- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by

Open Letters: Our New Opinion-Writing Contest
We invite students to write public-facing letters to people or groups about issues that matter to them. Contest dates: March 13 to May 1.
By The Learning Network
What’s bothering you? Who could do something about it? What could you say to them that would persuade them to care, or to make change?
And … what if we all read your letter? How could you make us care too?
These are some of the questions we’re asking you to ponder for our new Open Letter Contest. An open letter is a published letter of protest or appeal usually addressed to an individual, group or institution but intended for the general public. Think of the many “Dear Taylor Swift” open letters you can find online and on social media: Sure, they’re addressed to Ms. Swift, but they’re really a way for the writer to share opinions and feelings on feminism, or ticket sales, or the music industry, or … the list goes on.
As you might already know if you’ve read Martin Luther King’s famous Letter From Birmingham Jail , an open letter is a literary device. Though it seems on the surface to be intended for just one individual or group, and therefore usually reads like a personal letter (and can make readers feel they are somehow “listening in” on private thoughts), it is really a persuasive essay addressed to the public. This recent letter signed by over 1,000 tech leaders about the dangers of A.I. , this funny 2020 letter addressed to Harry and Meghan , and this video letter from young Asian Americans to their families about Black Lives Matter are all examples of the tradition.
Now we’re inviting you to try it yourself. Write your own open letter, to anyone you like on any issue you care about, as long as it is also appropriate and meaningful for a general Times audience.
Whom should you write to? What should you say? How do open letters work?
The rules and FAQ below, along with our Student Opinion forum and related how-to guide , can walk you through ways to get started.
This is a new contest and we expect questions. Please ask any you have in the comments and we’ll answer you there, or write to us at [email protected]. And, consider hanging this PDF one-page announcement on your class bulletin board.
Here’s what you need to know:
The challenge, a few rules, resources for students and teachers, frequently asked questions, submission form.
Write an open letter to a specific audience that calls attention to an issue or problem and prompts reflection or action on it.
Whether you choose to write to your parents, teachers, school board members or mayor; a member of Congress; the head of a corporation; an artist or entertainer; or a metonym like “Silicon Valley” or “The Kremlin,” ask yourself, What do I care about? Who can make changes, big or small, local or global, to address my issue or problem? What specifically do I want my audience to understand or do? And how can I write this as an “open letter,” compelling not just to me and the recipient, but to the general audience who will be reading my words?
The Times has published numerous open letters over the years, to both famous and ordinary people. You can find a long list of free examples in our related guide .
This contest invites students to express themselves and imagine that their words can lead to real change.
Your open letter MUST:
Focus on an issue you care about and with which you have some experience. You can write about almost anything you like, whether it’s a serious issue like bullying , or something more lighthearted like why bugs deserve respect , but we have found over the years that the most interesting student writing grows out of personal experience. Our related Student Opinion forum and how-to guide can help you come up with ideas.
Address a specific audience relevant to the issue. Choose an individual, group, organization or institution who is in a position to make change or promote understanding about your topic.
Call for action, whether the change you seek is something tangible , like asking Congress to enact a law or demanding a company stop a harmful practice, or something more abstract, like inviting your audience to reflect on something they may have never considered.
Be suitable and compelling for a wide general audience . An open letter simultaneously addresses an explicit recipient — whether Joe Biden or your gym teacher — as well as us, the general public, your implicit audience. Though your letter might seem to be meant just for one person, it is really trying to persuade all readers. Make sure you write it in such a way that it is relevant, understandable, appropriate and meaningful for anyone who might come across it in The New York Times. (Again, our related guide can help.)
Be written as a letter, in a voice and tone that is appropriate for both your audience and purpose. Are you simply taking an argumentative essay you’ve written for school already and slapping a “Dear X” on top of it and a “Sincerely, Y” on the bottom? No. A letter — even an open letter — is different from a formal essay, and your writing should reflect that. Can you be informal? Funny? If that makes sense for your purpose and audience, then yes, please.
Our related guide, and the many examples we link to, can help you think about this, but we hope the format of a letter will let you loosen up a bit and express yourself in your natural voice. (For example, you’ll be writing as “I” or “we,” and addressing your letter’s recipient as “you.”)
Also attempt to persuade a general audience. Though it is written in the form of a letter, it is an opinion piece, and you are trying to make a case and support it with evidence, as you would any argument. Remember that you are trying to change hearts and minds, so you’ll be drawing on the same rhetorical strategies as you might have for our long-running editorial contest . (Again, more on this in the related guide .)
Make your case in 460 words or fewer. Your title and sources are not part of the word count.
Inform with evidence from at least two sources, including one from The Times and one from outside The Times. We hope this contest encourages you to deepen your understanding of your topic by using multiple sources, ideally ones that offer a range of perspectives. Just make sure those sources are trustworthy .
Because this is a letter, not a formal essay, we are not asking you to provide in-text citations, but we will be asking you to list the sources you used — as many as you like — in a separate field that does not contribute to your word count. Keep in mind, however, that if you include evidence from those sources, our readers (and judges) should always be able to tell where it came from. Be careful to put quotations around any direct quotes you use, and cite the source of anything you paraphrase.
In addition to the guidelines above, here are a few more details:
You must be a student ages 13 to 19 in middle school or high school to participate , and all students must have parent or guardian permission to enter. Please see the F.A.Q. section for additional eligibility details.
The writing you submit should be fundamentally your own — it should not be plagiarized, created by someone else or generated by artificial intelligence.
Your open letter should be original for this contest. That means it should not already have been published at the time of submission, whether in a school newspaper, for another contest or anywhere else.
Keep in mind that the work you send in should be appropriate for a Times audience — that is, something that could be published in a family newspaper (so, please, no curse words).
You may work alone or in groups , but students should submit only one entry each.
You must also submit a short, informal “artist’s statement” as part of your submission, that describes your writing and research process. These statements, which will not be used to choose finalists, help us to design and refine our contests. See the F.A.Q. to learn more.
All entries must be submitted by May 1, at 11:59 p.m. Pacific time using the electronic form at the bottom of this page.
Use these resources to help you write your open letter:
Our step-by-step guide : To be used by students or teachers, this guide walks you through the process of writing an open letter.
A list of free examples of open letters published both in and outside The New York Times, which you can find in our step-by-step guide .
A writing prompt: To Whom Would You Write an Open Letter? This prompt offers students a “rehearsal space” for thinking about to whom they’d like to write, the reason they’re writing and why they think that issue is important — not only for the recipient but also for a wider audience.
Argumentative writing prompts: We publish new argumentative writing prompts for students each week in our Student Opinion and Picture Prompt columns. You can find them all, as they publish, here , or many of them, organized by topic, in our new collection of over 300 prompts .
Argumentative writing unit: This unit includes writing prompts, lesson plans, webinars and mentor texts. While it was originally written to support our Student Editorial Contest , the resources can help students make compelling arguments, cite reliable evidence and use rhetorical strategies for their open letters as well.
Our contest rubric : This is the rubric judges will use as they read submissions to this contest.
Below are answers to your questions about writing, judging, the rules and teaching with this contest. Please read these thoroughly and, if you still can’t find what you’re looking for, post your query in the comments or write to us at [email protected].
Questions About Writing
How is this contest different from your long-running Editorial Contest? Can we still use those materials?
For a decade we ran an editorial contest , and the students who participated wrote passionately about all kinds of things — A.I. , fast fashion , race , trans rights , college admissions , parental incarceration , fan fiction , snow days , memes , being messy and so much more . You can still write about the issues and ideas that fire you up — it’s just that this time around you’ll be framing your work as a letter to a person who has the power to make change on or bring understanding to that issue.
Our related guide has more about the differences between a traditional opinion essay and an open letter, but the many materials we developed for that earlier contest are also woven into the guide, as concepts like ethos, logos and pathos are still very much relevant to this challenge.
I have no idea what to write about. Where should I start?
Our Student Opinion forum can help via its many questions that encourage you to brainstorm both the audience you might write to and the topics you’d like to address.
Can I actually send my open letter?
You can! Just wait until after you have submitted your work to us to do so. (As always for our contests, you retain the copyright to the piece you submit, and can do whatever you like with it.)
Questions About Judging
How will my open letter be judged?
Your work will be read by New York Times journalists, as well as by Learning Network staff members and educators from around the United States. We will use this rubric to judge entries.
What’s the “prize”?
Having your work published on The Learning Network and being eligible to have your work published in the print New York Times.
When will the winners be announced?
About 8-10 weeks after the contest has closed.
My piece wasn’t selected as a winner. Can you tell me why?
We typically receive thousands of entries for our contests, so unfortunately, our team does not have the capacity to provide individual feedback on each student’s work.
QUESTIONS ABOUT THE RULES
Who is eligible to participate in this contest?
This contest is open to students ages 13 to 19 who are in middle school or high school around the world. College students cannot submit an entry. However, high school students (including high school postgraduate students) who are taking one or more college classes can participate. Students attending their first year of a two-year CEGEP in Quebec Province can also participate. In addition, students age 19 or under who have completed high school but are taking a gap year or are otherwise not enrolled in college can participate.
The children and stepchildren of New York Times employees are not eligible to enter this contest. Nor are students who live in the same household as those employees.
Can I have someone else check my work?
We understand that students will often revise their work based on feedback from teachers and peers. That is allowed for this contest. However, be sure that the final submission reflects the ideas, voice and writing ability of the student, not someone else.
Do I need a Works Cited page?
Yes. We provide you with a separate field to list the sources you used to inform or write your open letter. You’re allowed to format your list however you want; we will not judge your entry based on formatting in this section. Internal citations in your letter are not necessary.
Why are you asking for an Artist’s Statement about our process? What will you do with it?
All of us who work on The Learning Network are former teachers. One of the many things we miss, now that we work in a newsroom rather than a classroom, is being able to see how students are reacting to our “assignments” in real time — and to offer help, or tweaks, to make those assignments better. We’re asking you to reflect on what you did and why, and what was hard or easy about it, in large part so that we can improve our contests and the curriculum we create to support them. This is especially important for new contests, like this one.
Another reason? We have heard from many teachers that writing these statements is immensely helpful to students. Stepping back from a piece and trying to put into words what you wanted to express, and why and how you made artistic choices to do that, can help you see your piece anew and figure out how to make it stronger. For our staff, they offer important context that help us understand individual students and submissions, and learn more about the conditions under which students around the world create.
Whom can I contact if I have questions about this contest or am having issues submitting my entry?
Leave a comment on this post or write to us at [email protected].
QUESTIONS ABOUT TEACHING WITH THIS CONTEST
Do my students need a New York Times subscription to access these resources?
No. All of the resources on The Learning Network are free.
If your students don’t have a subscription to The New York Times, they can also get access to Times pieces through The Learning Network . All the activities for students on our site, including mentor texts and writing prompts, plus the Times articles they link to, are free. Students can search for articles using the search tool on our home page.
How do my students prove to me that they entered this contest?
After they press “Submit” on the form below, they will see a “Thank you for your submission.” line appear. They can take a screenshot of this message. Please note: Our system does not currently send confirmation emails.
Please read the following carefully before you submit:
Students who are 13 and older in the United States or the United Kingdom, or 16 and older elsewhere in the world, can submit their own entries. Those who are 13 to 15 and live outside the United States or the United Kingdom must have an adult submit on their behalf.
All students who are under 18 must provide a parent or guardian’s permission to enter.
You will not receive email confirmation of your submission. After you submit, you will see the message “Thank you for your submission.” That means we received your entry. If you need proof of entry for your teacher, please screenshot that message.
If you have questions about your submission, please write to us at [email protected] and provide the email address you used for submission.
How to Write an Open Letter: A Comprehensive Guide
.png)
Did you know that the first ever open letter in history was created in 1640? A group of English nobles wrote to King Charles I to voice their opinion against the absolutist rule of the king and his dislike of the critics. Of course, at that time, this act was seen as something amazing. The letter was quickly distributed across England and ultimately led to the English Civil War.
Some would say that not much has changed since then, and the methods of raising public awareness are still the same. You can write an open letter on any topic that worries you as long as you find your target audience.
What Is an Open Letter?
First, let’s start with the theoretical foundation so we are on the same page. Open letter can be a powerful instrument in spreading awareness about something that worries you. They can mobilize people to take action or to call for social justice, peace, and human rights. Basically, an open letter is intended for either a wide audience or for one person.
Apart from personal use, open letters can be published in periodicals, journals, or even online on official websites. There are many famous open letter examples in history that you might have already known about, but we will explore them later.
In this guide, we will present all the features and nuances of open letters. This type of correspondence might be difficult to write, so it’s always better to hire a writer on EssayHub! We will also take a closer look at open letter examples, such as the case of Elisabeth Deluca.
Reasons and Goals for Writing an Open Letter
No matter what the reason, the main goal of open letters is to make a difference in the world. Usually, they are addressed to government officials, corporate executives, the general public, or even celebrities. Let’s take a look at what are the purposes of creating an open letter:
.png)
- To raise awareness about an important issue that is often ignored;
- To call for action on a specific issue, like climate change.
- To demonstrate a strong opinion or point of view, like criticism.
- To expose or call out a powerful person, to they can take accountability for their actions.
- To inspire others to take action on an important issue, for example, to vote or to donate.
It’s pretty obvious all of these purposes are of paramount importance to the general public. You can use open letters to amplify the voices of those who often remain unheard.
Writing an Open Letter: Pros and Cons
Before we explore how to write an open letter, it’s crucial to know what its features and strong and weak points are. Writing an open letter is not an easy task, so you have a lot to consider. You need to consider the pros and cons before deciding whether to write one.
- they can reach a wide audience;
- they can start an active discussion on a certain topic;
- they can be a way to share your story;
- they can be a way to connect with other individuals with the same shared values.
At the same time, there are some nuances to crafting an open letter, as for any other type of paper. You can ask for help from a write my college essay for me services online in case you are overwhelmed!
- they are time-consuming to write;
- they put you in the spotlight;
- they might not get the reaction that you hoped for.

