demonstrating your expertise in a particular area.
- Contributing to Knowledge: Dissertations are often based on original research that can contribute to the knowledge base of a field. If you are passionate about advancing knowledge in a particular area, writing a dissertation can help you achieve that goal.
- Meeting Academic Requirements : If you are a graduate student, writing a dissertation may be a requirement for completing your program. Be sure to check with your academic advisor to determine if this is the case for you.
Purpose of Dissertation
some common purposes of a dissertation include:
- To contribute to the knowledge in a particular field : A dissertation is often the culmination of years of research and study, and it should make a significant contribution to the existing body of knowledge in a particular field.
- To demonstrate mastery of a subject: A dissertation requires extensive research, analysis, and writing, and completing one demonstrates a student’s mastery of their subject area.
- To develop critical thinking and research skills : A dissertation requires students to think critically about their research question, analyze data, and draw conclusions based on evidence. These skills are valuable not only in academia but also in many professional fields.
- To demonstrate academic integrity: A dissertation must be conducted and written in accordance with rigorous academic standards, including ethical considerations such as obtaining informed consent, protecting the privacy of participants, and avoiding plagiarism.
- To prepare for an academic career: Completing a dissertation is often a requirement for obtaining a PhD and pursuing a career in academia. It can demonstrate to potential employers that the student has the necessary skills and experience to conduct original research and make meaningful contributions to their field.
- To develop writing and communication skills: A dissertation requires a significant amount of writing and communication skills to convey complex ideas and research findings in a clear and concise manner. This skill set can be valuable in various professional fields.
- To demonstrate independence and initiative: A dissertation requires students to work independently and take initiative in developing their research question, designing their study, collecting and analyzing data, and drawing conclusions. This demonstrates to potential employers or academic institutions that the student is capable of independent research and taking initiative in their work.
- To contribute to policy or practice: Some dissertations may have a practical application, such as informing policy decisions or improving practices in a particular field. These dissertations can have a significant impact on society, and their findings may be used to improve the lives of individuals or communities.
- To pursue personal interests: Some students may choose to pursue a dissertation topic that aligns with their personal interests or passions, providing them with the opportunity to delve deeper into a topic that they find personally meaningful.
Advantage of Dissertation
Some advantages of writing a dissertation include:
- Developing research and analytical skills: The process of writing a dissertation involves conducting extensive research, analyzing data, and presenting findings in a clear and coherent manner. This process can help students develop important research and analytical skills that can be useful in their future careers.
- Demonstrating expertise in a subject: Writing a dissertation allows students to demonstrate their expertise in a particular subject area. It can help establish their credibility as a knowledgeable and competent professional in their field.
- Contributing to the academic community: A well-written dissertation can contribute new knowledge to the academic community and potentially inform future research in the field.
- Improving writing and communication skills : Writing a dissertation requires students to write and present their research in a clear and concise manner. This can help improve their writing and communication skills, which are essential for success in many professions.
- Increasing job opportunities: Completing a dissertation can increase job opportunities in certain fields, particularly in academia and research-based positions.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
Dissertation Structure & Layout 101: How to structure your dissertation, thesis or research project.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) Reviewed By: David Phair (PhD) | July 2019
So, you’ve got a decent understanding of what a dissertation is , you’ve chosen your topic and hopefully you’ve received approval for your research proposal . Awesome! Now its time to start the actual dissertation or thesis writing journey.
To craft a high-quality document, the very first thing you need to understand is dissertation structure . In this post, we’ll walk you through the generic dissertation structure and layout, step by step. We’ll start with the big picture, and then zoom into each chapter to briefly discuss the core contents. If you’re just starting out on your research journey, you should start with this post, which covers the big-picture process of how to write a dissertation or thesis .

*The Caveat *
In this post, we’ll be discussing a traditional dissertation/thesis structure and layout, which is generally used for social science research across universities, whether in the US, UK, Europe or Australia. However, some universities may have small variations on this structure (extra chapters, merged chapters, slightly different ordering, etc).
So, always check with your university if they have a prescribed structure or layout that they expect you to work with. If not, it’s safe to assume the structure we’ll discuss here is suitable. And even if they do have a prescribed structure, you’ll still get value from this post as we’ll explain the core contents of each section.
Overview: S tructuring a dissertation or thesis
- Acknowledgements page
- Abstract (or executive summary)
- Table of contents , list of figures and tables
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: Literature review
- Chapter 3: Methodology
- Chapter 4: Results
- Chapter 5: Discussion
- Chapter 6: Conclusion
- Reference list
As I mentioned, some universities will have slight variations on this structure. For example, they want an additional “personal reflection chapter”, or they might prefer the results and discussion chapter to be merged into one. Regardless, the overarching flow will always be the same, as this flow reflects the research process , which we discussed here – i.e.:
- The introduction chapter presents the core research question and aims .
- The literature review chapter assesses what the current research says about this question.
- The methodology, results and discussion chapters go about undertaking new research about this question.
- The conclusion chapter (attempts to) answer the core research question .
In other words, the dissertation structure and layout reflect the research process of asking a well-defined question(s), investigating, and then answering the question – see below.

To restate that – the structure and layout of a dissertation reflect the flow of the overall research process . This is essential to understand, as each chapter will make a lot more sense if you “get” this concept. If you’re not familiar with the research process, read this post before going further.
Right. Now that we’ve covered the big picture, let’s dive a little deeper into the details of each section and chapter. Oh and by the way, you can also grab our free dissertation/thesis template here to help speed things up.
The title page of your dissertation is the very first impression the marker will get of your work, so it pays to invest some time thinking about your title. But what makes for a good title? A strong title needs to be 3 things:
- Succinct (not overly lengthy or verbose)
- Specific (not vague or ambiguous)
- Representative of the research you’re undertaking (clearly linked to your research questions)
Typically, a good title includes mention of the following:
- The broader area of the research (i.e. the overarching topic)
- The specific focus of your research (i.e. your specific context)
- Indication of research design (e.g. quantitative , qualitative , or mixed methods ).
For example:
A quantitative investigation [research design] into the antecedents of organisational trust [broader area] in the UK retail forex trading market [specific context/area of focus].
Again, some universities may have specific requirements regarding the format and structure of the title, so it’s worth double-checking expectations with your institution (if there’s no mention in the brief or study material).