How to Write an Open Letter: a Guide
In most cases, open letter format is pretty straightforward. You need to explain the reason for writing your paper, the main issue at hand, and the solution to this issue. But first, let’s discuss the target audience for your letter.
How to Choose a Target Audience for Open Letters
You need to thoroughly think about who will be reading your letter. Here are some questions that you can ask:
- Who will be interested in the issue you are writing about?
- Who has the power to make a difference on this issue?
- Who is most likely to be convinced by your message?
Also, it’s critical to use the full titles of officials and government representatives in your letter.
Correct Open Letter Format
Right now, there is no one-size-fits-all format for this type of correspondence. Every issue and reason for writing an open letter is unique. This is why you probably have to adjust your writing process a lot. On the other hand, there are some general guidelines on how to format an open letter.
.png)
Start with a strong introduction. You need to capture the attention of the readers immediately, so the first letter should be captivating and intriguing. You want your readers to feel your pain and fight for your cause.
Explain your purpose. After grabbing the attention of your readers, explain why you wrote this letter at this time. What is the main issue that you are thinking about, and what do you propose to do about it?
Give evidence to support your claims. Of course, using strong words and phrases is important. But it’s always better to go with structured evidence instead of emotional claims. Your evidence can include statistics, research studies, or even personal stories.
End with a call to action. This is the place where you tell your readers what you want them to do once again. Maybe it’s signing a petition, donating to a charity, or contacting elected officials.
Step 1. Defining and Presenting the Issue
Here, you need to convince the audience that your problem is significant and it has a negative impact on people around you. When presenting the issue, it is important to be specific and to provide evidence to support your claims. You can use statistics, research studies, or personal stories to add to the overall impact of the issue. Here is what you can explore:
- What is the purpose of an open letter?
- What is the problem?
- Who is affected by it?
- Why is it important to the general public?
Also, remember to be respectful to all people who are connected to your cause. Try to avoid personal attacks, even when you disagree with something. This will show that you can remain professional in spite of the circumstances.
Step 2. Explaining your Motivation and Connection to the Cause
The second step in this process is to create a connection between you, your cause, and your readers. It’s always a good idea to present your personal connection to the issue and why you are passionate about it. For example, sharing your personal story is a powerful way to establish a relationship with the audience. They always like to know the face behind a letter!
When thinking about how to write an open letter, consider your own feelings in this case. What would you like to read if you were a government official? What would make you care about the presented issue? What would make you build trust and credibility with the writer? For this, try to get back to your target audience and adjust your letter to them.
Step 3. Presenting the Solution to the Problem
Now that you already hooked the reader with your issue, it’s time to present your solution. It’s your choice whether to write about specific actions or just to raise awareness about your cause. Still, you need to include a call to action and say what you want your reader to do after reading an open letter. For this part, you shouldn’t be too authoritative but rather encouraging.
Here are some examples of sentences that encourage people to take action:
- I urge you to take the following actions…
- I ask you to support policies…
- I encourage you to start an active discussion about…
- Together, we can change our future…
As you can see, it’s not about telling people what to do.
Famous Open Letter Examples in History
Open letter to Elisabeth DeLuca, Subway owner
In 2022, a group of workers at DeLuca's Coffee Roasters wrote an open letter to the company's founder and CEO, Elisabeth DeLuca. Elisabeth DeLuca is an entrepreneur and the owner of several companies, including Subway and DeLuca’s Coffee Roasters.
She has been featured in many magazines and newspapers, where she has been praised for her success in the coffee industry. However, in 2022, something changed when more than 100 people accused her of abusive behavior and toxic working conditions. The letter said that DeLuca regularly screamed at her workers.
People also said that she created a climate of fear and abuse in the workplace. The purpose of the open letter was to raise awareness of the alleged abuse at DeLuca's Coffee Roasters and to pressure DeLuca to change her behavior. As a result of a reaction from the community, DeLuca resigned as CEO.

Open letter to President Biden on the climate crisis
This is an excellent example of scientists taking a stand. In 2023, more than 1,000 researchers and climate experts urged President Biden to take more action on climate change. They expressed their opinion about a climate catastrophe and proposed their plan of action for the future.
Correspondence between Einstein and Freud
In 1932, Albert Einstein wrote a letter ‘Why War?’ to Sigmund Freud. This was not a typical modern format of an open letter but rather a dialogue about the psychological roots of armed conflict.
So there you have it, everything you need to know about open letters. As you can see, this task can be challenging. You need to put your thoughts on paper in such a way that your readers feel inspired to take action. It’s always a good idea to hire a writer on EssayHub to get help with the writing part. Expert writers will make your text more persuasive without losing meaning!
Using an open letter as a tool for change might not be as glamorous as you think. On the other hand, this is a powerful platform for raising awareness, voicing your concerns, and educating the general public.

- Plagiarism Report
- Unlimited Revisions
- 24/7 Support
The Correspondence Project: A Lesson of Letters

- Resources & Preparation
- Instructional Plan
- Related Resources
Students practice writing effective letters for a variety of real-life situations, such as responding to a prompt on a standardized test, corresponding with distant family members, or communicating with a business. They begin by reviewing the differences between business and friendly letter formats, using examples and a Venn diagram. Next, students write two letters, choosing from a list of prompts that include letters for varying audiences and purposes. After completing drafts and revisions, students complete their final versions using an online tool.
Featured Resources
Letter Generator : This online tool allows students to read about the parts of a letter. They can then write and print their own friendly or business letter. Interactive Venn Diagram : Use this online tool to organize ideas for a compare and contrast essay, or while reading to compare and contrast two works of literature.
From Theory to Practice
In Both Art and Craft: Teaching Ideas That Spark Learning , Diana Mitchell explains that teaching is "about gently uncovering ways for students to find their way into the learning by making connections within themselves" (23). Students are more likely to "find their way into learning" when assignments have clear application to real-world tasks. As Mitchell explains it, these types of assignments, "have a ‘nowness' about them; there is a reason for an importance to doing them at this point in time" (24). In addition, personal connections are made more easily when students have a degree of choice within a writing assignment. Mitchell triumphs assignments that "are fun and interesting," as well as those that "provide lots of possibilities and tap into . . . imagination" (24). In that spirit, this lesson in letter writing provides a functional application for writing and, at the same time, encourages students to make personal connections through a variety of letter topics. Further Reading
Common Core Standards
This resource has been aligned to the Common Core State Standards for states in which they have been adopted. If a state does not appear in the drop-down, CCSS alignments are forthcoming.
State Standards
This lesson has been aligned to standards in the following states. If a state does not appear in the drop-down, standard alignments are not currently available for that state.
NCTE/IRA National Standards for the English Language Arts
- 3. Students apply a wide range of strategies to comprehend, interpret, evaluate, and appreciate texts. They draw on their prior experience, their interactions with other readers and writers, their knowledge of word meaning and of other texts, their word identification strategies, and their understanding of textual features (e.g., sound-letter correspondence, sentence structure, context, graphics).
- 4. Students adjust their use of spoken, written, and visual language (e.g., conventions, style, vocabulary) to communicate effectively with a variety of audiences and for different purposes.
- 5. Students employ a wide range of strategies as they write and use different writing process elements appropriately to communicate with different audiences for a variety of purposes.
- 6. Students apply knowledge of language structure, language conventions (e.g., spelling and punctuation), media techniques, figurative language, and genre to create, critique, and discuss print and nonprint texts.
- 8. Students use a variety of technological and information resources (e.g., libraries, databases, computer networks, video) to gather and synthesize information and to create and communicate knowledge.
- 11. Students participate as knowledgeable, reflective, creative, and critical members of a variety of literacy communities.
- 12. Students use spoken, written, and visual language to accomplish their own purposes (e.g., for learning, enjoyment, persuasion, and the exchange of information).
Materials and Technology
Computers with Internet access for student use
- Contemplating Correspondence
- Contemplating Correspondence Key
- Correspondence Project Prompts
- Business and Friendly Letter Samples
- Rubric for Correspondence Project
- Venn Diagram
Preparation
- Review the Correspondence Project Prompts and determine the requirements for the class. Decide on the number of letters students will write as well as any letters that you will require. You may wish to choose specific prompts to ensure that students write at least one letter using business format and one using friendly format. You can also require 2 letters and allow students to choose additional letters freely.
- Venn Diagram handout (if computer access is not available)
- Make one copy of the Contemplating Correspondence Key for yourself.
- Make overhead transparencies of the Business and Friendly Letter Samples and the Venn Diagram handout (needed only if computer access is not available).
- Test the interactive Venn Diagram and Letter Generator on your computers to familiarize yourself with the tools and ensure that you have the Flash plug-in installed. You can download the plug-in from the technical support page .
Student Objectives
Students will
- review examples of business and friendly letters.
- compare business and friendly letter formats.
- write letters in response to specific writing prompts.
- apply knowledge of language structure and conventions.
- adjust their use of writing conventions, style, and vocabulary for a variety of audiences and purposes.
Session One
- Distribute copies of the Contemplating Correspondence sheet.
- Explain that most questions have more than one “correct” answers. Suggest that students leave any questions that they are unsure about blank and return to them after the class discussion of the sheets.
- Allow students a few minutes to respond.
- Review the students' responses to the Contemplating Correspondence sheet, using the questions as a springboard for a brief class discussion about writing letters. Refer to the Contemplating Correspondence Key to ensure students recognize the most basic details.
- Tell students that they will be completing a letter writing project. Before writing the letters, however, they will review standard business and friendly letter formats.
- Discuss the difference between the friendly letter format and a friendly tone. Explain that people can use the friendly letter format for letters that have a more formal tone (e.g., a condolence letter to someone the author does not know well).
- Share the Friendly Letter Sample by distributing copies to students, and displaying the sample using an overhead transparency.
- Have students take turns reading the body of the letter aloud.
- Identify the main parts of a friendly letter (heading, greeting, body, closing, and signature) by allowing student volunteers to take turns using a non-permanent transparency marker to label each of the five main parts. Ask students to label their handouts in the same manner.
- Use Writing the Basic Business Letter from the Purdue OWL to supplement the discussion of the parts of letters.
Session Two
- Review the information covered in Session One by asking students what they remember about friendly letter format.
- Tell students that during this session, they will be reviewing business letter format.
- Ask students if business letter format is for use only by businesses. Use student responses as a springboard for discussion on the various uses for business letters (e.g., applying for employment, expressing a consumer complaint to company).
- Share the Business Letter Sample by distributing copies to students and displaying the sample by using an overhead transparency.
- Identify the main parts of a business letter (heading, inside address, greeting, body, closing, and signature) by allowing student volunteers to take turns using a non-permanent transparency marker to label each of the six main parts. Instruct students to label their handouts in the same manner.
- Again, you can use Writing the Basic Business Letter from the Purdue OWL to supplement the discussion of the parts of letters.
- Discuss the differences between the full-block and modified-block formats. Point to the additional sample letters from the Purdue OWL or Sample Complaint Letter to discuss the formats.
- Have students compare friendly and business letter formats using the interactive Venn Diagram . Teachers also may wish to have students complete a separate Venn Diagram to compare and contrast full-block and modified-block formats. If computer access is not available, distribute copies of the Venn Diagram handout to students and display the diagram using an overhead transparency. Allow students to complete the diagram together by allowing student volunteers to take turns using a non-permanent transparency maker to identify common and dissimilar traits between the two letter formats. Students should follow along by filling in their own diagrams on their handouts.
- Distribute the Correspondence Project Prompts and the Rubric for Correspondence Project to students. Explain the requirements you have chosen for the project, giving students details on the number of letters they should write and any required prompts they must respond to.
- Review the Rubric for Correspondence Project and ensure that students understand the expectations for the project.
- In the remaining time, have students begin the process of choosing letters to write and drafting their correspondence. Explain that students will continue this work during the next class session.
Session Three
- Review the Correspondence Project Prompts and the Rubric for Correspondence Project . Answer any questions regarding the project.
- Tell students that the goal for this session is to complete drafts of at least two letters.
- Make newspapers, scissors, and tape available to students for use with the first prompt (a job application letter).
- Circulate among students as they work, and assist as needed.
- Students who require extra time to complete their drafts should do so as homework.
Session Four
- Check for completion of at least two letters.
- Review the Correspondence Project Prompts and the Rubric for Correspondence Project .
- Tell students that the goal for this session is to complete drafts for the remaining letters.
- Students who require extra time to complete their letters should do so as homework.
- Ask students to bring all completed drafts with them to the next class session.
Session Five
- Review the Rubric for Correspondence Project .
- Introduce students to the interactive Letter Generator , and explain that they will be revising their drafts and using this tool to create final versions of their work.
- Allow students time to revise their drafts. Revision options are endless and open to teacher preference. Students may proofread and revise independently, through “pair and share” edit sessions with classmates, or by basing revisions on teacher remarks and comments if the teacher wishes to collect the drafts prior to Session Five and return them with comments at the beginning of the session.
- Students should complete their draft revisions and create final versions using the interactive Letter Generator .
- If needed, add a sixth session to the lesson to allow students time to complete their letters using the interactive Letter Generator .
- Communicating on Local Issues: Exploring Audience in Persuasive Letter Writing
- Draft Letters: Improving Student Writing through Critical Thinking
- E-pals Around the World
- Exploring Literature through Letter-Writing Groups
- Persuading an Audience: Writing Effective Letters to the Editor
- Worth Its Weight: Letter Writing with “The Things They Carried”
- Consider introducing pen pals or “key pals” into your classroom community. Many programs are available online and can easily be located through most of the popular search engines using the keyword search “school pen pals.”
- Depending on the grade and skill level of students, a mini-lesson on properly addressing an envelope and folding a letter might be a worthwhile addition to this project.
- Use the online interactive Postcard Creator as a lesson extension or letter alternative. Many of the friendly letter prompts would adapt easily to a postcard format.
- The EDSITEment lesson I'm Gonna Sit Right Down and Write Someone a Letter offers a collection of historically significant letters and can provide a useful extension to this lesson.
Student Assessment / Reflections
- Assess students’ understanding of the purposes and formats of business and friendly letters through observation and anecdotal notes of student participation during classroom discussions.
- Assess students’ use of interactive tools through observation and anecdotal notes of student work while using the interactive tools.
- Check for proper completion of the interactive Venn Diagram contrasting letter formats.
- Use the Rubric for Correspondence Project to assess the letters students have written.
- Student Interactives
- Calendar Activities
The Letter Generator is a useful tool for students to learn the parts of a business or friendly letter and then compose and print letters for both styles of correspondence.
The Postcard Creator helps students learn to identify all the typical parts of a postcard, and then generate their own postcard messages by typing information into letter templates. After printing their texts, students can illustrate the front of their postcards in a variety of ways, including drawing, collage, and stickers.
This interactive tool allows students to create Venn diagrams that contain two or three overlapping circles, enabling them to organize their information logically.
Add new comment
- Print this resource
Explore Resources by Grade
- Kindergarten K
How to Write an Open Letter
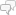

The open letter is playing a growing role in modern communication because it’s an excellent way of reaching a wide audience. The definition of an open letter is that it is open to the public, not a closed and private communication between two individuals.
There tend to be two main types of open letter:
1. The first is an un addressed letter to be read by a large number of people. For example, a letter an employer sends to all employees or a letter from a company to all its customers.
2. The second type of open letter is addressed to a specific individual but is intended to be read by a large number of people. Journalists or political activists often publish letters addressed to politicians or public officials in a newspaper or magazine so their views can be shared with the publication’s readers.
As social media and networks go from strength to strength, the open letter is evolving and becoming an increasingly popular way to communicate.
Important Questions to Ask
- Who is your audience? Identifying typical readers of your letter will enable you to pitch the tone and language of your letter so that it’s engages your reader. This is important because their name isn’t at the top of the letter, so the letter has to find other ways of ‘speaking’ to them. Different letters to different newspapers are tailored to suit the tone of the readership- traditional, ‘broadsheet’ newspapers will use a completely different tone to a tabloid publication.
- What is your letter about? You should be able to summarise the point of your letter in a single sentence. If you can’t, find ways to simplify your argument or view. The tighter your subject area, the more powerful your letter will be. If the letter has impact, the reader will read from the first word to the last.
- What are you trying to achieve? All letters have a purpose. The open letter has a very specific purpose because you have chosen to communicate in such an open way. This will determine the style, tone and content of your letter. Perhaps the letter is designed to motivate people to act or follow instructions, maybe you want to provoke discussion, create specific emotions or raise awareness and stimulate thought.
The Next Steps
This should reflect the importance of each point and the order in which they should appear in the letter. Make sure that each point follows the previous in a logical and flowing way. If you don’t achieve this, the effect is jarring and it will alienate the reader.
Writing the Letter
When you have finished writing the letter, scan the document briefly for basic errors like spelling or grammar mistakes. Put the letter away and re-visit it later. This gives you some distance from your writing, even if it’s only for an hour and allows you reassess your work objectively.
- Using a preaching or sanctimonious tone.
- Waffling too much or wandering off the subject.
- Using an attacking or aggressive tone which alienates the reader.
- Make sure the beginning is powerful, that the middle is strong and logical and the ending returns full circle to make a convincing conclusion.
Open letters can be incredibly powerful but they have many pitfalls because they have to deliver targeted messages to more than one person. If your message is strong and the method you use to help you write the letter is logical and well-considered, you should be able to write a letter to be proud of.

- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
An Open Letter ... About Open Letters
Linton Weeks
Dear Open Letter Writers,
Are you open to the idea that the open letter has become the victim of its own success?
Open your browser and you can read that all kinds of people are sending open letters — letters meant to be read by everyone. In the recent past, celebrity attorney Gloria Allred posted an open letter to Rush Limbaugh . Presidential aspirant Mitt Romney sent one to voters in Alaska , and the Iraq and Afghanistan Veterans of America released one addressed to President Obama, asking him to set aside a National Day of Action to recognize military veterans.