Acknowledgements
This page provides you with an opportunity to say thank you to those who helped you along your research journey. Generally, it’s optional (and won’t count towards your marks), but it is academic best practice to include this.
So, who do you say thanks to? Well, there’s no prescribed requirements, but it’s common to mention the following people:
- Your dissertation supervisor or committee.
- Any professors, lecturers or academics that helped you understand the topic or methodologies.
- Any tutors, mentors or advisors.
- Your family and friends, especially spouse (for adult learners studying part-time).
There’s no need for lengthy rambling. Just state who you’re thankful to and for what (e.g. thank you to my supervisor, John Doe, for his endless patience and attentiveness) – be sincere. In terms of length, you should keep this to a page or less.
Abstract or executive summary
The dissertation abstract (or executive summary for some degrees) serves to provide the first-time reader (and marker or moderator) with a big-picture view of your research project. It should give them an understanding of the key insights and findings from the research, without them needing to read the rest of the report – in other words, it should be able to stand alone .
For it to stand alone, your abstract should cover the following key points (at a minimum):
- Your research questions and aims – what key question(s) did your research aim to answer?
- Your methodology – how did you go about investigating the topic and finding answers to your research question(s)?
- Your findings – following your own research, what did do you discover?
- Your conclusions – based on your findings, what conclusions did you draw? What answers did you find to your research question(s)?
So, in much the same way the dissertation structure mimics the research process, your abstract or executive summary should reflect the research process, from the initial stage of asking the original question to the final stage of answering that question.
In practical terms, it’s a good idea to write this section up last , once all your core chapters are complete. Otherwise, you’ll end up writing and rewriting this section multiple times (just wasting time). For a step by step guide on how to write a strong executive summary, check out this post .
Need a helping hand?
Table of contents
This section is straightforward. You’ll typically present your table of contents (TOC) first, followed by the two lists – figures and tables. I recommend that you use Microsoft Word’s automatic table of contents generator to generate your TOC. If you’re not familiar with this functionality, the video below explains it simply:
If you find that your table of contents is overly lengthy, consider removing one level of depth. Oftentimes, this can be done without detracting from the usefulness of the TOC.
Right, now that the “admin” sections are out of the way, its time to move on to your core chapters. These chapters are the heart of your dissertation and are where you’ll earn the marks. The first chapter is the introduction chapter – as you would expect, this is the time to introduce your research…
It’s important to understand that even though you’ve provided an overview of your research in your abstract, your introduction needs to be written as if the reader has not read that (remember, the abstract is essentially a standalone document). So, your introduction chapter needs to start from the very beginning, and should address the following questions:
- What will you be investigating (in plain-language, big picture-level)?
- Why is that worth investigating? How is it important to academia or business? How is it sufficiently original?
- What are your research aims and research question(s)? Note that the research questions can sometimes be presented at the end of the literature review (next chapter).
- What is the scope of your study? In other words, what will and won’t you cover ?
- How will you approach your research? In other words, what methodology will you adopt?
- How will you structure your dissertation? What are the core chapters and what will you do in each of them?
These are just the bare basic requirements for your intro chapter. Some universities will want additional bells and whistles in the intro chapter, so be sure to carefully read your brief or consult your research supervisor.
If done right, your introduction chapter will set a clear direction for the rest of your dissertation. Specifically, it will make it clear to the reader (and marker) exactly what you’ll be investigating, why that’s important, and how you’ll be going about the investigation. Conversely, if your introduction chapter leaves a first-time reader wondering what exactly you’ll be researching, you’ve still got some work to do.
Now that you’ve set a clear direction with your introduction chapter, the next step is the literature review . In this section, you will analyse the existing research (typically academic journal articles and high-quality industry publications), with a view to understanding the following questions:
- What does the literature currently say about the topic you’re investigating?
- Is the literature lacking or well established? Is it divided or in disagreement?
- How does your research fit into the bigger picture?
- How does your research contribute something original?
- How does the methodology of previous studies help you develop your own?
Depending on the nature of your study, you may also present a conceptual framework towards the end of your literature review, which you will then test in your actual research.
Again, some universities will want you to focus on some of these areas more than others, some will have additional or fewer requirements, and so on. Therefore, as always, its important to review your brief and/or discuss with your supervisor, so that you know exactly what’s expected of your literature review chapter.

Now that you’ve investigated the current state of knowledge in your literature review chapter and are familiar with the existing key theories, models and frameworks, its time to design your own research. Enter the methodology chapter – the most “science-ey” of the chapters…
In this chapter, you need to address two critical questions:
- Exactly HOW will you carry out your research (i.e. what is your intended research design)?
- Exactly WHY have you chosen to do things this way (i.e. how do you justify your design)?
Remember, the dissertation part of your degree is first and foremost about developing and demonstrating research skills . Therefore, the markers want to see that you know which methods to use, can clearly articulate why you’ve chosen then, and know how to deploy them effectively.
Importantly, this chapter requires detail – don’t hold back on the specifics. State exactly what you’ll be doing, with who, when, for how long, etc. Moreover, for every design choice you make, make sure you justify it.
In practice, you will likely end up coming back to this chapter once you’ve undertaken all your data collection and analysis, and revise it based on changes you made during the analysis phase. This is perfectly fine. Its natural for you to add an additional analysis technique, scrap an old one, etc based on where your data lead you. Of course, I’m talking about small changes here – not a fundamental switch from qualitative to quantitative, which will likely send your supervisor in a spin!
You’ve now collected your data and undertaken your analysis, whether qualitative, quantitative or mixed methods. In this chapter, you’ll present the raw results of your analysis . For example, in the case of a quant study, you’ll present the demographic data, descriptive statistics, inferential statistics , etc.
Typically, Chapter 4 is simply a presentation and description of the data, not a discussion of the meaning of the data. In other words, it’s descriptive, rather than analytical – the meaning is discussed in Chapter 5. However, some universities will want you to combine chapters 4 and 5, so that you both present and interpret the meaning of the data at the same time. Check with your institution what their preference is.
Now that you’ve presented the data analysis results, its time to interpret and analyse them. In other words, its time to discuss what they mean, especially in relation to your research question(s).
What you discuss here will depend largely on your chosen methodology. For example, if you’ve gone the quantitative route, you might discuss the relationships between variables . If you’ve gone the qualitative route, you might discuss key themes and the meanings thereof. It all depends on what your research design choices were.
Most importantly, you need to discuss your results in relation to your research questions and aims, as well as the existing literature. What do the results tell you about your research questions? Are they aligned with the existing research or at odds? If so, why might this be? Dig deep into your findings and explain what the findings suggest, in plain English.
The final chapter – you’ve made it! Now that you’ve discussed your interpretation of the results, its time to bring it back to the beginning with the conclusion chapter . In other words, its time to (attempt to) answer your original research question s (from way back in chapter 1). Clearly state what your conclusions are in terms of your research questions. This might feel a bit repetitive, as you would have touched on this in the previous chapter, but its important to bring the discussion full circle and explicitly state your answer(s) to the research question(s).