Just this week, Sudan Change Now posted an open letter praising actor George Clooney for drawing attention to turmoil in Sudan. Dozens of independent filmmakers are protesting a PBS scheduling decision in an open letter. And billionaire investor Carl Icahn has issued an open letter to shareholders of an energy company.
Nowadays, calling something an open letter seems like redundant, repetitious repetition. After all, what isn't open anymore? We tweet the most private thought or deed on Twitter, pin it onto Pinterest, plaster it on a Facebook wall, upload it to YouTube.
In this era of total openness — open criticism, open primaries, open relationships and open source everything — the questions arise: Is the idea of calling something an open letter arguably, well, rather quaint? And is it perhaps time to close the book on open letters?
Famous Open Letters
Way back in the 20th century, when people led private lives and wrote personal letters and messages meant only for the eyes of the recipients — and most communication stayed that way — an open letter carried some weight. A few even changed history.
And such has been the case through history. The Oxford English Dictionary defines an open letter as one intended for a more public readership, as by deliberate publication in a newspaper or journal. The phrase harks back to at least 1798 in England.
Over time, the open letter became more popular. Just last year, the BBC noted that more and more people are writing open letters. The story cited a couple of famous ones:
* In 1898, writer Emile Zola sent an open letter, titled "J'accuse," to the president of France, charging the government with practicing anti-Semitism by unlawfully keeping alleged spy Alfred Dreyfus in prison.
* In 1963, Martin Luther King Jr. wrote an open letter — in support of nonviolence in the civil rights movement — from a jail in Birmingham, Ala. The letter included the classic observation that "Injustice anywhere is a threat to justice everywhere."
But the increase in open letters has not necessarily translated into an increase in their influence.

At The Washington Post, Vince Rinehart, an editor on the multiplatform desk, has taken turns over the years as an editor for the Letters to the Editor section. Among the correspondence of complaints and praisings, he says, the Post received lots of open letters. And "the editorial staff routinely rejects them, in part because such letters are typically sent to a ton of publications and other places at once, and the Post insists on exclusivity in letters."
The Post editorial page's philosophy, he explains, "has always been that letters are a conversation between the Post and its readers and that the conversation starts with things the Post writes."
Cautionary Tale
People may be writing more open letters, but do they still pack a punch? With the proliferation of online petitions, message boards and other relentless blogospheric activity, is there still a place for open letters?
Samara O'Shea, author of For the Love of Letters and proprietor of a letter writing service, says, "I believe that a formal, open letter continues to hold power."
For example, she cites Warren Buffett's open letter to Congress , "Stop Coddling the Super Rich," published in The New York Times in August 2011. The letter "ignited a great response," O'Shea says. President Obama referred to Buffett's ideas for taxing the rich in his 2012 State of the Union address.
O'Shea believes that people should continue to write open letters "if they feel moved by an issue or think they can influence an outcome."
But, she says, remember that many forms of communication are now considered tantamount to open letters. "A blog is basically an open letter," says O'Shea, whose own blog is titled LetterLover . "As is an offhanded comment caught on camera."
People should exercise caution with messages that aren't meant to be open letters, she advises. As illustration, she points to the case of June Talvitie-Siple, a teacher who ranted on Facebook about her frustration with students. "The school board considered it an open letter, rather than a private comment," O'Shea says, "and she was fired. Reread everything before posting online and make sure you'd stand by it if the boss or the general public were to see it."
And, O'Shea says, "I advise against writing an open letter — or any letter — when you are angry or in immediate, defensive response to another open letter. Write the letter when you are calm and be ready to stand by your words if there's a backlash or condescending comments."
In other words, an open letter is also an open invitation — to criticism.

How to write a letter
HOW TO WRITE A LETTER: A GUIDE FOR TEACHERS AND STUDENTS

In this age of digital communication, writing letters is becoming something of a lost art. Emails and text messages can be sent instantly and for a fraction of the cost good old-fashioned snail mail can offer.
So, why bother teaching letter-writing at all? Well, though electronic ‘letters’ are often freer in formatting and language than physical letters, we can also apply letter-writing rules to electronic media. However, physical letters do offer some distinct benefits of their own too.
A WELL-WRITTEN LETTER CAN CHANGE THE WORLD.
Whilst we pride ourselves here on how to write a great essay, information report, or another text type that is primarily used in an educational setting, the ability to craft a powerful letter or email has literally changed people’s lives, altered the course of history and been the difference between life and death in some cases.
It can be the one opportunity to remove all the noise and confusion on any subject area and honestly tell someone how you feel straight from the heart. Pen to paper.
For whatever reason, a thousand emails, tweets, and likes will never have the same impact as a well-crafted handwritten letter. Its very creation and existence show your reader how passionate and genuine about what it contains.
Letters fall under the transactional writing category; if you want to know more about transactional texts, be sure to check out our in-depth guide here.

COMPLETE LETTER WRITING UNIT FOR STUDENTS

Over 100 PAGES of engaging RESOURCES , various letter SAMPLES , LESSON PLANS and INTERACTIVE DIGITAL RESOURCES to teach your students how to write amazing LETTERS and EMAILS .
Teach this life skill with confidence through this excellent ALL-IN-ONE RESOURCE . No preparation is required.
3 REASONS TO TEACH LETTER WRITING
1. the personal touch: .

Those of us who grew up in an age before the internet got going will remember the excitement of waiting for and receiving a letter. Many of us will have had childhood pen pals we never met or received love letters from our teenage sweethearts. Maybe some treasured letters are still securely stored in a bedside drawer.
There is something extremely personal and intimate about the letter that email cannot capture. Letters are physical, and their increasing rarity makes them seem even more intimate today.
In this day and age, receiving a personally written letter is something a unicorn in communication terms. Students who know how to produce a well-crafted letter can use it to their advantage. For example, any business hiring manager will undoubtedly be numbed by the constant torrent of emails flooding their inbox.
That mailed resume accompanied by a handwritten letter that waits for them on their desk in the morning will surely stand out and secure an attentive read. The letter, in its various forms, is guaranteed to stand out and make an impact in an age where the vast majority of communication is digital.
3. Handwriting

Just as letter writing has declined in popularity, so too has the emphasis on well-developed handwriting skills. You can, if you wish, take the opportunity here to have the students work on their handwriting skills.
While students may protest that they can accomplish the task much quicker by word-processing, another benefit of handwriting a letter is that the speed becomes almost meditative. This allows students to focus carefully on their grammar and punctuation without always resorting to the crutch of spell-checkers and grammar correction software.
FORMAL AND INFORMAL LETTER WRITING: WHAT’S THE DIFFERENCE?
The table below outlines whether your letter should be written formally or informally, with some suggested prompts . Whilst there are many similarities, a formal letter should always be considered as a document with a real purpose and ramifications.
FORMAL LETTER FEATURES
USED FOR PROFESSIONAL COMMUNICATION THESE DOCUMENTS FOLLOW A PRESCRIBED FORMAT. THEY ARE WRITTEN IN A PASSIVE VOICE FOR A SPECIFIC PURPOSE AND IN MANY CASES ARE LEGALLY BINDING. SOME EXAMPLES ARE.
INVITATION Make someone feel special about an upcoming event.
APPLICATION Write a professional letter of application for a job or group you wish to join.
REFEREE / REFERENCE Vouch for another’s skills, personality or credibility.
ACCEPTANCE & REJECTION Approve or deny an applicant in a professional manner.
MAKE AN OFFER Make a formal and binding offer in writing.
EXIT / RESIGNATION Formally leave or step down in a professional and dignified manner.
INFORMAL LETTER FEATURES
USED FOR PERSONAL COMMUNICATION THESE LETTERS HAVE NO PRESCRIBED FORMAT AND ARE WRITTEN IN AN ACTIVE VOICE.
THANK YOU Let someone know you appreciate their efforts.
CONGRATULATIONS Acknowledge someone’s achievements in life.
GRIEVANCE / LOSS Acknowledge someones personal loss or suffering and let them know you care.
FRIENDSHIP & LOVE Tell someone how special they are to you and why?
LETTER TO THE EDITOR / MAYOR ETC. Let someone know how their actions and adversely affect you and others.
LETTER TO SELF Give your older or younger self some words of advice and wisdom.
INFORMATIONAL UPDATE Write a letter back home telling them what you have been up to.
HOW TO WRITE FORMAL LETTERS
The writing process begins with planning.
As with all genres of writing, the process of formal letter writing should start with planning. This should involve sketching a brief outline from which to work rather than a comprehensive detailing of minutiae. The plan should include:
- Note addresses, names etc. – who are you writing to?
- Record the purpose of the letter – what do you want to say?
- List points to be made (each will form a paragraph) – how will you say it?
- State action point – what do you want the reader to do?
Formal letters can be written for a wide range of purposes and may come in various shapes, including a letter of complaint, a cover letter accompanying a job application, a letter of invitation, a reference letter, or a proposal letter – to name a few. Though each will adhere to its own rules of formatting and tone when writing formal letters, students should avoid using slang or contractions.
Language should be straightforward and polite. Encourage students to avoid bursts of purple prose in favor of direct, functional language. Usually, a formal letter will be written to achieve a particular end and should be written with that end foremost in mind. Students should avoid meanderings and stay firmly focused on the task at hand.
TIPS FOR WRITING GREAT FORMAL LETTERS

- The writer’s address should be in the top right-hand corner.
- The date should be written below the writer’s address
- The recipient’s name and address are below that on the left-hand side
- Use the correct opening (Dear Sir / Madam, Dear Mrs Ferguson, etc.)
- Use Standard English
- The opening sentence should explain the purpose of the letter
- Each paragraph should make a single specific point
- Use an appropriate formal tone and register in the wording of the letter
- Avoid contractions, slang, and abbreviations
- The concluding ‘action point’ paragraph states what you want the recipient to do
- The formal ending, such as Yours Sincerely or Yours Faithfully
A Note on Salutations
If the student knows the intended recipient’s name, start with Dear Mr. / Mrs Surname and end with Yours Sincerely. If they don’t know the recipient’s name, start with Dear Sir / Madam and end with Yours Faithfully.
Use of Rhetorical Devices
As mentioned, formal letter writing focuses on attempting to convince someone to take some course of action or other. To do this, it is helpful to employ some rhetorical devices to make the writing more persuasive . Some useful techniques to encourage your students to employ include:
Direct Address: Using the pronoun ‘you’ in a formal letter makes the reader feel that you are speaking directly to them. This helps to engage the reader and encourage them to continue reading the letter.

Emotive Language: Where students are trying to convince the reader to take a course of action, the use of emotive language can often be a powerful tool. Students can use either positive or negative colored words to create the desired response in the reader.
Facts and Figures: Another way to persuade and convince is to employ facts and figures to support the points made in the letter.
FORMAL LETTER STUDENT EXAMPLES

How to write an informal letter
Common features of informal letters:.
There are far fewer rules to follow when writing an informal letter, but there are still some practical guidelines to follow that will prove helpful for students engaged in writing informally.
As with any piece of writing, it is important to consider who the audience is and the reason for writing in the first place. In particular, this will help decide the tone and the language register. The more intimate the relationship, the more informal the language can be.
Though the letter will be informal, it will still have a purpose. Information should still be organized into paragraphs, as would be done with a formal, more ‘official’ letter. Students sometimes struggle with this aspect, as they often conflate ‘informal’ with ‘disorganized.’ Making them plan their informal letter before writing can help ensure it is sufficiently organized.
HOW TO START AN INFORMAL LETTER
Informal letters will start with a greeting appropriate to how close the relationship is. For acquaintances, this may be ‘Dear Tom,’ (using the first name instead of the surname) to a very informal ‘Hi Jane,’. Don’t forget the comma after the name!
After the greeting, a general opening sentence should follow. Usually, this will be something like a ‘How are you?’ or a ‘How have you been?’. If the recipient is married or has kids, you may wish to ask how their spouse or children are.
Next, students should state the reason for writing. The language should be open and friendly in tone and, in contrast to the formal letter, colloquial language, idiomatic expressions, and contractions are perfectly okay and even desirable.
Just as the opening salutation to an informal letter is much more relaxed, so too will the closing salutation. There are many possibilities for the students to choose here, and their decision will depend on who they are writing to and their personal preferences. Some examples of possible closings include ‘Love’, ‘Best regards’, ‘All the best’, and ‘Thanks’.
INFORMAL LETTER STUDENT EXAMPLES

Teaching Resources
Use our resources and tools to improve your student’s writing skills through proven teaching strategies.
PRACTICE LETTER WRITING WITH THESE ACTIVITIES FOR STUDENTS
The most effective way for students to internalize all the features of letter writing, formal or informal, is to gain experience by writing various letters for differing purposes. The following activities offer some suggestions for students to get practising today:
1. FICTION AS A SPRINGBOARD
Have students write as if they were a character from a piece of fiction you have been reading in class. Choosing a dramatic point in the plot , ask students to imagine they are one of the characters writing a letter to another character in the story. This writer may be either formal or informal, depending on the scenario presented. This will give students realistic letter-writing practice while also getting them to engage closely with the text and respond imaginatively to its themes.
2. THE AGONY AUNT
Either offer a range of possible life predicaments or cut out the questions from the ‘agony aunt’ page of a local newspaper. Students must write back offering advice in response to the predicaments expressed in the question or predicament. The response should be written in full letter format. This activity also lends itself to several variations. The response may be written to a close friend, for example, or written from the perspective of a professional agony aunt employing a more formal tone and presentation.
3. A LETTER OF COMPLAINT
Have students think of their favorite candy bar or clothing item. Encourage them to imagine they have bought this product lately and found it to be substandard. Students must write a formal letter of complaint to the manufacturer outlining their complaint and recommending a course of action to satisfactorily resolve that complaint. They must use all the features of a formal letter as outlined above.

HOW TO MAKE YOUR HANDWRITTEN LETTERS LOOK OLD AND AUTHENTIC.
- Write in pencil or a calligraphy pen,
- screw them up tightly and carefully unfold and flatten.
- Lightly dab coffee stains over the paper to make it look aged.
- Carefully singe or burn the edges of your paper.
- Add some sepia-filtered photos for effect.
SIGNING-OFF
As students become more confident in their understanding of letter-writing formats, encourage them to exchange letters with each other for peer assessment. You may wish to provide them with a checklist of features to look for while reading over their partner’s work.
Letter-writing can also be a great way to partner up with schools overseas; often, children studying English as a second language will be delighted to receive letters from (and write to) students in English-speaking countries. And though email increasingly encroaches on the traditional territory of the letter, many of the skills garnered in the practice of letter writing are transferable to the modern manifestation. There is ample opportunity here to link letter-writing learning with approaches to writing emails too.
Letter-writing can provide a focus for a wide range of learning objectives while also teaching students valuable practical skills that will serve them well beyond their school years, both in their personal and work lives. And who knows, perhaps in years to come, one of the letters your student writes in your class may become a treasured keepsake in someone’s bedside drawer.
LETTER WRITING GRAPHIC ORGANIZERS (TEMPLATES)

WRITING CHECKLIST & RUBRIC BUNDLE FOR ALL TEXT TYPES

HOW TO WRITE A FORMAL LETTER TUTORIAL VIDEO

OTHER GREAT ARTICLES RELATED TO LETTER WRITING
Transactional Writing

Personal Narrative Writing Guide

How to Write a Recount Text (And Improve your Writing Skills)
Content for this page has been written by Shane Mac Donnchaidh. A former principal of an international school and university English lecturer with 15 years of teaching and administration experience. Editing and support content has been provided by the literacyideas team.
- U.S. Locations
- UMGC Europe
- Learn Online
- Find Answers
- 855-655-8682
- Current Students
UMGC Effective Writing Center The Perfect Business Letter
Explore more of umgc.
- Writing Resources
When sitting down to complete a business letter assignment in school, students know intuitively that they are engaging in a type of writing that is much different from the typical school assignment. One goal of this resource is to upgrade that intuitive understanding to conscious status and, by doing so, sharpen your understanding of the distinct differences between business and academic writing that must be observed as you transition between the two worlds.
School Writing v. Business Writing
It may sound crass, but the difference between the two can be summarized simply: In school you write to get grades. In the real world, you write to do your job.
It's helpful to think of most school writing as a type of exam: You write to demonstrate to a specific teacher that you understand and can use material in a specific discipline. Those who become outstanding writers in school have usually mastered an important skill of audience analysis: figuring out exactly what an audience of one (the teacher) wants and how he or she wants it delivered.
The audience of one in school becomes the audience of many in the work world. Moreover, everyone who may read your business writing will not be known to you. Especially when your business writing travels outside the company, as it does when in letter format, you have little idea of how many people may read it, much less who they are. And the real kicker is that, unlike teachers, few in the business world get paid to read your writing no matter how poor it is. Other key differences include the following:
Clearly, when authoring a business document, you are taking on a higher degree of responsibility because of potential consequences, both positive and negative, that the writing can have. These consequences are particularly serious for the writer since the lifespan of whatever you write in the work place is potentially your entire career, compared to the duration of a course in school.
Get career planning tips from the advisors at UMGC .
How to Create Your Business Letter
These inherent differences between the two worlds of writing--business and academic--are also reflected in the steps successful writers follow when creating real-world documents like business letters.
Analyze Audience
It's helpful to divide your audience into primary and secondary members. Your primary audience is those whom you are certain will read what you write. The secondary audience is those who may be likely to read it. Your task is to speak directly to the needs of the primary audience while keeping in mind this secondary audience: what they know about the topic and their possible attitudes.
Clarify Purpose
In order for your writing and its purpose to be clear for your audience, it must be twice as clear for you, the writer. Good business writers can provide sharp, succinct answers to the question, "What do I want my readers to know and/or do after reading what I write?" Write the answer down and filter all writing choices through its prism.
Based on the crystal clear idea of what the writing hopes to achieve, the outline represents how the writer will achieve it by arranging information and instructions in the exact order the audience should encounter them for best effect.
The formats for business and technical writing are well known and expected by your audience. These standard formats are usually (1) adhered to rigorously and (2) are modified by any guidelines you have been given by your organization.
Draft & Revise
The first draft is your first opportunity to combine all of the above. However, it should be far from your last. Gone are the days of "once and done" the night before the assignment is due. Especially important is building in some time for a draft to get cold before you revisit with fresh eyes.
Get Feedback
Never let your audience be just the second set of eyes to see what you have written. In between yourself and your audience, insert a knowledgeable person who will act as a proxy for your audience and give you honest feedback.
Business Letter Styles
The two most common formats of business letters today are the full-block format and modified-block format. Note that the full-block format should be used only with letterhead. One variation on these two styles includes indenting paragraphs in the body section. As always, follow the style preferred by your organization unless there is a clear reason not to.
Our helpful admissions advisors can help you choose an academic program to fit your career goals, estimate your transfer credits, and develop a plan for your education costs that fits your budget. If you’re a current UMGC student, please visit the Help Center .
Personal Information
Contact information, additional information.
By submitting this form, you acknowledge that you intend to sign this form electronically and that your electronic signature is the equivalent of a handwritten signature, with all the same legal and binding effect. You are giving your express written consent without obligation for UMGC to contact you regarding our educational programs and services using e-mail, phone, or text, including automated technology for calls and/or texts to the mobile number(s) provided. For more details, including how to opt out, read our privacy policy or contact an admissions advisor .
Please wait, your form is being submitted.
By using our website you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about how we use cookies by reading our Privacy Policy .
- Sign Up for Mailing List
- Search Search
Username or Email Address
Remember Me

Resources for Teachers: Creating Writing Assignments
This page contains four specific areas:
Creating Effective Assignments
Checking the assignment, sequencing writing assignments, selecting an effective writing assignment format.
Research has shown that the more detailed a writing assignment is, the better the student papers are in response to that assignment. Instructors can often help students write more effective papers by giving students written instructions about that assignment. Explicit descriptions of assignments on the syllabus or on an “assignment sheet” tend to produce the best results. These instructions might make explicit the process or steps necessary to complete the assignment. Assignment sheets should detail:
- the kind of writing expected
- the scope of acceptable subject matter
- the length requirements
- formatting requirements
- documentation format
- the amount and type of research expected (if any)
- the writer’s role
- deadlines for the first draft and its revision
Providing questions or needed data in the assignment helps students get started. For instance, some questions can suggest a mode of organization to the students. Other questions might suggest a procedure to follow. The questions posed should require that students assert a thesis.
The following areas should help you create effective writing assignments.
Examining your goals for the assignment
- How exactly does this assignment fit with the objectives of your course?
- Should this assignment relate only to the class and the texts for the class, or should it also relate to the world beyond the classroom?
- What do you want the students to learn or experience from this writing assignment?
- Should this assignment be an individual or a collaborative effort?
- What do you want students to show you in this assignment? To demonstrate mastery of concepts or texts? To demonstrate logical and critical thinking? To develop an original idea? To learn and demonstrate the procedures, practices, and tools of your field of study?
Defining the writing task
- Is the assignment sequenced so that students: (1) write a draft, (2) receive feedback (from you, fellow students, or staff members at the Writing and Communication Center), and (3) then revise it? Such a procedure has been proven to accomplish at least two goals: it improves the student’s writing and it discourages plagiarism.
- Does the assignment include so many sub-questions that students will be confused about the major issue they should examine? Can you give more guidance about what the paper’s main focus should be? Can you reduce the number of sub-questions?
- What is the purpose of the assignment (e.g., review knowledge already learned, find additional information, synthesize research, examine a new hypothesis)? Making the purpose(s) of the assignment explicit helps students write the kind of paper you want.
- What is the required form (e.g., expository essay, lab report, memo, business report)?
- What mode is required for the assignment (e.g., description, narration, analysis, persuasion, a combination of two or more of these)?
Defining the audience for the paper
- Can you define a hypothetical audience to help students determine which concepts to define and explain? When students write only to the instructor, they may assume that little, if anything, requires explanation. Defining the whole class as the intended audience will clarify this issue for students.
- What is the probable attitude of the intended readers toward the topic itself? Toward the student writer’s thesis? Toward the student writer?
- What is the probable educational and economic background of the intended readers?
Defining the writer’s role
- Can you make explicit what persona you wish the students to assume? For example, a very effective role for student writers is that of a “professional in training” who uses the assumptions, the perspective, and the conceptual tools of the discipline.

Defining your evaluative criteria
1. If possible, explain the relative weight in grading assigned to the quality of writing and the assignment’s content:
- depth of coverage
- organization
- critical thinking
- original thinking
- use of research
- logical demonstration
- appropriate mode of structure and analysis (e.g., comparison, argument)
- correct use of sources
- grammar and mechanics
- professional tone
- correct use of course-specific concepts and terms.
Here’s a checklist for writing assignments:
- Have you used explicit command words in your instructions (e.g., “compare and contrast” and “explain” are more explicit than “explore” or “consider”)? The more explicit the command words, the better chance the students will write the type of paper you wish.
- Does the assignment suggest a topic, thesis, and format? Should it?
- Have you told students the kind of audience they are addressing — the level of knowledge they can assume the readers have and your particular preferences (e.g., “avoid slang, use the first-person sparingly”)?
- If the assignment has several stages of completion, have you made the various deadlines clear? Is your policy on due dates clear?
- Have you presented the assignment in a manageable form? For instance, a 5-page assignment sheet for a 1-page paper may overwhelm students. Similarly, a 1-sentence assignment for a 25-page paper may offer insufficient guidance.
There are several benefits of sequencing writing assignments:
- Sequencing provides a sense of coherence for the course.
- This approach helps students see progress and purpose in their work rather than seeing the writing assignments as separate exercises.
- It encourages complexity through sustained attention, revision, and consideration of multiple perspectives.
- If you have only one large paper due near the end of the course, you might create a sequence of smaller assignments leading up to and providing a foundation for that larger paper (e.g., proposal of the topic, an annotated bibliography, a progress report, a summary of the paper’s key argument, a first draft of the paper itself). This approach allows you to give students guidance and also discourages plagiarism.
- It mirrors the approach to written work in many professions.
The concept of sequencing writing assignments also allows for a wide range of options in creating the assignment. It is often beneficial to have students submit the components suggested below to your course’s STELLAR web site.
Use the writing process itself. In its simplest form, “sequencing an assignment” can mean establishing some sort of “official” check of the prewriting and drafting steps in the writing process. This step guarantees that students will not write the whole paper in one sitting and also gives students more time to let their ideas develop. This check might be something as informal as having students work on their prewriting or draft for a few minutes at the end of class. Or it might be something more formal such as collecting the prewriting and giving a few suggestions and comments.
Have students submit drafts. You might ask students to submit a first draft in order to receive your quick responses to its content, or have them submit written questions about the content and scope of their projects after they have completed their first draft.
Establish small groups. Set up small writing groups of three-five students from the class. Allow them to meet for a few minutes in class or have them arrange a meeting outside of class to comment constructively on each other’s drafts. The students do not need to be writing on the same topic.
Require consultations. Have students consult with someone in the Writing and Communication Center about their prewriting and/or drafts. The Center has yellow forms that we can give to students to inform you that such a visit was made.
Explore a subject in increasingly complex ways. A series of reading and writing assignments may be linked by the same subject matter or topic. Students encounter new perspectives and competing ideas with each new reading, and thus must evaluate and balance various views and adopt a position that considers the various points of view.
Change modes of discourse. In this approach, students’ assignments move from less complex to more complex modes of discourse (e.g., from expressive to analytic to argumentative; or from lab report to position paper to research article).
Change audiences. In this approach, students create drafts for different audiences, moving from personal to public (e.g., from self-reflection to an audience of peers to an audience of specialists). Each change would require different tasks and more extensive knowledge.
Change perspective through time. In this approach, students might write a statement of their understanding of a subject or issue at the beginning of a course and then return at the end of the semester to write an analysis of that original stance in the light of the experiences and knowledge gained in the course.
Use a natural sequence. A different approach to sequencing is to create a series of assignments culminating in a final writing project. In scientific and technical writing, for example, students could write a proposal requesting approval of a particular topic. The next assignment might be a progress report (or a series of progress reports), and the final assignment could be the report or document itself. For humanities and social science courses, students might write a proposal requesting approval of a particular topic, then hand in an annotated bibliography, and then a draft, and then the final version of the paper.
Have students submit sections. A variation of the previous approach is to have students submit various sections of their final document throughout the semester (e.g., their bibliography, review of the literature, methods section).
In addition to the standard essay and report formats, several other formats exist that might give students a different slant on the course material or allow them to use slightly different writing skills. Here are some suggestions:
Journals. Journals have become a popular format in recent years for courses that require some writing. In-class journal entries can spark discussions and reveal gaps in students’ understanding of the material. Having students write an in-class entry summarizing the material covered that day can aid the learning process and also reveal concepts that require more elaboration. Out-of-class entries involve short summaries or analyses of texts, or are a testing ground for ideas for student papers and reports. Although journals may seem to add a huge burden for instructors to correct, in fact many instructors either spot-check journals (looking at a few particular key entries) or grade them based on the number of entries completed. Journals are usually not graded for their prose style. STELLAR forums work well for out-of-class entries.
Letters. Students can define and defend a position on an issue in a letter written to someone in authority. They can also explain a concept or a process to someone in need of that particular information. They can write a letter to a friend explaining their concerns about an upcoming paper assignment or explaining their ideas for an upcoming paper assignment. If you wish to add a creative element to the writing assignment, you might have students adopt the persona of an important person discussed in your course (e.g., an historical figure) and write a letter explaining his/her actions, process, or theory to an interested person (e.g., “pretend that you are John Wilkes Booth and write a letter to the Congress justifying your assassination of Abraham Lincoln,” or “pretend you are Henry VIII writing to Thomas More explaining your break from the Catholic Church”).
Editorials . Students can define and defend a position on a controversial issue in the format of an editorial for the campus or local newspaper or for a national journal.
Cases . Students might create a case study particular to the course’s subject matter.
Position Papers . Students can define and defend a position, perhaps as a preliminary step in the creation of a formal research paper or essay.
Imitation of a Text . Students can create a new document “in the style of” a particular writer (e.g., “Create a government document the way Woody Allen might write it” or “Write your own ‘Modest Proposal’ about a modern issue”).
Instruction Manuals . Students write a step-by-step explanation of a process.
Dialogues . Students create a dialogue between two major figures studied in which they not only reveal those people’s theories or thoughts but also explore areas of possible disagreement (e.g., “Write a dialogue between Claude Monet and Jackson Pollock about the nature and uses of art”).
Collaborative projects . Students work together to create such works as reports, questions, and critiques.

An ISA vetted Industry Pro has requested content for your project Tomorrowland. Respond to the request
Submit today and you'll receive $20 off your submission to Table Read My Screenplay Screenplay. Learn More
An industry Pro has requested content for your project Tomorrowland. Respond to the request
You have been tagged as an attachment to the project Once Upon a Time in Hollywood 2. View my credits

That's all your notifications from the last 60 days.
ISA Insider
- Post Article
- Post Pro Tip
- Post Podcast
- Manage Content
Browse All Gigs
My submissions.
- Manage Gigs
Marketing Services - New
Logline review, script notes, development evaluation, producer-level feedback - new, my feedback, programs / contests, browse all programs, isa diversity initiative, isa fast track fellowship, isa pitch challenge.
- Add a Program
- Manage Programs
Writers / Projects
Writer’s showcase, success stories, isa development slate, isa top 25 screenwriters, events / classes, upcoming events, the craft course - online only, 30-day challenge, virtual pitch practice, pitch deck office hours, custom pitch deck design, coming soon.
The ISA is your go-to source for great networking events, and classes to take your career to the next level.
Welcome to the new ISA platform in beta. As you explore, please help us improve by providing feedback .
Open writing assignments (owas) - demystifying the secret club, karisa tate.
- . August 25, 2020