Next, you’ll typically discuss the implications of your findings? In other words, you’ve answered your research questions – but what does this mean for the real world (or even for academia)? What should now be done differently, given the new insight you’ve generated?
Lastly, you should discuss the limitations of your research, as well as what this means for future research in the area. No study is perfect, especially not a Masters-level. Discuss the shortcomings of your research. Perhaps your methodology was limited, perhaps your sample size was small or not representative, etc, etc. Don’t be afraid to critique your work – the markers want to see that you can identify the limitations of your work. This is a strength, not a weakness. Be brutal!
This marks the end of your core chapters – woohoo! From here on out, it’s pretty smooth sailing.
The reference list is straightforward. It should contain a list of all resources cited in your dissertation, in the required format, e.g. APA , Harvard, etc.
It’s essential that you use reference management software for your dissertation. Do NOT try handle your referencing manually – its far too error prone. On a reference list of multiple pages, you’re going to make mistake. To this end, I suggest considering either Mendeley or Zotero. Both are free and provide a very straightforward interface to ensure that your referencing is 100% on point. I’ve included a simple how-to video for the Mendeley software (my personal favourite) below:
Some universities may ask you to include a bibliography, as opposed to a reference list. These two things are not the same . A bibliography is similar to a reference list, except that it also includes resources which informed your thinking but were not directly cited in your dissertation. So, double-check your brief and make sure you use the right one.
The very last piece of the puzzle is the appendix or set of appendices. This is where you’ll include any supporting data and evidence. Importantly, supporting is the keyword here.
Your appendices should provide additional “nice to know”, depth-adding information, which is not critical to the core analysis. Appendices should not be used as a way to cut down word count (see this post which covers how to reduce word count ). In other words, don’t place content that is critical to the core analysis here, just to save word count. You will not earn marks on any content in the appendices, so don’t try to play the system!
Time to recap…
And there you have it – the traditional dissertation structure and layout, from A-Z. To recap, the core structure for a dissertation or thesis is (typically) as follows:
- Acknowledgments page
Most importantly, the core chapters should reflect the research process (asking, investigating and answering your research question). Moreover, the research question(s) should form the golden thread throughout your dissertation structure. Everything should revolve around the research questions, and as you’ve seen, they should form both the start point (i.e. introduction chapter) and the endpoint (i.e. conclusion chapter).
I hope this post has provided you with clarity about the traditional dissertation/thesis structure and layout. If you have any questions or comments, please leave a comment below, or feel free to get in touch with us. Also, be sure to check out the rest of the Grad Coach Blog .