If you’re a screenwriter and you’ve ever thought — what's an open writing assignment? You are not alone. Although landing an open writing assignment (OWA) is one of the many ways screenwriters can go about making money (the holy grail in screenwriting), there’s still so much mystery surrounding them. In a sense, it’s a bit of a secret club. You have to know the right people and hang out in the right circles to even get an invite. To help demystify this secret club and learn more about how to score a coveted invitation, we sat down with award-winning screenwriter and independent producer, Rebecca Norris. What exactly is an open writing assignment? In my experience, an open writing assignment is a situation where someone is hiring a screenwriter to perform screenwriting work made for hire. The person commissioning the work might be hiring on behalf of a studio, or might be an independent producer, director, or even a businessperson outside of the industry with money, who has had a burning desire to make a film for years. However you slice it, it’s a script that a screenwriter is getting paid to write, but the source material or original concept did not originate with the screenwriter. The person or entity doing the hiring owns the copyright. Often, it’s an existing novel or story that needs to be adapted into a film, someone’s childhood memories or life story being written for the screen, or an original idea a producer or director has that they want a screenwriter to bring to fruition. Many times, the work is a rewrite or polish of an existing script.
How do you go out for an open writing assignment? I’m sure everyone comes across OWAs in varying ways. My assignments have all come through direct referrals. In addition to being a screenwriter, I’m a filmmaker and have been a story analyst for several years, reading for production companies, contests, and fellowship programs. I also worked at a production company, where I gave notes on projects we had in development and production. After moving on from that, I started a private consulting service for writers and filmmakers by referral. A lot of my writing work has come through consulting clients who needed to hire a writer, and happened to like my take and ideas on their projects, and brought me aboard. One time it was a director who had a film he was getting financed, and after he read suggestions I had given for improving the dialogue, asked me to do a polish and comedy punch-up on his script. Another time it was a director/producer who had written a rough draft of a script, and had financing on board, but the script needed a full rewrite before going into production. He didn’t consider himself a writer and didn’t have the time or desire to do it himself, so he asked me to do the rewrite. The situations have varied. For your current assignment, how did you land the OWA? A producer was referred to me who wanted notes on a rough draft of a treatment he had written, but was also looking for writing services, since he wanted to focus on producing rather than developing the script himself. He liked my take on his project and the ideas I brought to the table, and offered me a contract to write the film. He had ideas sketched out for characters and plot, but it’s my job now to flesh those out into a feature film.
When you go into pitch for an OWA, how do you prepare? Is it different than how you would prepare to pitch for an original script? In my case, I had already given my take on my clients’ scripts through my development notes, so I suppose that essentially took the place of what a pitch would have accomplished. I imagine that they could have consulted with a number of writers, and possibly had, but since they already had detailed 10-20 page reports on what I thought would improve their material, and we had built up a rapport, they felt I was the right choice for their projects and asked me to come aboard. In general, however, yes, as I have seen it, the process is that execs take meetings with several different writers all giving their takes on the material. The difference between pitching for an OWA and an original spec is that for an OWA, the material originates with the producer. So, for instance, if a producer has the rights to a novel to adapt, then writers would have to read that novel and then pitch ideas; it would all depend on what the producer needs to see. For an original spec, you’re pitching your own concept, so you need to know and believe in your story inside and out, and have the goods to back it up with the script. Having relationships in place, good reps, and/or a great query letter can help to get people to read your original work. In your experience, do you find that it’s easier to get hired on an OWA than sell a spec script or pitch?
I do think that work on existing IP or an existing idea is likely easier to come by than selling an original script, simply because there’s more of that type of work available. It can be hard to get people to read original work. Everyone wants material that’s based on something that’s known, that already has traction and a fan base. That shouldn’t discourage writers from creating their own original work, however. Writing original material is the best way to stay fresh and keep your personal voice alive and well. As tough as it can be, original specs do sell, and it’s best to always have one or two at the ready that can be sold or used as writing samples.
What has been your personal experience with working on OWAs? My general experience has been very positive. I have only come aboard projects with stories that I cared about and thought had a lot of potential, with producers I had a rapport with. It can take many months to fully develop an idea and then write the script, so you have to love the story and get along well with the producers. It can be a fun and exciting process, but there can also be frustrations and bumps in the road, as you discover what works and what doesn’t in the story. The pre-production process can also be tumultuous, with everything from financing challenges to locations falling through. Above all, you have to have patience for the process, and be open to hearing and implementing notes on the script from any number of different people, including notes that you may not necessarily agree with.
What would be your best advice for an upcoming screenwriter or someone who wants to level up their career? I’d say the best advice I can give is to persevere. A screenwriting career is a long and winding road. Persevere. There are many ups and downs. Persevere. There are times when work is busy and times when it’s slow. Persevere. Your script may be rejected by any number of contests, fellowships, agents, managers, producers. Retool. Rewrite. Improve your craft. Persevere.
As you mentioned, a screenwriting career is a long and winding road. If writers are feeling burnt out, what do you suggest? I have also found that branching out into other genres can be helpful in rekindling a love of writing if you’re feeling frustrated as a screenwriter. If you have writer’s block, or you’re burned out, try something new! There is no law that says because you’re a screenwriter you can’t write in other genres as well. Writers write! Write a poem. A short story. A novel. A comic. A children’s book.
Anything that you're currently working on? We’d love to share your work with our audience. I have been taking my own advice. (Ha!) In addition to my writing assignment, I have a new original screenplay that I recently finished, UNBURIED. It’s the story of a wisecracking, chronic hoarder who must clean up her home within 72 hours or be put out on the street. It actually originated as a stageplay I wrote a few years back when I was feeling burned out and wanted to change things up. I workshopped the play in the Seedlings playwriting program at the wonderful Theatricum Botanicum theater in Los Angeles, which was an invaluable experience. I started out my career working in theater and had truly missed it. Over the last year, I also wrote several children’s poems, as well as a picture book, and started on a YA novel that I intend to adapt into a screenplay down the line. So between all that and chasing a toddler around, I stay busy!
Thank you sharing with us, Rebecca! To stay up to date on all her newest projects, be sure to connect with her on Twitter: @beckaroohoo

DON’T MISS THESE CONTESTS

- Cash, Production Services, Con

- Cash, Consultant, Connections

- Representation, Workshops, Con

- Resource, Connections, Resourc
SUBMIT TO WRITING GIGS
Top screenwriting info straight to your inbox.
Articles, Videos, Podcasts, Special Offers & Much More
Thanks for subscribing email.

We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you accept and understand our Privacy Settings .