Psst… there’s more (for free)
This post is part of our dissertation mini-course, which covers everything you need to get started with your dissertation, thesis or research project.
You Might Also Like:

36 Comments
many thanks i found it very useful
Glad to hear that, Arun. Good luck writing your dissertation.
Such clear practical logical advice. I very much needed to read this to keep me focused in stead of fretting.. Perfect now ready to start my research!
what about scientific fields like computer or engineering thesis what is the difference in the structure? thank you very much
Thanks so much this helped me a lot!
Very helpful and accessible. What I like most is how practical the advice is along with helpful tools/ links.
Thanks Ade!
Thank you so much sir.. It was really helpful..
You’re welcome!
Hi! How many words maximum should contain the abstract?
Thank you so much 😊 Find this at the right moment
You’re most welcome. Good luck with your dissertation.
best ever benefit i got on right time thank you
Many times Clarity and vision of destination of dissertation is what makes the difference between good ,average and great researchers the same way a great automobile driver is fast with clarity of address and Clear weather conditions .
I guess Great researcher = great ideas + knowledge + great and fast data collection and modeling + great writing + high clarity on all these
You have given immense clarity from start to end.
Morning. Where will I write the definitions of what I’m referring to in my report?
Thank you so much Derek, I was almost lost! Thanks a tonnnn! Have a great day!
Thanks ! so concise and valuable
This was very helpful. Clear and concise. I know exactly what to do now.
Thank you for allowing me to go through briefly. I hope to find time to continue.
Really useful to me. Thanks a thousand times
Very interesting! It will definitely set me and many more for success. highly recommended.
Thank you soo much sir, for the opportunity to express my skills
Usefull, thanks a lot. Really clear
Very nice and easy to understand. Thank you .
That was incredibly useful. Thanks Grad Coach Crew!
My stress level just dropped at least 15 points after watching this. Just starting my thesis for my grad program and I feel a lot more capable now! Thanks for such a clear and helpful video, Emma and the GradCoach team!
Do we need to mention the number of words the dissertation contains in the main document?
It depends on your university’s requirements, so it would be best to check with them 🙂
Such a helpful post to help me get started with structuring my masters dissertation, thank you!
Great video; I appreciate that helpful information
It is so necessary or avital course
This blog is very informative for my research. Thank you
Doctoral students are required to fill out the National Research Council’s Survey of Earned Doctorates
wow this is an amazing gain in my life
This is so good
How can i arrange my specific objectives in my dissertation?
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- What Is A Literature Review (In A Dissertation Or Thesis) - Grad Coach - […] is to write the actual literature review chapter (this is usually the second chapter in a typical dissertation or…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Microsoft 365 Life Hacks > Writing > How AI can help you improve your thesis statement
How AI can help you improve your thesis statement
Creating a thesis statement can be a challenging undertaking. Thankfully, today’s writers can use AI to assist in the creation process. While writing with AI can feel intimidating, the right tools and knowing how to use them can enhance your thesis statement and guide you through the creation process. From generating ideas to polishing your final draft, here’s how to use AI to create a quality thesis.

Selecting a topic
AI-powered tools have access to vast databases of academic papers, journals, and other scholarly materials. If you’re trying to choose a thesis topic or questioning the viability of your current topic, AI can assist by brainstorming ideas and highlighting relevant research you can use as evidence for your claims.
Creating an initial draft
AI tools can help you create a preliminary draft of your thesis statement, which you can continue to build on as your argument and research evolve. You can request a fresh draft at any stage in the writing process, as AI only requires basic information about your topic and area of research to get started. Based on your input, the AI tool will utilize its database of knowledge to generate a thesis statement.

Get the most out of your documents with Word
Elevate your writing and collaborate with others - anywhere, anytime
Refining your thesis with AI feedback
Once you have a solid draft, utilize AI feedback to refine your writing. Ask for an analysis of your thesis statement for clarity, coherence, grammar, and more. By highlighting areas for improvement, AI can help refine your thesis statement so it accurately conveys your research focus and argument. There are a few ways this process not only improves the quality of your statement but also enhances your understanding of what makes an effective thesis:
- Efficiency. AI tools can significantly speed up the brainstorming and drafting phases, giving you more time to focus on researching and outlining your thesis. This is especially useful for tight deadlines.
- Objectivity. AI feedback is based on data and algorithms that can provide a largely unbiased perspective on the quality of your thesis statement. This objective analysis can help you improve your thesis and overall writing.
- Consistency. AI tools can help you align the rest of your paper with your initial thesis statement to ensure consistency throughout your work.
Choosing the right AI tool for academic writing
When seeking an AI assistant for thesis drafting, choose AI tools, including GPTs, designed for professional or academic writing . AI applications that are familiar with academia can offer feedback and suggestions tailored to fit the conventions of scholarly writing.
AI has revolutionized academic writing, offering powerful tools for creating and refining thesis statements. By leveraging AI tools, you can achieve a higher level of clarity and persuasiveness in your work, so try them out the next time you need to write an academic paper!
Get started with Microsoft 365
It’s the Office you know, plus the tools to help you work better together, so you can get more done—anytime, anywhere.
Topics in this article
More articles like this one.