Understanding Assignments
What this handout is about.
The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms and practices into meaningful clues to the type of writing your instructor expects. See our short video for more tips.
Basic beginnings
Regardless of the assignment, department, or instructor, adopting these two habits will serve you well :
- Read the assignment carefully as soon as you receive it. Do not put this task off—reading the assignment at the beginning will save you time, stress, and problems later. An assignment can look pretty straightforward at first, particularly if the instructor has provided lots of information. That does not mean it will not take time and effort to complete; you may even have to learn a new skill to complete the assignment.
- Ask the instructor about anything you do not understand. Do not hesitate to approach your instructor. Instructors would prefer to set you straight before you hand the paper in. That’s also when you will find their feedback most useful.
Assignment formats
Many assignments follow a basic format. Assignments often begin with an overview of the topic, include a central verb or verbs that describe the task, and offer some additional suggestions, questions, or prompts to get you started.
An Overview of Some Kind
The instructor might set the stage with some general discussion of the subject of the assignment, introduce the topic, or remind you of something pertinent that you have discussed in class. For example:
“Throughout history, gerbils have played a key role in politics,” or “In the last few weeks of class, we have focused on the evening wear of the housefly …”
The Task of the Assignment
Pay attention; this part tells you what to do when you write the paper. Look for the key verb or verbs in the sentence. Words like analyze, summarize, or compare direct you to think about your topic in a certain way. Also pay attention to words such as how, what, when, where, and why; these words guide your attention toward specific information. (See the section in this handout titled “Key Terms” for more information.)
“Analyze the effect that gerbils had on the Russian Revolution”, or “Suggest an interpretation of housefly undergarments that differs from Darwin’s.”
Additional Material to Think about
Here you will find some questions to use as springboards as you begin to think about the topic. Instructors usually include these questions as suggestions rather than requirements. Do not feel compelled to answer every question unless the instructor asks you to do so. Pay attention to the order of the questions. Sometimes they suggest the thinking process your instructor imagines you will need to follow to begin thinking about the topic.
“You may wish to consider the differing views held by Communist gerbils vs. Monarchist gerbils, or Can there be such a thing as ‘the housefly garment industry’ or is it just a home-based craft?”
These are the instructor’s comments about writing expectations:
“Be concise”, “Write effectively”, or “Argue furiously.”
Technical Details
These instructions usually indicate format rules or guidelines.
“Your paper must be typed in Palatino font on gray paper and must not exceed 600 pages. It is due on the anniversary of Mao Tse-tung’s death.”
The assignment’s parts may not appear in exactly this order, and each part may be very long or really short. Nonetheless, being aware of this standard pattern can help you understand what your instructor wants you to do.
Interpreting the assignment
Ask yourself a few basic questions as you read and jot down the answers on the assignment sheet:
Why did your instructor ask you to do this particular task?
Who is your audience.
- What kind of evidence do you need to support your ideas?
What kind of writing style is acceptable?
- What are the absolute rules of the paper?
Try to look at the question from the point of view of the instructor. Recognize that your instructor has a reason for giving you this assignment and for giving it to you at a particular point in the semester. In every assignment, the instructor has a challenge for you. This challenge could be anything from demonstrating an ability to think clearly to demonstrating an ability to use the library. See the assignment not as a vague suggestion of what to do but as an opportunity to show that you can handle the course material as directed. Paper assignments give you more than a topic to discuss—they ask you to do something with the topic. Keep reminding yourself of that. Be careful to avoid the other extreme as well: do not read more into the assignment than what is there.
Of course, your instructor has given you an assignment so that he or she will be able to assess your understanding of the course material and give you an appropriate grade. But there is more to it than that. Your instructor has tried to design a learning experience of some kind. Your instructor wants you to think about something in a particular way for a particular reason. If you read the course description at the beginning of your syllabus, review the assigned readings, and consider the assignment itself, you may begin to see the plan, purpose, or approach to the subject matter that your instructor has created for you. If you still aren’t sure of the assignment’s goals, try asking the instructor. For help with this, see our handout on getting feedback .
Given your instructor’s efforts, it helps to answer the question: What is my purpose in completing this assignment? Is it to gather research from a variety of outside sources and present a coherent picture? Is it to take material I have been learning in class and apply it to a new situation? Is it to prove a point one way or another? Key words from the assignment can help you figure this out. Look for key terms in the form of active verbs that tell you what to do.
Key Terms: Finding Those Active Verbs
Here are some common key words and definitions to help you think about assignment terms:
Information words Ask you to demonstrate what you know about the subject, such as who, what, when, where, how, and why.
- define —give the subject’s meaning (according to someone or something). Sometimes you have to give more than one view on the subject’s meaning
- describe —provide details about the subject by answering question words (such as who, what, when, where, how, and why); you might also give details related to the five senses (what you see, hear, feel, taste, and smell)
- explain —give reasons why or examples of how something happened
- illustrate —give descriptive examples of the subject and show how each is connected with the subject
- summarize —briefly list the important ideas you learned about the subject
- trace —outline how something has changed or developed from an earlier time to its current form
- research —gather material from outside sources about the subject, often with the implication or requirement that you will analyze what you have found
Relation words Ask you to demonstrate how things are connected.
- compare —show how two or more things are similar (and, sometimes, different)
- contrast —show how two or more things are dissimilar
- apply—use details that you’ve been given to demonstrate how an idea, theory, or concept works in a particular situation
- cause —show how one event or series of events made something else happen
- relate —show or describe the connections between things
Interpretation words Ask you to defend ideas of your own about the subject. Do not see these words as requesting opinion alone (unless the assignment specifically says so), but as requiring opinion that is supported by concrete evidence. Remember examples, principles, definitions, or concepts from class or research and use them in your interpretation.
- assess —summarize your opinion of the subject and measure it against something
- prove, justify —give reasons or examples to demonstrate how or why something is the truth
- evaluate, respond —state your opinion of the subject as good, bad, or some combination of the two, with examples and reasons
- support —give reasons or evidence for something you believe (be sure to state clearly what it is that you believe)
- synthesize —put two or more things together that have not been put together in class or in your readings before; do not just summarize one and then the other and say that they are similar or different—you must provide a reason for putting them together that runs all the way through the paper
- analyze —determine how individual parts create or relate to the whole, figure out how something works, what it might mean, or why it is important
- argue —take a side and defend it with evidence against the other side
More Clues to Your Purpose As you read the assignment, think about what the teacher does in class:
- What kinds of textbooks or coursepack did your instructor choose for the course—ones that provide background information, explain theories or perspectives, or argue a point of view?
- In lecture, does your instructor ask your opinion, try to prove her point of view, or use keywords that show up again in the assignment?
- What kinds of assignments are typical in this discipline? Social science classes often expect more research. Humanities classes thrive on interpretation and analysis.
- How do the assignments, readings, and lectures work together in the course? Instructors spend time designing courses, sometimes even arguing with their peers about the most effective course materials. Figuring out the overall design to the course will help you understand what each assignment is meant to achieve.
Now, what about your reader? Most undergraduates think of their audience as the instructor. True, your instructor is a good person to keep in mind as you write. But for the purposes of a good paper, think of your audience as someone like your roommate: smart enough to understand a clear, logical argument, but not someone who already knows exactly what is going on in your particular paper. Remember, even if the instructor knows everything there is to know about your paper topic, he or she still has to read your paper and assess your understanding. In other words, teach the material to your reader.
Aiming a paper at your audience happens in two ways: you make decisions about the tone and the level of information you want to convey.
- Tone means the “voice” of your paper. Should you be chatty, formal, or objective? Usually you will find some happy medium—you do not want to alienate your reader by sounding condescending or superior, but you do not want to, um, like, totally wig on the man, you know? Eschew ostentatious erudition: some students think the way to sound academic is to use big words. Be careful—you can sound ridiculous, especially if you use the wrong big words.
- The level of information you use depends on who you think your audience is. If you imagine your audience as your instructor and she already knows everything you have to say, you may find yourself leaving out key information that can cause your argument to be unconvincing and illogical. But you do not have to explain every single word or issue. If you are telling your roommate what happened on your favorite science fiction TV show last night, you do not say, “First a dark-haired white man of average height, wearing a suit and carrying a flashlight, walked into the room. Then a purple alien with fifteen arms and at least three eyes turned around. Then the man smiled slightly. In the background, you could hear a clock ticking. The room was fairly dark and had at least two windows that I saw.” You also do not say, “This guy found some aliens. The end.” Find some balance of useful details that support your main point.
You’ll find a much more detailed discussion of these concepts in our handout on audience .
The Grim Truth
With a few exceptions (including some lab and ethnography reports), you are probably being asked to make an argument. You must convince your audience. It is easy to forget this aim when you are researching and writing; as you become involved in your subject matter, you may become enmeshed in the details and focus on learning or simply telling the information you have found. You need to do more than just repeat what you have read. Your writing should have a point, and you should be able to say it in a sentence. Sometimes instructors call this sentence a “thesis” or a “claim.”
So, if your instructor tells you to write about some aspect of oral hygiene, you do not want to just list: “First, you brush your teeth with a soft brush and some peanut butter. Then, you floss with unwaxed, bologna-flavored string. Finally, gargle with bourbon.” Instead, you could say, “Of all the oral cleaning methods, sandblasting removes the most plaque. Therefore it should be recommended by the American Dental Association.” Or, “From an aesthetic perspective, moldy teeth can be quite charming. However, their joys are short-lived.”
Convincing the reader of your argument is the goal of academic writing. It doesn’t have to say “argument” anywhere in the assignment for you to need one. Look at the assignment and think about what kind of argument you could make about it instead of just seeing it as a checklist of information you have to present. For help with understanding the role of argument in academic writing, see our handout on argument .
What kind of evidence do you need?
There are many kinds of evidence, and what type of evidence will work for your assignment can depend on several factors–the discipline, the parameters of the assignment, and your instructor’s preference. Should you use statistics? Historical examples? Do you need to conduct your own experiment? Can you rely on personal experience? See our handout on evidence for suggestions on how to use evidence appropriately.
Make sure you are clear about this part of the assignment, because your use of evidence will be crucial in writing a successful paper. You are not just learning how to argue; you are learning how to argue with specific types of materials and ideas. Ask your instructor what counts as acceptable evidence. You can also ask a librarian for help. No matter what kind of evidence you use, be sure to cite it correctly—see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial .
You cannot always tell from the assignment just what sort of writing style your instructor expects. The instructor may be really laid back in class but still expect you to sound formal in writing. Or the instructor may be fairly formal in class and ask you to write a reflection paper where you need to use “I” and speak from your own experience.
Try to avoid false associations of a particular field with a style (“art historians like wacky creativity,” or “political scientists are boring and just give facts”) and look instead to the types of readings you have been given in class. No one expects you to write like Plato—just use the readings as a guide for what is standard or preferable to your instructor. When in doubt, ask your instructor about the level of formality she or he expects.
No matter what field you are writing for or what facts you are including, if you do not write so that your reader can understand your main idea, you have wasted your time. So make clarity your main goal. For specific help with style, see our handout on style .
Technical details about the assignment
The technical information you are given in an assignment always seems like the easy part. This section can actually give you lots of little hints about approaching the task. Find out if elements such as page length and citation format (see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial ) are negotiable. Some professors do not have strong preferences as long as you are consistent and fully answer the assignment. Some professors are very specific and will deduct big points for deviations.
Usually, the page length tells you something important: The instructor thinks the size of the paper is appropriate to the assignment’s parameters. In plain English, your instructor is telling you how many pages it should take for you to answer the question as fully as you are expected to. So if an assignment is two pages long, you cannot pad your paper with examples or reword your main idea several times. Hit your one point early, defend it with the clearest example, and finish quickly. If an assignment is ten pages long, you can be more complex in your main points and examples—and if you can only produce five pages for that assignment, you need to see someone for help—as soon as possible.
Tricks that don’t work
Your instructors are not fooled when you:
- spend more time on the cover page than the essay —graphics, cool binders, and cute titles are no replacement for a well-written paper.
- use huge fonts, wide margins, or extra spacing to pad the page length —these tricks are immediately obvious to the eye. Most instructors use the same word processor you do. They know what’s possible. Such tactics are especially damning when the instructor has a stack of 60 papers to grade and yours is the only one that low-flying airplane pilots could read.
- use a paper from another class that covered “sort of similar” material . Again, the instructor has a particular task for you to fulfill in the assignment that usually relates to course material and lectures. Your other paper may not cover this material, and turning in the same paper for more than one course may constitute an Honor Code violation . Ask the instructor—it can’t hurt.
- get all wacky and “creative” before you answer the question . Showing that you are able to think beyond the boundaries of a simple assignment can be good, but you must do what the assignment calls for first. Again, check with your instructor. A humorous tone can be refreshing for someone grading a stack of papers, but it will not get you a good grade if you have not fulfilled the task.
Critical reading of assignments leads to skills in other types of reading and writing. If you get good at figuring out what the real goals of assignments are, you are going to be better at understanding the goals of all of your classes and fields of study.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
69 Writing Letters to Elected Officials
Writing letters to elected officials.
- What is a letter to an elected official?
- Why write to elected officials?
- When should you write to elected officials?
- How do you write to public officials?
- Should you use e-mail?
WHAT IS A LETTER TO AN ELECTED OFFICIAL?
By now you are probably looking for ways to get your issue noticed by people who have the power to help you. To get the best results, you will probably want to try several of the direct action methods discussed in this chapter. In this section, we will show you the best way to write a letter to your elected officials.
A well-written personal letter may be the most effective way to communicate with elected officials. They want to know how their constituents feel about issues, especially when those issues involve decisions made by them.
Your elected officials usually know what advocacy groups are saying about an issue, but they may not understand how a particular decision affects you. A well-written letter describing your experiences, observations, and opinions may help persuade an official in your favor.
Until a short time ago, you had two options if you wanted to contact an elected official: telephone and the mail. In the last several years, e-mail has been added and become the medium of choice. It’s fast, it gets read, and – at least in the U.S. – virtually all elected officials, from town councils to the President, use and welcome e-mail communication. Any guidelines for writing letters in this section – the style to use, the information to include – apply to e-mail as well. A letter to your Congressman, whether it’s sent through the post office or electronically, should be formal and as well-written as you can make it. A political communication, to be taken seriously, should send the message that you care enough about the subject to take some care in writing about it. In the days before e-mail, officials generally considered letters more important than phone calls, because they took more thought and effort. A proper e-mail letter carries the same message – this person has really thought about this, and has put some work into sending his opinion.
WHY WRITE TO ELECTED OFFICIALS?
Maybe you’re not convinced that writing a letter to your elected official is the best way to spend your time. There are several reasons it’s worth your while, including:
- To explain to an official how a particular issue affects you or your group.
- To express support for a proposed law, policy, or course of action.
- To oppose a proposed law, policy, or course of action.
In any of the above cases, the letter may include information about the issue that the official may not have, or suggest an alternate course of action that she hasn’t previously heard about.
- To demonstrate to an official that his constituents are aware of an issue and have a real interest in the outcome.
- To inform an official about an issue or situation, giving background and history that she may not have.
- To attempt to persuade an official to vote in a certain way on an issue, or to take other related action.
- To build your reputation as a thoughtful person in the eyes of the officials, and thus make your criticism or support more influential, or to put yourself in the position of the person to be consulted when the official needs information about your issue.
- To request a meeting to discuss the issue or some related matter of concern.
- To thank an official for support given, or action taken.
- To criticize an official for a past vote or action.
- To put an official on notice that you and your group are watching his actions, and that he needs to take your votes into account at election time.
- To ask an official to state her position on a particular issue, or to reveal her voting record.
- To ask for help or support.
This type of letter often falls under the heading of “constituent support,” and concern individual problems with government – being denied military disability payments, for example, or being singled out for harassment by a local official. The reason it’s included in this list is that it can sometimes lead an official to work to change procedures, policies, or laws that discriminate against or make life harder for a whole class of people – veterans, farmers, widows, etc.. Another purpose of this type of letter is to enlist the official’s support in a community or larger initiative of some sort. This may be a request that he become a legislative champion for the effort, that he simply lend his name to the initiative’s list of public supporters or sponsors, or that he serve on a board or steering committee for the effort.
The letter may include information about the issue that the official may not have, or suggest an alternate course of action that she hasn’t previously heard about.
This type of letter often falls under the heading of “constituent support,” and concern individual problems with government – being denied military disability payments, for example, or being singled out for harassment by a local official. The reason it’s included in this list is that it can sometimes lead an official to work to change procedures, policies, or laws that discriminate against or make life harder for a whole class of people – veterans, farmers, widows, etc..
Another purpose of this type of letter is to enlist the official’s support in a community or larger initiative of some sort. This may be a request that he become a legislative champion for the effort, that he simply lend his name to the initiative’s list of public supporters or sponsors, or that he serve on a board or steering committee for the effort.
WHEN SHOULD YOU WRITE LETTERS TO ELECTED OFFICIALS?
When would you want to write that letter? Whenever an issue arises that concerns your group, but especially when:
- You want an official to consider a certain action or policy (e.g., increasing funding for a program for senior citizens).
- There is an upcoming vote on a policy that concerns your group. Letters are most effective when the vote is about to be taken. This is a good time to use e-mail.
- You want to respond (positively or negatively) to a completed action or a change in policy (e.g., enacting a law that requires people to wear seatbelts).
- You want to point out a deficiency or need in a particular area (e.g. more public transportation to the community health clinics, more police patrols through your neighborhood).
- You need information (e.g. about what happened the last time a certain issue came up for a vote).
- You need advice (how to approach another official, what kind of event will attract large numbers of officials to take notice, etc.). In this instance, you’d probably be writing to an official that you’ve already had positive contact with.
Another way to look at this question is to think about when a letter will have the most effect. There are particular times when letters are more likely to be carefully considered, and when officials are more likely to be responsive.
- Just before an election. Most elected officials become extremely anxious to please when they’re running for reelection.
- Right before an important vote. Officials will usually be receiving communication from many people on both sides of the issue when an important vote is coming up, so this is an especially crucial time to let your opinion be known.
- Just before and in the midst of the budget process. One of the most important things that legislators, town councils, and some other bodies do is set the budget for the coming year. Whether your concern is local, regional, state or provincial, or nationwide, most of the coming year’s policy and action related to health and human services, the environment, public safety, education, transportation, and a number of other important issues is determined, not by laws, but by the amount of money allowed for them in the annual budget. If you have priorities for funding, now is the time to make them known.
- Immediately after an official has done something you approve or disapprove of. There are two reasons why this communication should be immediate. The first is so that the action is still fresh in the official’s mind, and he can respond to your support or criticism. The second is that he will be hearing from folks on the other side, and he needs to know either that not everyone approves of his action, or that, regardless of all the negative letters, there are people out there who think he’s doing the right thing. Officials need to know who supports or objects to which of their positions. It can help them continue to work for the things you care about in the face of opposition, or can push them in that direction if they’re not doing it already.
The really crucial times to write this sort of letter are when an official is under attack for doing something you believe in – think of officials in the American South in the 1950’s and ‘60’s who supported racial integration – or has just done something outrageous – given out a billion-dollar contract in return for a huge bribe, for example. In either of these cases, the official needs to know either that you support her wholeheartedly, and will work to help her, or that you want her to resign now, and will work to have her prosecuted and jailed.
HOW DO YOU WRITE LETTERS TO PUBLIC OFFICIALS?
So how do you write letters to public officials, anyhow? We have a number of guidelines that should help you not only write the letter, but increase the chances that it will be actually read and taken seriously.
DECIDE ON THE RECIPIENT.
Get the name, title, and address of the official who will make the decision about your issue. Watch to make sure that all names are spelled correctly and that you have the proper address. An incorrect name counts against you. An incorrect address may mean your letter might not arrive at all.
If you’re concerned with politics or issues at all, you should make it your business to know the names and contact information (address, office phone, and e-mail) of all those who represent you, from the most local to the federal government. In the U.S., at least, you can get to know your representatives at any level of government if you make the effort. If you’re an activist, you may meet with them, or at least speak to them or their aides fairly regularly. If that’s the case, letters from you will be taken seriously.
OPEN THE LETTER IN AN OFFICIAL MANNER.
If you are writing to an elected official, show respect for the position by using the title of the office, and the official’s full name. In any other letter, use the familiar term “Dear,” the title Mr., Mrs., Ms., Miss, or Dr., and the official’s full name.
Example: January 5, 2008 Title [Name of Representative or Senator] House of Representatives [OR] U.S. Senate Office Address Washington, D.C. 20515
EXPLAIN THE PURPOSE FOR YOUR LETTER.
Let your reader know immediately what your letter is about. Tell him/her why you are concerned or pleased that a particular decision is being considered.
Example: The proposed increase in the gasoline tax will make the cost of transportation unreasonably high for commuters in the metropolitan area.
SUMMARIZE YOUR UNDERSTANDING OF THE ISSUE/DECISION BEING CONSIDERED.
State the general impact that you expect to occur if a particular decision is made.
Example: The creation of a peer-counseling program at our high school will help reduce the number of teen pregnancies in our community.
EXPLAIN YOUR POSITION ON THIS ISSUE.
Describe in detail why you feel the decision made will lead to the impact you foresee.
Example: This will provide opportunities for our high school students to discuss pressures they experience with their peers at this critical time in their lives.
DESCRIBE WHAT ANY CHANGES WILL MEAN TO YOU, AND TO OTHERS.
Describe specifically the positive or negative effects the decision will have on you personally and on those you represent. The more people affected by the decision, the more convincing you may be.
Example: This program will help provide career opportunities for teenagers in our community.
IDENTIFY OTHERS WHO MAY BE AFFECTED BY THIS DECISION.
Tell the official which, and how many, people will be affected. Statistics can be very helpful here.
Example: A recent study showed that 80% of minors who smoke obtain cigarettes at stores that do not ask for any identification. Increased enforcement of the existing laws prohibiting tobacco sales to minors could significantly reduce the rate of smoking among our youth.
ACKNOWLEDGE PAST SUPPORT.
Mention appropriate actions and decisions the official has made in the past and express thanks for them.
Example: We appreciate your past support of the bill protecting the rights of emergency medical crews to not be tested for HIV.
DESCRIBE WHAT ACTION YOU HOPE THE OFFICIAL WILL TAKE.
State specifically what action you (and those you represent) hope the official will take–and by what date, if there is a deadline.
Example: We hope you realize the best course of action to protect our community’s infants and young children is to vote “yes” to House Bill #689b.
IF YOU HAVE WRITTEN A LETTER THAT OPPOSES SOME ACTION, OFFER AN ALTERNATIVE.
Example: I believe that rather than increasing the number of police cars patrolling our neighborhood, a cheaper and more effective alternative would be to work with our community to develop a community-policing program.
IF YOU HAVE TIME AND YOU ARE COMMITTED, ASK HOW YOU CAN HELP
Example: Our group is more than willing to explore the various options in helping make our community a safer place to live.
CLOSE AND SIGN YOUR LETTER.
Thank the official and sign your full name. Make sure your address, and phone number are included.
CHECK YOUR LETTER FOR SPELLING AND GRAMMATICAL ERRORS.
Correct spelling and grammar won’t do the job by themselves, but they can help. Why not give your letter every possible advantage?
LETTER-WRITING CAMPAIGNS
So far, we’ve discussed individual letters. A letter-writing tactic that can be particularly effective is a letter-writing campaign, where dozens, hundreds, or even thousands of people write either to the same official (if they’re all in, or somehow represent people who are in, her district) or to many officials about a specific vote, policy, or budget item. This can be extremely effective, especially when the letter-writers are people who don’t usually contact their elected officials.
In Massachusetts, when funding for Adult Basic Education (ABE) and English as a Second or Other Language (ESOL) was being debated in the state legislature, over a thousand ABE and ESOL students wrote letters to their representatives explaining why funding was important to them personally. At the same time, program staff and administrators, volunteers, and advocates wrote letters to their own representatives explaining why ABE and ESOL were important to their communities and to the state. The letters from students were particularly powerful, many of them explaining that a year or two earlier, they couldn’t have written those letters. It was the opportunity to enter an ABE or ESOL program that had made the difference. Legislators responded, and funding for adult education was significantly increased.
If you want to engage in a letter-writing campaign, you have to prepare properly. Many people, especially people who see themselves as powerless and unimportant, and who may have little education, are intimidated by the thought of writing to someone in power. In many countries, writing such a letter can carry a certain amount of economic, social, or physical risk. (After a State House rally in the same year as the letter-writing campaign described above, one ESOL student was overheard to remark, “In my country, they shoot you for this.”) Even in democracies governed by the rule of law, people may be fearful of being punished for speaking out.
In addition to reluctance based on feelings of fear and intimidation, many people affected by an issue – especially those with low levels of education – can be embarrassed by their poor writing skills, or feel that they don’t have anything convincing to say. They need help putting their letters together, and they need a model to go by. The coordinators of the letter-writing campaign should be aware of what they have to do to meet these needs.
First, the campaign should contact potential letter writers with a request for letters, and a simple but complete explanation of why the campaign is needed, and what the important issues relating to it are. People can’t write letters that make sense unless they understand clearly why they’re writing. The chances are that, while advocates can – and perhaps do – go over the politics of the issue in their sleep, most people affected by it know very little about how it plays out politically, or even about how the political system handles issues. The better they understand what’s happening and the specific job their letters are expected to do, the more persuasive the letters they can write.
Along with this, the campaign should provide one or more templates for letters. A template is a pattern for the letters, illustrating the form of the letter on the page, with the sender’s and recipient’s addresses and date in the appropriate places at the top, and a formal signature at the bottom, as well as a sample of the content of the letter.
A template literally means a cut-out pattern that is used to make several identical pieces of wood, metal, or some other material that are part of something larger. A builder might use a paper or wooden template to cut a number of identical rafters to hold up a roof, for example.
In general, people affected by the issue should include : A description of who they are – single working mother, person with a disability, job training participant, ex-Marine. The fact that they’re residents of the official’s district, or participants in a program in his district. What they want the official to do. Their connection to the issue – program participant, staff person, community volunteer, parent of a child with disabilities.
Anywhere from one sentence up to a paragraph or two explaining what the issue means to them and/or how it has affected them personally. For program participants and others affected by the issue, this is by far the most important part of the letter. Officials are more often swayed by personal stories than by impersonal statistics, no matter how telling those statistics may be. If people can explain how a program changed their lives for the better, or how the lack of services has been a barrier for them, it’s likely that officials will pay attention.
Finally, campaign coordinators should make sure that those for whom letter-writing is difficult have access to help. In the Massachusetts adult education campaign, that was easy: letters were often written as part of a class, and students approached them as writing assignments, completing two or three drafts before the letter was ready to be sent. In other situations, you’ll have to make sure that program staff and others are available to encourage and empower people, and to help them write the best letters they can.
SHOULD YOU USE E-MAIL?
With the speed and ease of delivery, it’s common to use e-mail and send your correspondence via the computer. Doing so, particularly for formal letters, has several advantages:
- It is much faster than normal mail. This also makes it possible for the official to respond much more quickly.
- It saves the trouble of addressing an envelope, buying a stamp, and mailing your letter.
- Electronic mail is less likely to get lost on the receiver’s desk.
However, note that the last can also be a disadvantage . Unless the recipient goes through the trouble to print your message, it may be gone with one tap of the delete key – and out of mind as well. If you are going to use e-mail for your correspondence, be particularly clear and emphatic about your message from the beginning.
Writing letters to elected officials is a good way to explain how an issue affects you or your group. It also can build your reputation as a thoughtful person, giving you more influence with the people in power. A letter is also a good way to get your issue noticed by people who have the power to help you.
___You have decided who you will write to
___The official you have chosen has the authority to make a decision about your issue
___You have begun the letter in an official manner, including the official’s full name and title
___The purpose for which you are writing is clear
___You have summarized your understanding of the issue
___The general impact that you expect to occur if a particular decision is made is stated
___You have explained your position on this issue in detail
___The positive and negative effects the decision will have on you are described
___You have identified others who may be affected by the decision
___Statistics have been included if available and appropriate
___You have told the official about appropriate actions and decisions he or she has made in the past
___The action that you want taken is stated specifically
___If your letter opposes some action, you have offered an alternative
___You have offered your help if you have available time
___You have thanked the official for their time
___The letter is signed with your full name
___Your address and phone number are listed under your name at the end of the letter
___The letter you have written is free of spelling and grammatical errors
___You communicate with all potential letter writers at the start of a letter-writing campaign to inform them about the issue and the need for the campaign.
___You provide a template for the letters to be written.
___You make sure there’s help available for those for whom letter-writing is difficult.
___You use e-mail if you can.
EXAMPLE 1: PROPOSED ACTIONS TO PROTECT VULNERABLE GROUPS IN SPAIN DURING THE COVID-19 CRISIS
The sample letter details a message to the City Council in Seville, Spain, in the midst of the coronavirus pandemic. The correspondence is written by a research team at the University of Seville in collaboration with a group of NGOs, and addressed specifically to the city’s mayor, Juan Espadas. The community-based organizations recognize that the mayor is empowered with the capacity and privilege to make a difference in the functioning of the city’s most vulnerable neighbors, comprised largely of Roma and migrant settlements. Multiple organizations, detailed in the attached letter, ask of actions being taken to comply with recommendations adopted by the Spanish government and offer their support in urgent efforts to protect the lives of these at-risk populations during a time of unpredictability:
Mayor Juan Espadas Cejas Sevilla City Council C/ Plaza Nueva 1 41001 – Sevilla April 2, 2020 Dear Mayor Espadas: We hope that you, your relatives and friends are united and in good health. We would like to thank you and your team’s cooperation during the COVID-19 crisis. The scope of the challenge is immense, and it is necessary to recognize the valuable effort that city services are making in order to provide the best possible coverage for the needs of communities and neighborhoods.
We are a group of social and community organizations, judges, and university researchers very concerned about the consequences this crisis is having on our most vulnerable neighbors, especially those living in the settlements of El Vacie, San Rafael, Polígono Sur and Los Pinillos. A large part of this population are Roma families and, in some cases, migrants. To address the needs of these groups, the European Public Health Association (1) and the European Public Health Alliance (2) have made a series of recommendations that have been adopted by the Spanish government (3) and the Roma State Council (4). These documents demand that these vulnerable groups be provided with the necessary resources to be able to comply with confinement protocol and face the crisis in dignified conditions.
In relation to the mentioned segregated settlements, we ask you to inform us of the following actions: 1. Protocols to evaluate the needs of this population, as well as the degree of satisfaction and sufficiency of the measures implemented. 2. Concrete measures to offer an alternative housing option to those residents who do not have the necessary conditions to stay in their homes 24 hours a day in accordance with the hygienic sanitary protocols implemented by the authorities. 3. Measures to guarantee the necessary supplies in substandard housing of those neighbors who cannot decide to abandon their current residences. Specifically, we refer to water, electricity, communication, security and sanitation supplies. 4. Measures to guarantee sufficient coverage for their basic needs such as access to food, hygiene and disinfection products, as well as other basic consumer goods for special situations and needs. 5. Measures to guarantee sufficient and safe access to social and health services, medicines and other daily care, especially for those dependent persons who require special care (i.e. persons with disabilities, mental illness and chronic diseases). 6. Measures taken to protect children and their primary caregivers. 7. Measures to ensure the sustainability of the reintegration and rehousing plans that were being implemented prior to the COVID-19 crisis. 8. Measures to protect and care for the providers of services to these groups. 9. Measures to prevent and report acts of discrimination and racism and to protect neighbors from their consequences. 10. Measures to promote the psychological well-being and resilience of these populations.
Given the urgency of the situation, we would like to have this information as soon as possible and offer our support and collaboration as you consider necessary.
EXAMPLE 2: SUPPORTING A PROPOSED POLICY CHANGE
1324 114th St. Suite #174 Norwalk, CT 06801
March 24, 1999
Honorable Mayor Cala Milan:
I was pleased to hear that the City Commission was considering a proposal to strengthen the handicapped parking ordinance. I urge your support for it.
I am a disabled American veteran who uses a wheelchair. Despite my disability, I drive my own van, as many other disabled citizens do. I value being as independent as I can possibly be.
The new ordinance is designed to discourage non-handicapped persons from parking in spots that are reserved for those with physical disabilities. The proposal has already led to publicity about the problems citizens with disabilities have getting a convenient place to park. This has increased the sensitivity of the general public. Further, an occasional $250 ticket ought to keep those important spaces open for those who need them.
For me, this new ordinance will mean that I can drive anywhere in town I need to go and have a fair chance of being able to park and go in. The latest census statistics indicate there are over 1,200 people in our community who are similarly affected and who have similar needs.
Your votes on the architectural accessibility ordinance in the past have demonstrated your support for disability issues. I urge you now to vote in favor of the new parking ordinance. It will mean a lot to me personally, and to the many others in our community who are disabled. It may also bring in some additional revenue to the city.
If there is any way I might be of assistance, please don’t hesitate to call on me. Thank you for your support.
Stergios Hardage 14 Cottage Avenue Norwalk, CT 06801 (203) 555-8630
EXAMPLE 3: OPPOSING A PROPOSED POLICY CHANGE
7862 Seneca Wichita KS, 67134
Honorable Mayor Madio Smolanka:
As the coordinator of the Pleasant Rock Teen Pregnancy Prevention Program. I am writing to express my strongest concern over the proposed city funding cuts for the Teen Activities Center (TAC). Closing the Center would have several negative consequences for the youth of the city and the city itself. It would give our youth one less place they can go to relax and have a good time in a safe, healthy environment.
For my coalition, the closure of the center would have other, more direct consequences as well. Currently, our Teen Mothers’ Support Group meets at the center on a weekly basis to discuss the challenges of motherhood, finishing school, and getting jobs. More than two-thirds of the (25) participants do not have their own means of transportation; so it is imperative that meetings be held in the neighborhood of the participants (the Potwin area, where the TAC is located), or at least on a major bus route. No public building is nearly as well suited to meet both of these requirements, as is the TAC.
In addition, the Teen Center hosts a variety of activities that are athletic, artistic, or just plain fun for young people. Their ability to participate in these activities is vital to helping them acquire the self-esteem needed to say “no” to potentially unsafe behaviors, such as engaging in sex prematurely or experimenting with drugs, as well as stay in school and prepare for meaningful work.
You have always been sensitive to the needs of our young people, and have been quick to recognize that they are the future of our community. I urge you to vote against this new proposal to cut the funding for the Teen Activities Center. Surely cuts can be made that will be, in the end, less costly to all of us than threatening the well-being of our children.
If I can help in any way to defeat this proposal, let me know. Thank you.
Mary K. Steinert 1001 Park Walk Road Wichita, KS 67134 (316) 555-2685
Action Tips provides information for communicating with public officials, and the webpage includes an example letter.
Communication Tools for Advocacy from the National Association for Gifted Children provides information on different ways to communicate with policy makers.
Contact Officials is a site provided by the United States government with links that give you contact information for the official you’re interested in contacting.
Early Childhood Advocacy Toolkit provides resources on framing your message and communicating with the media as well as policy makers and elected officials.
Effective E-mail Communication from the University of North Carolina provides tips on professional e-mail writing and communicating via e-mail.
How Do I Write an Effective Advocacy Letter? Is a webpage from the Hearing Loss Association of America, Delaware Chapters, and it provides information specific to drafting advocacy letters to elected officials.
10 Tips provides 10 tips on effectively communicating with legislators to make your message stand out to them.
Writing Your Elected Official is a guide provided by the Children’s Defense Fund, and it provides information on effectively communicating with elected officials.
Podcast Resource
Here is a link to a podcast on Writing for Social Change: Letters to Legislators (Episode 56) from Walden University Writing Center–make sure to scroll/search for Episode 56 in the WriteCast Podcast Player box and click the Play button or read the transcript .
Print Resources
Bates, D. J.(1985). Writing with precision . Washington, DC: Acropolis.
Fitch, B. (2010). Citizen’s Handbook to Influencing Elected Officials: Citizen Advocacy in State Legislatures and Congress: A Guide for Citizen Lobbyists and Grassroots. The Capitol Net, Inc. This book offers practical guidance for reaching elected officials with a variety of different communication strategies.
Homan, M.(1994). Promoting community change: Making it happen in the real world . Pacific Grove, CA: Brooks-Cole Publishing Co.
Managing correspondence–Plain letters, [available from the Superintendent of Documents, Washington, DC: 20402]
Roman,K., & Raphaelson, J. (1992). Writing that works . New York, NY: Harper Collins.
Seekins, T., & Fawcett, S. The Research and Training Center on Independent Living.(1984). A guide to writing letters to public officials: Contributing to important decisions affecting you and others. University of Kansas.
Stonecipher, H. (1979). Editorial and persuasive writings: Opinion functions of the news media . New York, NY: Hastings House.
Write What Matters Copyright © 2020 by Liza Long; Amy Minervini; and Joel Gladd is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
AI, Your Side Hustle Hero to Make Money from Home
Think AI is just for super-smart scientists? Nope! There are tons of ways you can use AI to make some serious cash from home.
Ready to turn your tech-love into a side hustle? Here are some amazing ideas:
1. The Content Creation Powerhouse
Ai, your writing buddy.
Imagine having a writing assistant that never gets tired, bored, or has writer’s block! AI tools like Jasper and Rytr help you crank out blog posts, website copy, product descriptions, and even creative stuff like poems or short stories.
You can write paid articles for websites or companies, or use AI to make your own online business shine with tons of fresh content. AI can even help you find ideas and make sure your writing is on point!
Pics in a Flash
Ever wish you could draw anything you imagine? AI image generators like DALL-E and Midjourney let you do just that!
Just type in what you want to see – like “a cat flying a spaceship” or “a watercolor landscape of a hidden waterfall” – and the AI will create it.
You can sell your images on stock photo sites, use them to make your blog posts stand out, or turn them into cool digital art pieces you can sell online.
Movie Magician
AI can help you become the next editing superstar! Services can cut and paste video clips, add background music, and even turn your dialogue into subtitles for different languages.
Imagine helping YouTubers make their videos snappier, or editing short videos for businesses– it’s a skill you could even be paid for!
2. AI Expert Services
The global chat champ.
If you know another language (or more!), AI translation tools become your BFFs. Instead of taking forever on translations, AI does the basic work, and you fine-tune it for accuracy and style.
Get gigs translating websites so they reach worldwide markets, translating important documents, or even adding subtitles so movies and videos can be enjoyed by everyone!
Meet Your Robot Assistant
Businesses want to offer help 24/7, but that’s impossible for humans! That’s where chatbots come in.
Platforms like Dialogflow let you “train” little AI assistants to answer common questions, take orders, or gather information from potential customers even when everyone’s asleep.
It’s like coding and customer service rolled into one cool job.
Data Detective
AI is amazing at spotting patterns way too huge for humans to see alone. You can offer services by using AI to analyze mountains of social media chatter to see what people really think about products or brands.
Investors might pay you to use AI to spot stock market trends. Businesses might want you to use AI to track their rivals and see what sneaky plans they might be hatching!
3. Affiliate Marketing with a Techy Twist
Ai reviewer: the ultimate comparison tool.
Imagine being able to gather tons of information on different products in a flash! That’s what AI lets you do. Let’s say you want to review the best robot vacuums.
AI tools can help you scrape customer reviews, compare features across different brands, and even summarize the pros and cons. You write awesome reviews, include your special affiliate links, and whenever someone clicks your link and buys, you earn cash.
It’s like being a super-helpful shopping guide and getting paid for it!
Super-Niche Websites: Your Secret Weapon
Sometimes the biggest money isn’t in the broadest topics, but the super-focused ones. Imagine a website not about pets, but all about the cutest outfits for teacup poodles! AI tools help you find these “micro-niches” – topics huge groups of people are obsessed with but might have fewer websites dedicated to them.
Once you’ve picked your niche, AI can help with everything else. It can find keywords that help people find your site, suggest tons of article ideas, and even help you write some of the content.
AI can also help you find products related to your niche to promote with affiliate links, making your awesome website into a money-making machine.
4. Build Your AI Empire
Tool time: coding for cash.
If you have some coding skills, you can build super-useful, bite-sized AI tools that people will happily pay for. Think of common problems people have: resizing a ton of images is a pain, long articles can be a drag to read, and catching every single grammar error is tough.
You could build simple tools that offer AI-powered solutions – a quick image resizer, an article summarizer, or an extra-smart grammar checker. Sell these tools on online marketplaces, and suddenly you’re not just using AI, you’re selling it!
Plugin Power: Supercharge Popular Programs
Do you know your way around popular software like Photoshop, Excel, or even game design programs? You can become a plugin superstar! Create little add-ons that use AI to do cool new things.
Maybe your plugin adds AI filters to Photoshop, or teaches Excel to predict future patterns based on the data. Find platforms that allow developers to sell plugins for their software, and your creations could make you money while helping others work smarter.
AI Business Sensei: The Ultimate Consultant
If you get really good with AI, and understand how businesses work, you could make serious money as a consultant. Companies often have no idea how to start using AI to their advantage.
You could be the expert that helps them! Teach them how AI can find them new customers, help them analyze huge amounts of data to make better decisions, or even automate some parts of their business to save them time and money.
As AI gets more important, companies will be desperate for consultants like you!
Things to Remember:
Humans still needed: the ai hype is real, but….
AI is a powerful tool, but it’s still just that – a tool. It can mess up, make stuff that’s just plain weird, or even be used for harmful things if we’re not careful. That’s where you come in!
Your job is to double-check AI’s work, make sure it sounds natural and makes sense, add your own creative spark, and be the one to make sure the AI is doing good, not harm.
Find Your Thing: Be the Specialist
Trying to be an expert in everything AI-related is a recipe for a headache. Instead, become known as THE person for something specific.
Are you the best AI product reviewer for tech gadgets? The go-to person for building customer service chatbots? The genius who finds hidden stock market patterns using AI?
Specializing makes it easier for clients to find you and know exactly what you can do for them.
Never Stop Learning: The AI Train Keeps Rolling
AI technology changes at lightning speed! New tools, techniques, and updates are happening all the time. To stay ahead of the game, you’ve got to be curious and willing to learn.
Subscribe to tech newsletters, mess around with new AI programs as they come out, and take online courses. The more you know about cutting-edge AI, the more valuable your skills become!
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Sweepstakes
Zone of Interest director's Oscars speech denounced by hundreds of Jewish stars and creators
Actors Debra Messing, Jennifer Jason Leigh, Julianna Margulies, and Brett Gelman are some of the Hollywood professionals who signed an open letter in response to Jonathan Glazer's controversial speech.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_20200213_174800_940-c7d2deff3faa4d40923693560d77fe00.jpg)
More than 450 Jewish stars and other Hollywood professionals are denouncing Zone of Interest writer-director Jonathan Glazer ’s speech from the 2024 Oscars , in an open letter published by Variety on Monday.
In his controversial remarks on stage accepting the award for Best International Feature , Glazer connected his Holocaust film with the crisis in Gaza, saying, "Our film shows where dehumanization leads at its worst. It’s shaped all of our past and present. Right now, we stand here as men who refute their Jewishness and the Holocaust being hijacked by an occupation which has led to conflict for so many innocent people. Whether the victims of October — whether the victims of October the 7th in Israel or the ongoing attack on Gaza, all the victims of this dehumanization, how do we resist?”
The open letter , titled "Statement From Jewish Hollywood Professionals," began circulating on March 13, just days after the Oscars. It responds in part: "We refute our Jewishness being hijacked for the purpose of drawing a moral equivalence between a Nazi regime that sought to exterminate a race of people, and an Israeli nation that seeks to avert its own extermination."
Rodin Eckenroth/Getty
It continues, "Every civilian death in Gaza is tragic. Israel is not targeting civilians. It is targeting Hamas. The moment Hamas releases the hostages and surrenders is the moment this heartbreaking war ends. This has been true since the Hamas attacks of October 7th. The use of words like 'occupation' to describe an indigenous Jewish people defending a homeland that dates back thousands of years, and has been recognized as a state by the United Nations, distorts history."
The letter also states that Glazer's speech "gives credence to the modern blood libel that fuels a growing anti-Jewish hatred around the world, in the United States, and in Hollywood. The current climate of growing antisemitism only underscores the need for the Jewish State of Israel, a place which will always take us in, as no state did during the Holocaust depicted in Mr. Glazer’s film.”
Actors Debra Messing , Jennifer Jason Leigh , Julianna Margulies and Brett Gelman , director Eli Roth, writer Amy Sherman-Palladino , and producer Amy Pascal are some of the Hollywood stars who signed, as did many other creatives, executives, and Hollywood professionals. The letter aside, public response to Glazer's remarks has been divisive — in addition to the criticism , it has received some support from those calling for a cease-fire.
Glazer had no comment when contacted by EW. Reps for Messing, Leigh, Margulies, Roth, Sherman-Palladino, and Pascal did not immediately reply to EW's requests for comment.
The Zone of Interest filmmaker's acceptance speech has also received praise from other stars and creatives, including Mark Ruffalo, Melissa Barrera, and directors Boots Riley, Jesse Peretz, and Asif Kapadia, many of whom previously signed an open letter to President Joe Biden calling for immediate de-escalation and ceasefire in Gaza and Israel.
Nominated for five Academy Awards and winning two, The Zone of Interest follows the home life of Rudolf Höss, the commandant of Auschwitz, and stars Christian Friedel and Sandra Hüller. Glazer was joined by producers James Wilson and Len Blavatnik on the Oscars stage to accept the honor, though the latter later revealed Glazer did not consult him about the remarks beforehand. "He didn’t clear the speech,” a spokesperson for Blavatnik told The Hollywood Reporter . “But he’s incredibly proud of the film and the accolades it has received and he doesn’t want to distract from the important themes of the movie."
Another of Zone of Interest 's executive producers, Danny Cohen, previously said he "fundamentally" disagreed with the director's remarks. "It’s really important to recognize it’s upset a lot of people and a lot of people feel upset and angry about it. And I understand that anger frankly," Cohen said on the an episode of the Unholy podcast .
Watch Glazer's acceptance speech at the Oscars above.
Want more movie news? Sign up for Entertainment Weekly 's free newsletter to get the latest trailers, celebrity interviews, film reviews, and more.
Related content:
- Pro-ceasefire protesters make it all the way to the Oscars red carpet
- The Zone of Interest review: Jonathan Glazer's Holocaust film is an unrelenting portrait of the banality of evil
- Noah Schnapp says his thoughts on Israel-Hamas war have been 'misconstrued': 'I only want peace and safety'
Writing Cover Letters
What is a cover letter? What to include in a cover letter How to organize a cover letter Questions to guide your writing How to format a cover letter Sample cover letters
What is a cover letter?
To be considered for almost any position, you will need to write a letter of application. Such a letter introduces you, explains your purpose for writing, highlights a few of your experiences or skills, and requests an opportunity to meet personally with the potential employer.
Precisely because this letter is your introduction to an employer and because first impressions count, you should take great care to write an impressive and effective letter. Remember that the letter not only tells of your accomplishments but also reveals how effectively you can communicate.
The appropriate content, format, and tone for application letters vary according to the position and the personality of the applicant. Thus, you will want to ask several people (if possible) who have had experience in obtaining jobs or in hiring in your field to critique a draft of your letter and to offer suggestions for revision.
Despite the differences in what constitutes a good application letter, the suggestions on these pages apply generally.
What to include in a cover letter
- Try to limit your letter to a single page. Be succinct.
- Assess the employer’s needs and your skills. Then try to match them in the letter in a way that will appeal to the employer’s self-interest.
- As much as possible, tailor your letter to each job opportunity. Demonstrate, if possible, some knowledge of the organization to which you are applying.
- Write in a style that is mature but clear; avoid long and intricate sentences and paragraphs; avoid jargon. Use action verbs and the active voice; convey confidence, optimism, and enthusiasm coupled with respect and professionalism.
- Show some personality, but avoid hard-sell, gimmicky, or unorthodox letters. Start fast; attract interest immediately. For more information see Business Letter Format .
- Arrange the points in a logical sequence; organize each paragraph around a main point.
How to organize a cover letter
Below is one possible way to arrange the content of your cover letter.
Opening Paragraph
State why you are writing.
Establish a point of contact (advertisement in a specific place for a specific position; a particular person’s suggestion that you write): give some brief idea of who you are (a Senior engineering student at UW; a recent Ph.D. in History).
Paragraph(s) 2(-3)
Highlight a few of the most salient points from your enclosed resume.
Arouse your reader’s curiosity by mentioning points that are likely to be important for the position you are seeking.
Show how your education and experience suit the requirements of the position, and, by elaborating on a few points from your resume, explain what you could contribute to the organization.
(Your letter should complement, not restate, your resume.)
Closing paragraph
Stress action. Politely request an interview at the employer’s convenience.
Indicate what supplementary material is being sent under separate cover and offer to provide additional information (a portfolio, a writing sample, a sample publication, a dossier, an audition tape), and explain how it can be obtained.
Thank the reader for his/her consideration and indicate that you are looking forward to hearing from him/her.
Questions to guide your writing
- Who is my audience?
- What is my objective?
- What are the objectives and needs of my audience?
- How can I best express my objective in relationship to my audience’s objectives and needs?
- What specific benefits can I offer to my audience and how can I best express them?
- What opening sentence and paragraph will grab the attention of my audience in a positive manner and invite them to read further?
- How can I maintain and heighten the interest and desire of the reader throughout the letter?
- What evidence can I present of my value to my audience?
- If a resume is enclosed with the letter, how can I best make the letter advertise the resume?
- What closing sentence or paragraph will best assure the reader of my capabilities and persuade him or her to contact me for further information?
- Is the letter my best professional effort?
*From Ronald L. Kraunich, William J. Bauis. High Impact Resumes & Letters. Virginia Beach, VA: Impact Publications, 1982.
How to format a cover letter
- Type each letter individually, or use a word processor.
- Use good quality bond paper.
- Whenever possible, address each employer by name and title.
- Each letter should be grammatically correct, properly punctuated, and perfectly spelled. It also should be immaculately clean and free of errors. Proofread carefully!
- Use conventional business correspondence form. If you are not certain of how to do this, ask for help at the Writing Center.
Sample cover letters
Looking at examples of strong cover letters is a great way to understand how this advice can become implemented. We’ve compiled and annotated a range of different kinds of cover letters from different kinds of student applicants. We encourage you to look through these letters and see some of what we’ve highlighted as working particularly well in these real world examples.
- Cover Letter Example 1. Undergraduate student applying for a restaurant hosting position.
- Cover Letter Example 2. Undergraduate sophomore applying for an internship with a non-profit, political organization.
- Cover Letter Example 3. Graduate student applying for a Project Assistant position at UW-Madison. The original job posting for this position can be found here .
- Cover Letter Example 4. A graduated student with an English literature and Spanish language double major applying to work as a law firm legal assistant.
In addition to these sample cover letters, you can find a range of other, often discipline-specific cover letter examples through these UW-Madison resources:
- SuccessWorks has developed a useful resource that features an overview of cover letters. It provides a breakdown of this genre’s main parts as well as an example cover letter and resume, all in response to an included job posting for a position with Americas Society Council of the Americas. All of this is located here .
- UW-Madison’s Law School has several wonderful examples of cover letters for law-related jobs here . These are organized according how far the applicants were into their law school careers (i.e., L1, L2, and L3).
- The Career Center for the School of Education has information about cover letters as well as sample cover letter for someone applying to be an elementary school teacher here .