What is independent publishing?
Avoid the hassle of shopping your book around to publishing houses. Publish your book independently and understand the benefits it provides for your as an author.

What are literary tropes?
Engage your audience with literary tropes. Learn about different types of literary tropes, like metaphors and oxymorons, to elevate your writing.

What are genre tropes?
Your favorite genres are filled with unifying tropes that can define them or are meant to be subverted.

What is literary fiction?
Define literary fiction and learn what sets it apart from genre fiction.

Everything you need to achieve more in less time
Get powerful productivity and security apps with Microsoft 365

Explore Other Categories

Search wm.edu

- Arts & Sciences
- Anthropology
Honors students raise the “Barr” in inaugural Thesis in Three competition
https://www.wm.edu/as/charlescenter/about/news/honors-students-raise-the-barr-in-inaugural-thesis-in-three-competition.php

“As a Texan, the public school system made sure that I would always remember the Alamo,” explained government and anthropology major Erin Cearlock ’24, as she opened her “ Thesis in Three ” talk at the Graduate & Honors Research Symposium March 22 in Sadler.
“On the Pacific island of Rurutu, some 6,000 miles away in French Polynesia, the communities’ histories are at risk of not being remembered – or even worse – not remembered on their own terms,” Cearlock said. Cearlock reflected upon oral histories she collected and documented while on a Charles Center Honors Fellowship in Rurutu last summer. “I will always remember the Alamo,” Cearlock concluded, before honoring locals on the island who hope “that future Rurutuans will always remember the real Rurutu.” So began and ended Cearlock’s three-minute distillation of her 10,000-word Honors thesis, inviting the audience to journey through history and memory from Texas to Rurutu and back. The around-the-world trip in less than 180 seconds earned her the inaugural Barr Prize in public speaking and an accompanying $500 award. Though challenging and time consuming, the opportunity to participate in the event was well worth it, according to Cearlock. “This competition was really important for helping me to understand what the main goals of my research were and how to convey academic research to a non-academic audience,” she said.

Follow W&M on Social Media:
Williamsburg, Virginia
- Accessibility
- Consumer Information
- Non-Discrimination Notice
- Privacy & Security