Academic and Professional Writing
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Analysis Papers
Reading Poetry
A Short Guide to Close Reading for Literary Analysis
Using Literary Quotations
Play Reviews
Writing a Rhetorical Précis to Analyze Nonfiction Texts
Incorporating Interview Data
Grant Proposals
Planning and Writing a Grant Proposal: The Basics
Additional Resources for Grants and Proposal Writing
Job Materials and Application Essays
Writing Personal Statements for Ph.D. Programs
- Before you begin: useful tips for writing your essay
- Guided brainstorming exercises
- Get more help with your essay
- Frequently Asked Questions
Resume Writing Tips
CV Writing Tips
Cover Letters
Business Letters
Proposals and Dissertations
Resources for Proposal Writers
Resources for Dissertators
Research Papers
Planning and Writing Research Papers
Quoting and Paraphrasing
Writing Annotated Bibliographies
Creating Poster Presentations
Writing an Abstract for Your Research Paper
Thank-You Notes
Advice for Students Writing Thank-You Notes to Donors
Reading for a Review
Critical Reviews
Writing a Review of Literature
Scientific Reports
Scientific Report Format
Sample Lab Assignment
Writing for the Web
Writing an Effective Blog Post
Writing for Social Media: A Guide for Academics

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 3: Decide whom you'd like to write to and what you want to say. Step 4: Write your first draft as a letter, not an essay. Step 5: Make sure the tone is appropriate to your audience and ...
If you have questions about your submission, please write to us at [email protected] and provide the email address you used for submission. We invite students to write public-facing letters ...
Writing an open letter, a type of letter meant to be publicized to address a particular issue, generally entails a what-why-how logic throughout the paragraphs. The "what" part introduces the problem; the "why" explains the writer's motivation, and the "how" section contains the proposed solution. ...
Steps to Сreating a Perfect Open Letter. Now that we are on the same page about the open letters format, let's explore the main steps in this process. Step 1. Defining and Presenting the Issue. Here, you need to convince the audience that your problem is significant and it has a negative impact on people around you.
Assignment: For English 103 Courses (Writing about Writing, Writing for Health Science, ... "This Open Letter is a letter where the writer will attempt to convince an audience to change their mind about a specific subject. Address the letter to someone you know, to a political figure, or related organization and take a firm stance on a topic ...
Overview. Students practice writing effective letters for a variety of real-life situations, such as responding to a prompt on a standardized test, corresponding with distant family members, or communicating with a business. They begin by reviewing the differences between business and friendly letter formats, using examples and a Venn diagram.
The open letter is playing a growing role in modern communication because it's an excellent way of reaching a wide audience. The definition of an open letter is that it is open to the public, not a closed and private communication between two individuals. There tend to be two main types of open letter: 1.
Harvard College Writing Center 2 Tips for Reading an Assignment Prompt When you receive a paper assignment, your first step should be to read the assignment prompt carefully to make sure you understand what you are being asked to do. Sometimes your assignment will be open-ended ("write a paper about anything in the course that interests you").
The Oxford English Dictionary defines an open letter as one intended for a more public readership, as by deliberate publication in a newspaper or journal. The phrase harks back to at least 1798 in ...
1. FICTION AS A SPRINGBOARD. Have students write as if they were a character from a piece of fiction you have been reading in class. Choosing a dramatic point in the plot, ask students to imagine they are one of the characters writing a letter to another character in the story.
Context. In previous centuries, letter writing was a significant form of communication. Letters were normally kept private between the sender and recipient. Consequently, an open letter, usually published in a newspaper or magazine, was a then-rare opportunity for the general public to see what a public figure was saying to another public figure. Open letters, published in newspapers, became ...
Purpose. Business writing seeks to communicate work-related objectives and practices that help achieve a business-related goal. Academic writing conveys to the teacher /professor mastery of the subject and correctness of expression. Clarity. In business writing, priority is placed on using plain, direct language so that the greatest degree of ...
In my experience, students respond best to an assignment that has clear directions, a list of ideas to include in the letter, and specific writing expectations. Here are a few things that I've used and rotated through over the years: Begin your letter with a greeting. Compose a minimum of two paragraphs. In each paragraph, discuss something ...
They can write a letter to a friend explaining their concerns about an upcoming paper assignment or explaining their ideas for an upcoming paper assignment. If you wish to add a creative element to the writing assignment, you might have students adopt the persona of an important person discussed in your course (e.g., an historical figure) and ...
An Open Writing Assignment (OWA) is a limited open invitation call for pitches for specific projects from a producer or studio. Usually the production entity has a significant property investment already (e.g. a novel), and are looking for a professional writer to express how they would approach converting the property or idea into a workable ...
Although landing an open writing assignment (OWA) is one of the many ways screenwriters can go about making money (the holy grail in screenwriting), there's still so much mystery surrounding them. In a sense, it's a bit of a secret club. You have to know the right people and hang out in the right circles to even get an invite.
Open Letter Assignment Purpose: Write about your semester topic using a style and content that engages a public audience Compose texts for at least three different rhetorical situations, including academic, professional, and community/civic. Practice flexible reading, writing, and comprehension strategies Genre: Open Letter (Civic Writing) Background: Open letters have been around since the ...
August 01, 2022 12:43. Stage 32. Open Writing Assignment (OWA) An Open Writing Assignment (OWA) is a particular need for a script or a writer that comes directly from a production company, studio, financiere, manager or agent. Typically these companies only share their OWA's with agencies and management companies. The Writers' Room team ...
What this handout is about. The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms ...
Colleen Fontana (Student Essay), An Open Letter to Robert Levy in Response to His Article "They Never Learn" Conclusion; Writing Assignment: An Open Letter as Collaborative Rhetoric. Reading; Monica Allen (Student Essay), An Open Letter to Christopher Eide in Response to His Article "High-Performing Charter Schools Can Close the ...
OPEN THE LETTER IN AN OFFICIAL MANNER. If you are writing to an elected official, show respect for the position by using the title of the office, and the official's full name. ... letters were often written as part of a class, and students approached them as writing assignments, completing two or three drafts before the letter was ready to be ...
Assignment Letter Example - Project Approval. Dear [Recipient's Name], I am writing this letter to request your approval for [Project Name]. [Project Name] is a project that will involve [Project Objectives and Deliverables], and our team is looking forward to executing it efficiently and effectively.
More than 450 Jewish stars and creators — including Debra Messing, Jennifer Jason Leigh, Julianna Margulies, and Brett Gelman — signed an open letter denouncing 'Zone of Interest' director ...
Cover Letter Example 2. Undergraduate sophomore applying for an internship with a non-profit, political organization. Cover Letter Example 3. Graduate student applying for a Project Assistant position at UW-Madison. The original job posting for this position can be found here. Cover Letter Example 4.