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 3: Look for books and articles. Step 4: Find a niche. Step 5: Consider the type of research. Step 6: Determine the relevance. Step 7: Make sure it's plausible. Step 8: Get your topic approved. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about dissertation topics.
Here is a list of engaging dissertation topics in accounting: "Financial accounting's contribution to business strategy development.". "The things to take into account when investing in financial markets.". "How project accounting uses risk factors analysis.". "Systematic examination of art galleries cost accounting.".
So, you're finally nearing the end of your degree and it's now time to find a suitable topic for your dissertation or thesis. Or perhaps you're just starting out on your PhD research proposal and need to find a suitable area of research for your application proposal.. In this post, we'll provide a straightforward 6-step process that you can follow to ensure you arrive at a high-quality ...
Gender Dissertation Topics. The Impact of Gender Stereotypes on Career Choices. The Role of Gender-Based Violence in Perpetuating Gender Inequality. An Analysis of the Impacts of Intersectionality on Women of Color. An Investigation into the Relationship Between Politics and Women's Access to Healthcare.
A research topic is the subject of a research project or study - for example, a dissertation or thesis. A research topic typically takes the form of a problem to be solved, or a question to be answered. A good research topic should be specific enough to allow for focused research and analysis. For example, if you are interested in studying ...
How To Write A Dissertation: 8 Steps. Clearly understand what a dissertation (or thesis) is. Find a unique and valuable research topic. Craft a convincing research proposal. Write up a strong introduction chapter. Review the existing literature and compile a literature review.
The first step to writing a dissertation fast is to choose a topic to investigate.However, coming up with a relevant topic for the project can be hard and agonizing if you don't know how to go about it. That's why in this guide, you'll learn exactly how to choose dissertation topics for your project so you can get started with research as soon as possible.
The dissertation is one of the most testing academic assignments for undergraduate, graduate, or doctoral students. When writing a dissertation, you are expected to answer a particular research question and derive findings that can have implications for future research.. Nevertheless, writing can be a daunting task because dissertations are complex academic documents with intricate rules.
Choosing a dissertation topic can be both challenging and rewarding. While there are many factors in the process of your research you cannot change - time, resources, and institutional requirements - you can impact your dissertation topic by taking time to understand how you really want to spend the weeks and months, and possibly years ...
Here are ten good topics for a dissertation. Impact of the Internet on the social and spiritual values of students. Fostering a democratic culture of adolescents as the main function of an educational organization. Cultural self-determination of high school students in teaching social and humanitarian disciplines.
A dissertation should be based on an original research topic of your choosing. Your goal is to choose a dissertation topic that addresses an important, unanswered question in your field. The dissertation is likely to be a major dimension of your graduate school experience. This is especially true for students pursuing a degree at the doctoral ...
A dissertation proposal describes the research you want to do: what it's about, how you'll conduct it, and why it's worthwhile. You will probably have to write a proposal before starting your dissertation as an undergraduate or postgraduate student. A dissertation proposal should generally include: An introduction to your topic and aims
Start with the literature and focus on FRIN. Leverage your university's past dissertation database. Prioritize topics/areas that you have a genuine interest in. Play to your strengths in terms of topic and methodology. Keep it simple. 1. Start with the literature and focus on FRIN. The starting point for finding a solid research topic is to ...
Revised on 5 May 2022. A dissertation is a large research project undertaken at the end of a degree. It involves in-depth consideration of a problem or question chosen by the student. It is usually the largest (and final) piece of written work produced during a degree. The length and structure of a dissertation vary widely depending on the ...
Psychological Dissertation Topics. - The relationship between expectation, neurotic fear, frustration, and pain. - Depression and its impact on student performance. - Psychological treatment of the child's parents in the autistic spectrum. - The influence of the divorce of parents on the early development of the child.
1. Propose a Dissertation Topic. Near the beginning of a Doctor of Education program, you'll be expected to identify a dissertation topic that will require substantial research. This topic should revolve around a unique issue in education. Universities will often ask you to provide an idea for your topic when you're applying to the doctoral ...
The final step in a PhD or Master's course is the submission of a dissertation.A dissertation is a research paper that summarises the research conducted and includes findings either on a question or a topic chosen by the student. It is important as it demonstrates a student's knowledge of the subject and ability to use research methods to define a topic.
Dissertation typically involves the exploration of a particular research question or topic in-depth, and it requires students to conduct original research, analyze data, and present their findings in a scholarly manner. It is often the culmination of years of study and represents a significant contribution to the academic field.
So, you've got a decent understanding of what a dissertation is, you've chosen your topic and hopefully you've received approval for your research proposal.Awesome! Now its time to start the actual dissertation or thesis writing journey. To craft a high-quality document, the very first thing you need to understand is dissertation structure.In this post, we'll walk you through the ...
Selecting a topic. AI-powered tools have access to vast databases of academic papers, journals, and other scholarly materials. If you're trying to choose a thesis topic or questioning the viability of your current topic, AI can assist by brainstorming ideas and highlighting relevant research you can use as evidence for your claims.. Creating an initial draft
In the humanities and social sciences, many people believe that completing a Ph.D. involves spending years conducting research to write a dissertation that "extends the boundary of human knowledge.". But the real story is quite different from that. Although key, fulfilling your research project is the least important aspect of your Ph.D.
So began and ended Cearlock's three-minute distillation of her 10,000-word Honors thesis, inviting the audience to journey through history and memory from Texas to Rurutu and back. The around-the-world trip in less than 180 seconds earned her the inaugural Barr Prize in public speaking and an accompanying $500 award.